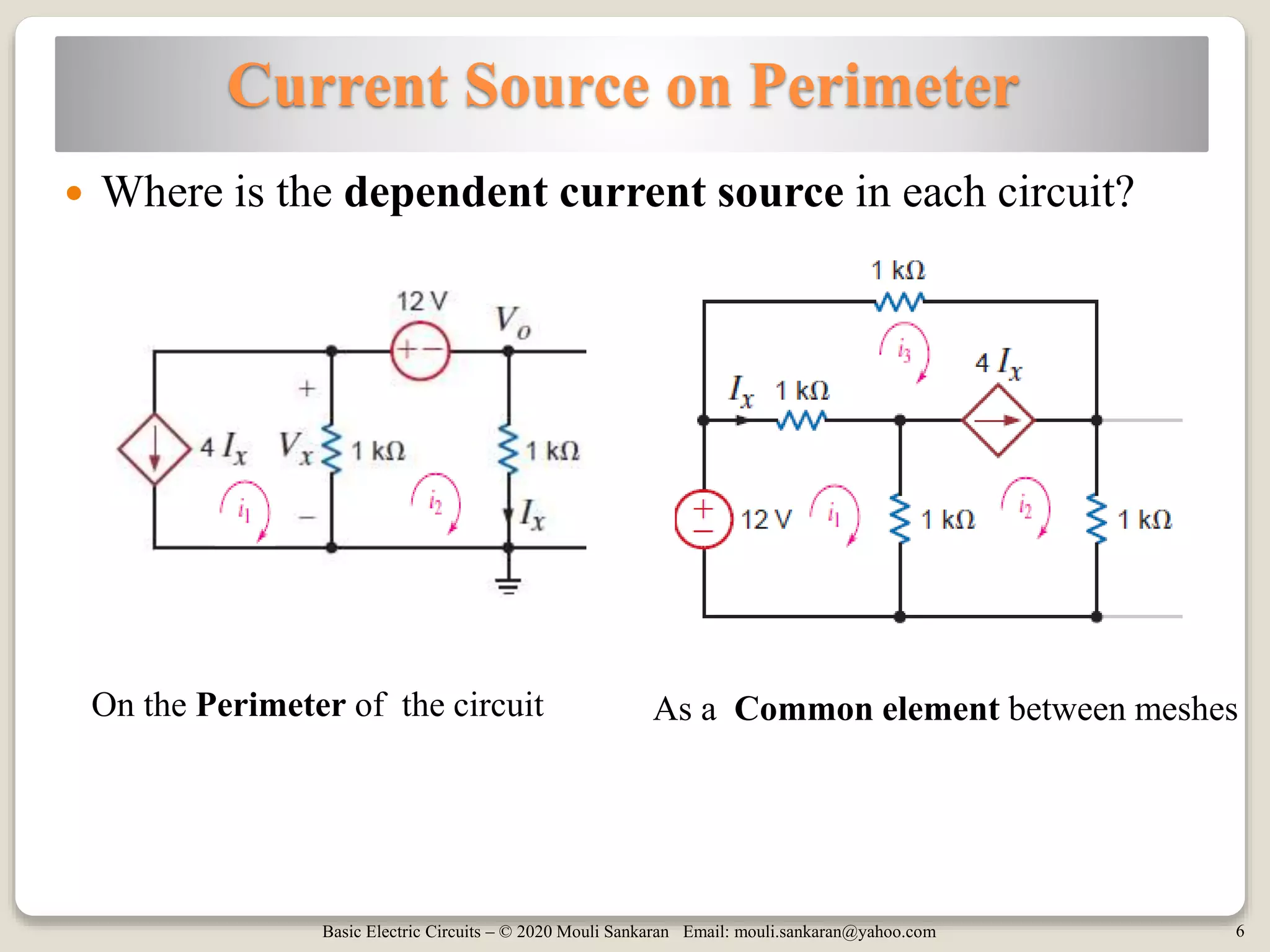
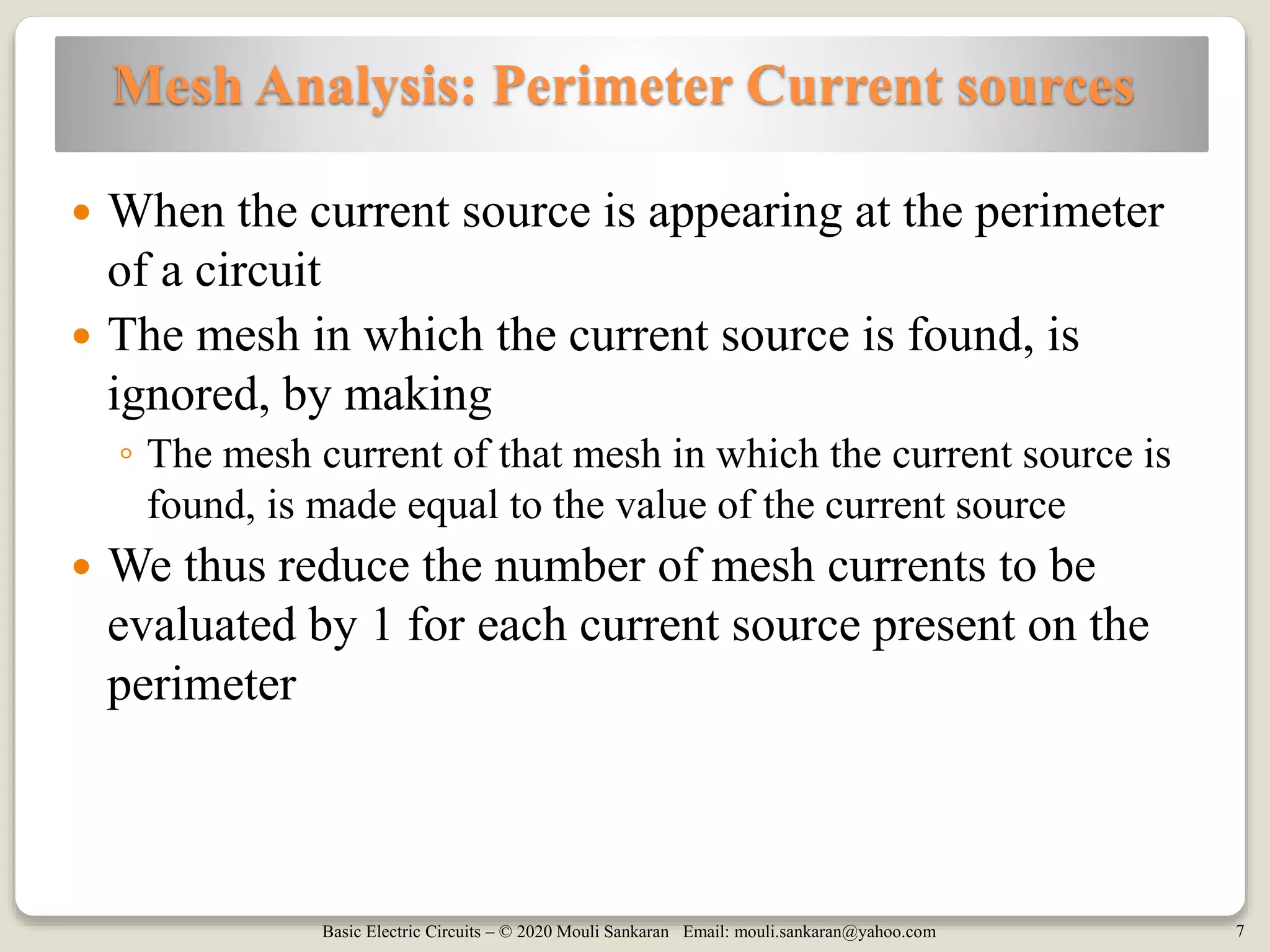
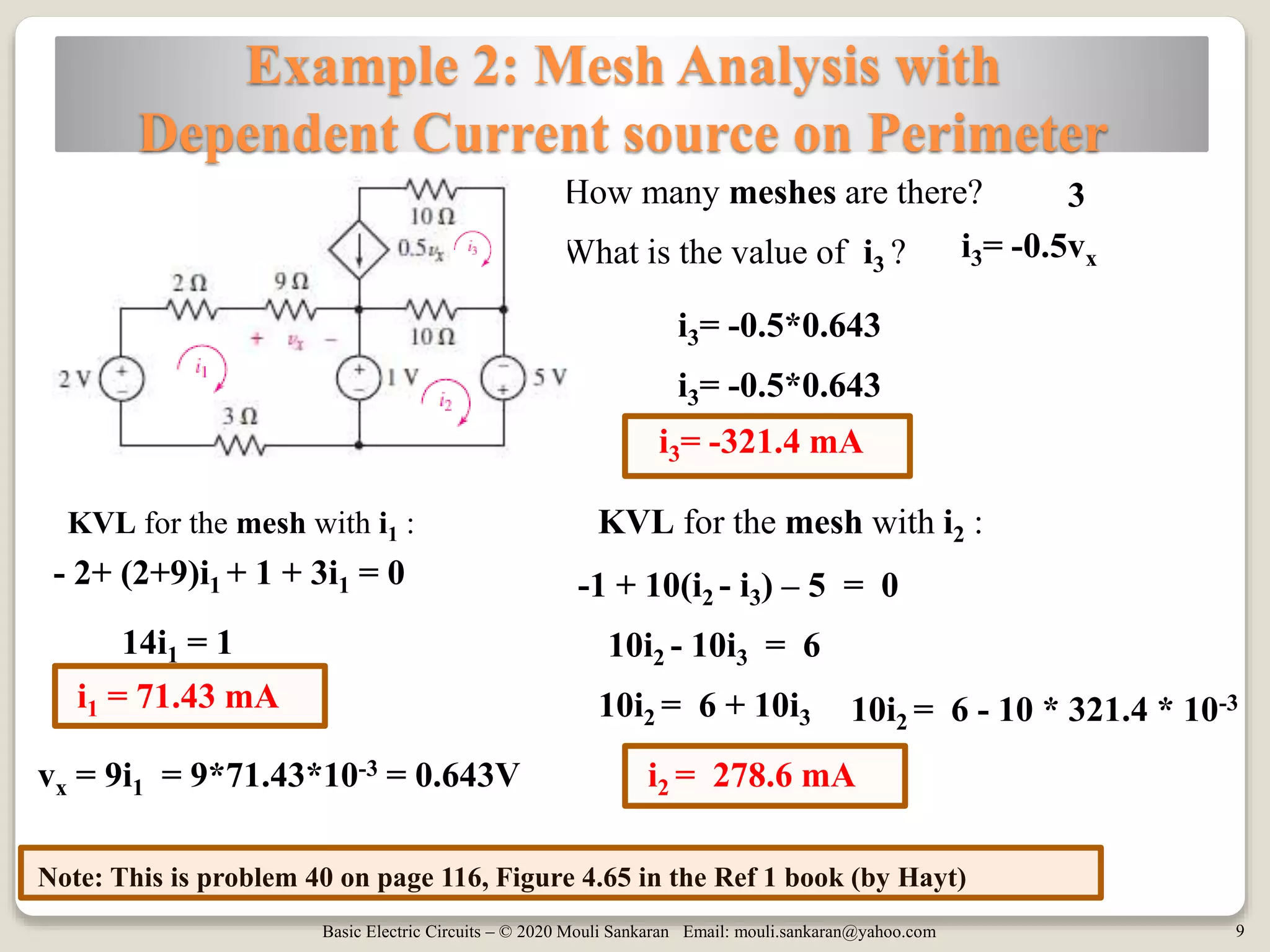
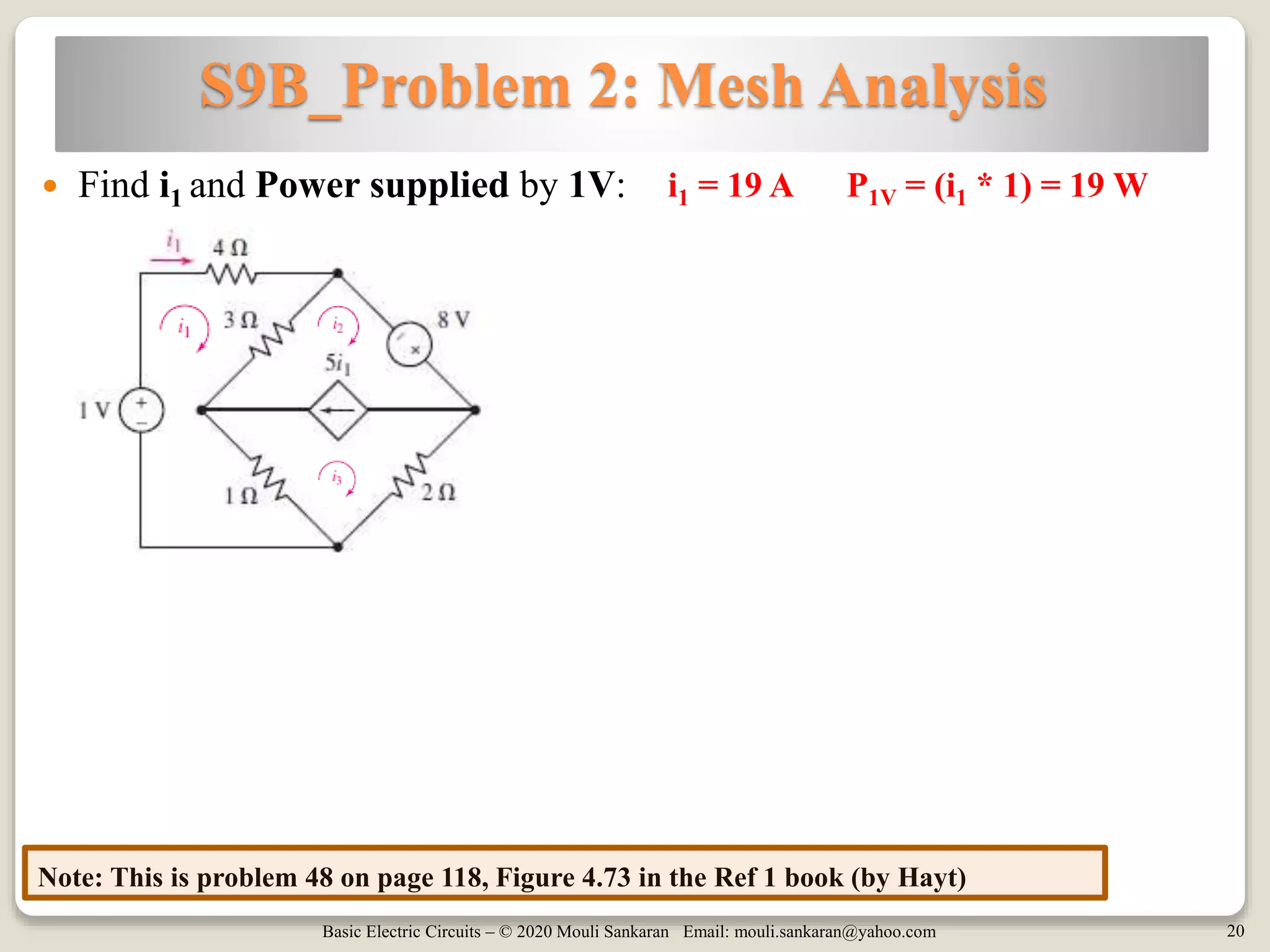
This document discusses mesh analysis for circuits containing current sources. It explains that current sources can be located either on the perimeter of meshes or between meshes. When on the perimeter, the mesh containing the source is ignored and its current is set equal to the source value. When between meshes, a supermesh is formed by combining the meshes. The document provides examples of both cases and summarizes the steps for mesh analysis, including forming KVL equations and solving the resulting system of equations. It concludes with assigning homework problems for further practice.