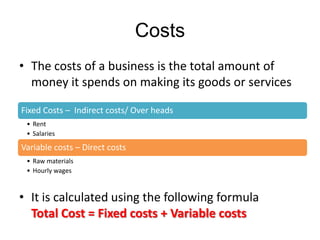
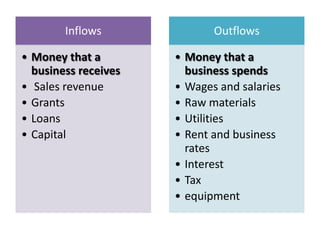
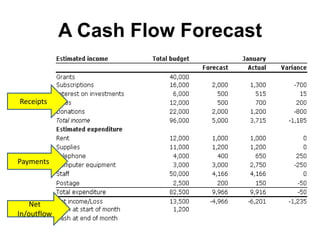
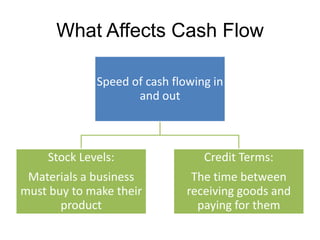
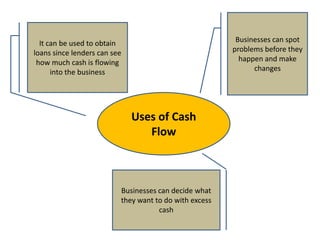
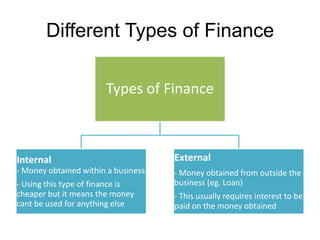
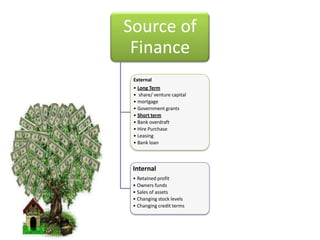
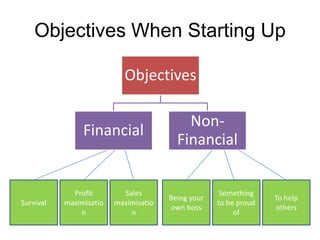
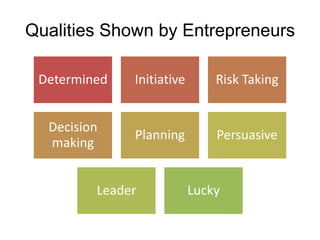
This document discusses starting a new business and obtaining financing. It covers objectives for starting a business like profit, sales, or being your own boss. Qualities of successful entrepreneurs like determination, initiative, and risk-taking are also outlined. The document then explains how to estimate revenues, costs, and profits including calculating sales, fixed and variable costs, and profit formulas. It discusses forecasting cash flows by looking at inflows, outflows, and creating a cash flow forecast. Finally, it covers why firms need financing and different sources of internal and external financing.

![Revenue
• Any money received by a business [from
selling goods or services]
• The total amount of revenue is calculated by:
Total Revenue = Price x Quantity
• A business can forecast its revenue by:
> Estimating the quantity it will sell by looking at its
market research
> Deciding what price they will charge for each unit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3-puttingabusinessideaintopractice-120124134923-phpapp02/85/Chapter-3-putting-a-business-idea-into-practice-4-320.jpg)