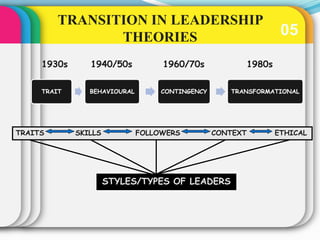
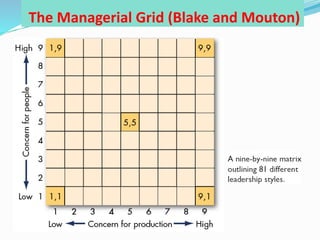
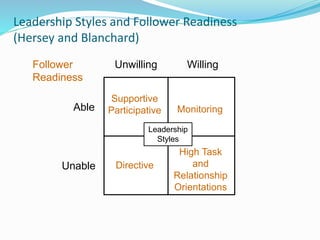
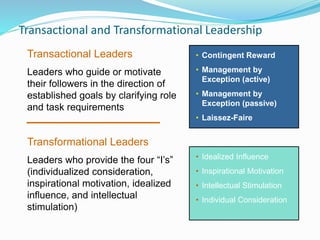
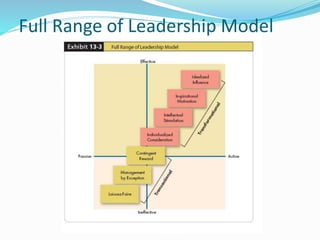
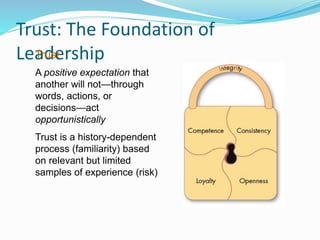
This document discusses various theories of leadership. It begins by defining leadership and distinguishing it from management. It then categorizes leadership theories into four approaches: trait, behavioral, contingency, and recent approaches. Several leadership theories are explained in more detail, including Great Man Theory, Trait Theory, Behavioral Theories like the Ohio State Studies and Managerial Grid, Contingency Theories like Fiedler's LPC Theory and Situational Theory, and characteristics of charismatic leadership. The document provides an overview of the history of leadership thought and key aspects of different leadership theories.