This document appears to be from a geography textbook and covers several key concepts:
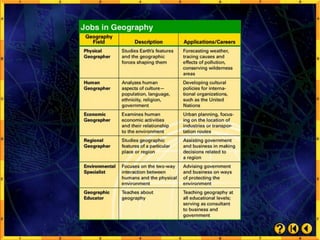
- Geography studies both physical features of the Earth as well as human activities and interactions with the environment.
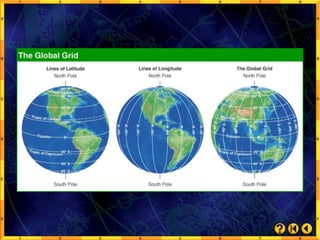
- Geographers use tools like maps and measurements to describe locations, regions, ecosystems, and relationships between places.
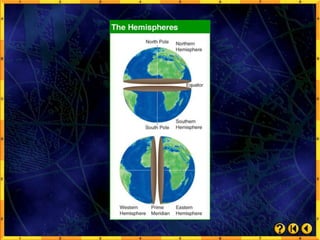
- Locations can be described in absolute or relative terms, and regions include formal, functional, and perceptual types based on shared characteristics.
- Physical systems and human activities both shape the Earth's surface and environments over time through migration, trade, and adaptation to barriers.





















![What can a geographer tell you about
your environment?
Possible answers: Geographers can
describe a place’s land [flat, mountainous]
and water [salt or fresh]. They can also give
the distances between all the places in a
region, and can describe the temperatures
and precipitation levels at different seasons
of the year. Geographers can also interpret
population patterns and explain cultural
relationships.
The Uses of Geography (cont.)
Click the mouse button or press the
Space Bar to display the answer.
(page 22)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gwgchapter011-221004141601-06afa795/85/gwg_chapter_01-1-ppt-27-320.jpg)