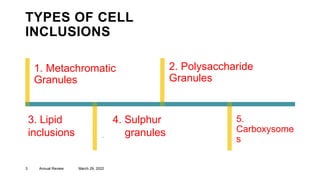
This document presents information about bacterial cell inclusions. It defines cell inclusions as storage materials found within the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells. The document then describes five main types of cell inclusions: 1) Metachromatic granules which are polyphosphate storage structures that take up dye differently, 2) Polysaccharide granules which store glycogen or starch, 3) Lipid inclusions which store lipids like polyhydroxybutyrate, 4) Sulfur granules found in sulfur-oxidizing bacteria, and 5) Carboxysomes which contain the enzyme RuBisCO for carbon dioxide fixation in photosynthetic bacteria.