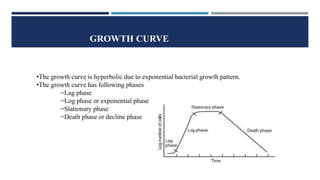
The document summarizes the bacterial growth curve, which shows the characteristic pattern of bacterial population growth over time when bacteria are inoculated into fresh liquid medium. The growth curve consists of four phases: 1) Lag phase where bacteria adjust to the new environment before dividing, 2) Log or exponential phase where bacteria divide rapidly at a constant rate, 3) Stationary phase where growth balances with death resulting in no net population change, and 4) Death phase where the population declines due to nutrient depletion and waste accumulation.