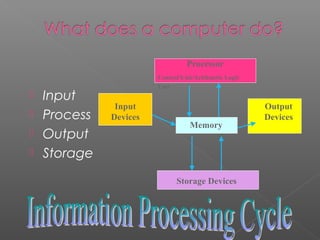
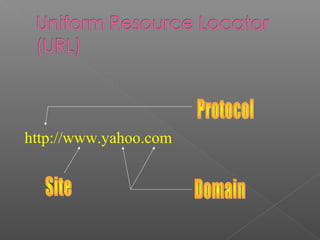
This document provides an overview of computer hardware and software components. It describes the basic parts of a computer including the processor, memory, storage devices, input devices, output devices, and communications devices. It also discusses operating systems, software applications, networks, the internet, and uses of technology such as e-mail and e-commerce. The document serves as an introductory guide to understanding computer systems and their functions.