The document provides an overview of basic computer concepts including:
1. It defines what a computer is and discusses its main historical developments from the 1800s to present day.
2. It explains that computers have two main parts - hardware, which are the physical and tangible components, and software, which are programs that tell the computer what to do.
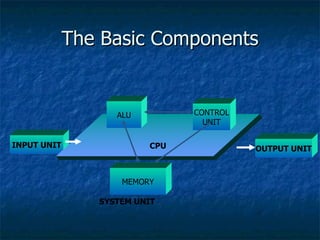
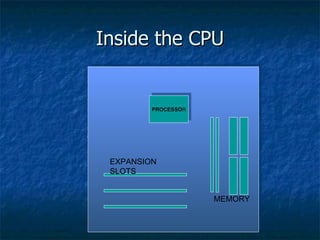
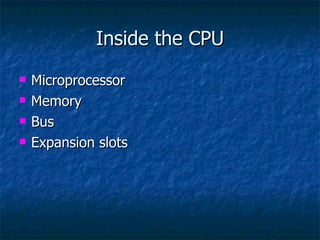
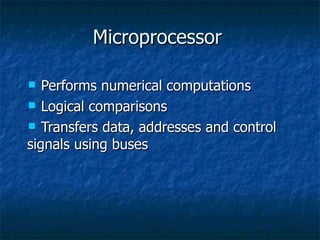
3. It describes the basic components of a computer including input, output, central processing, and memory units and provides examples of input and output devices.