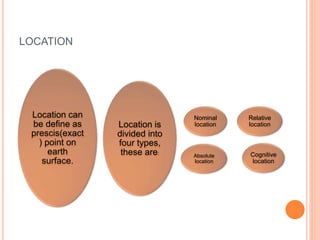
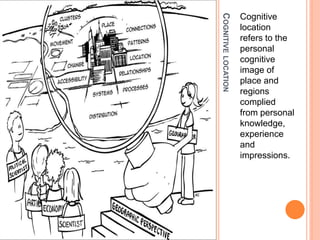
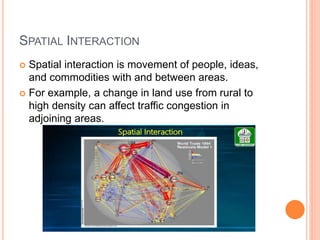
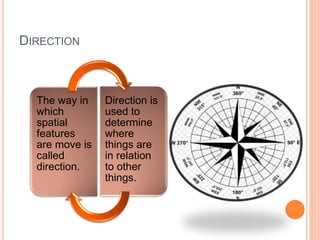
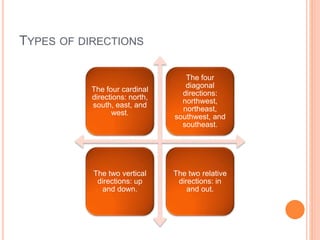
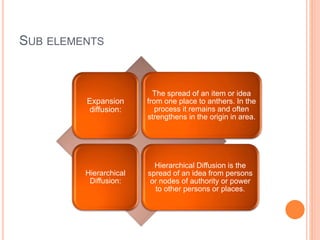
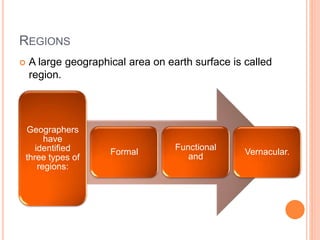
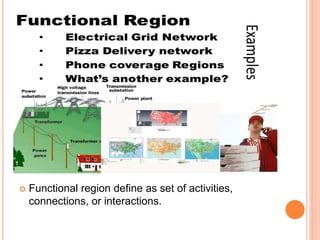
This document defines key concepts in geography. It discusses 12 concepts: location, distance, space, accessibility, spatial interaction, direction, size and scale, distribution, spatial diffusion, place, realms, and regions. It provides details on each concept, such as the four types of location (nominal, relative, absolute, cognitive) and how regions can be formal, functional, or vernacular. The document aims to outline fundamental geographical terms and concepts.