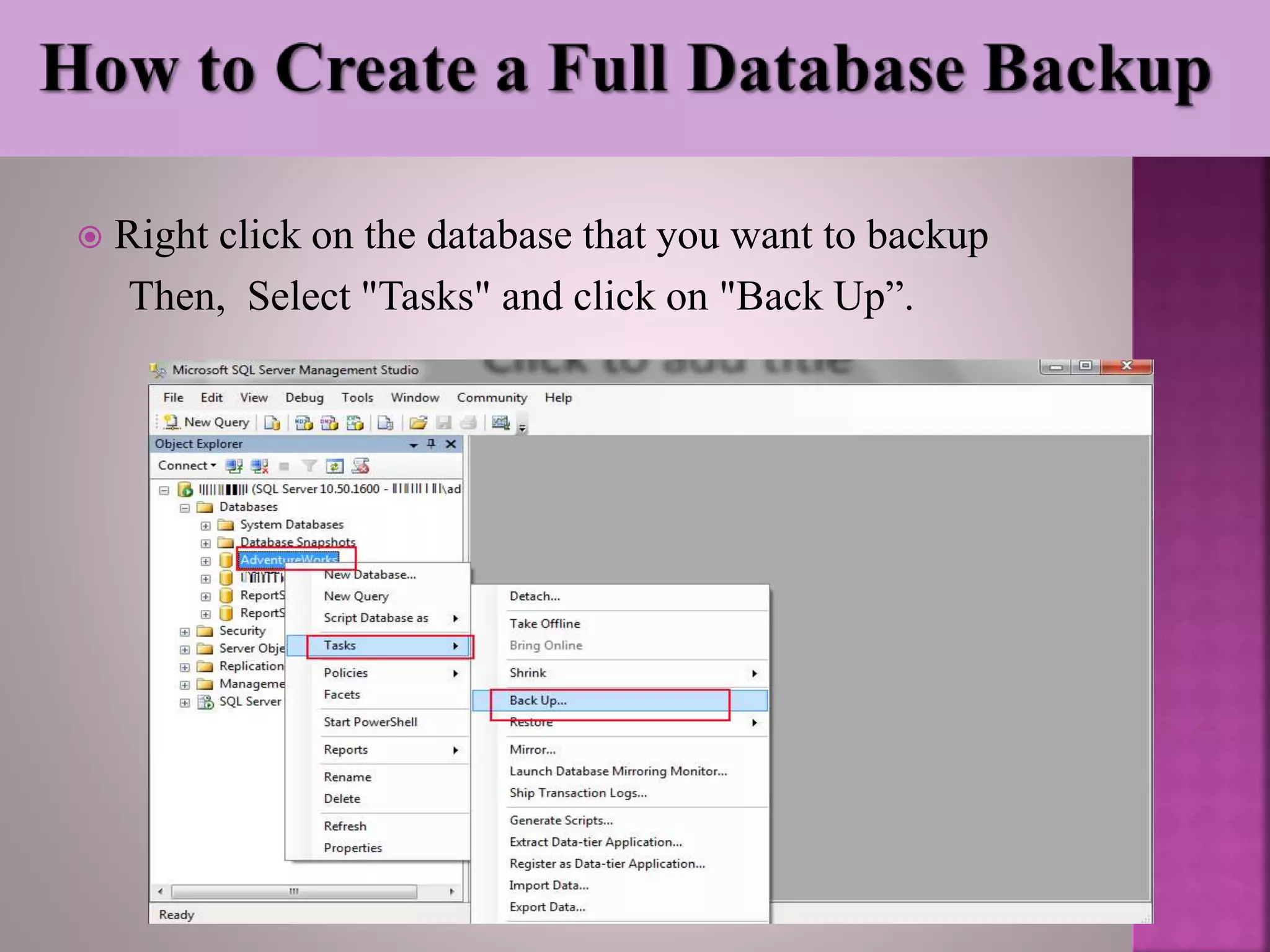
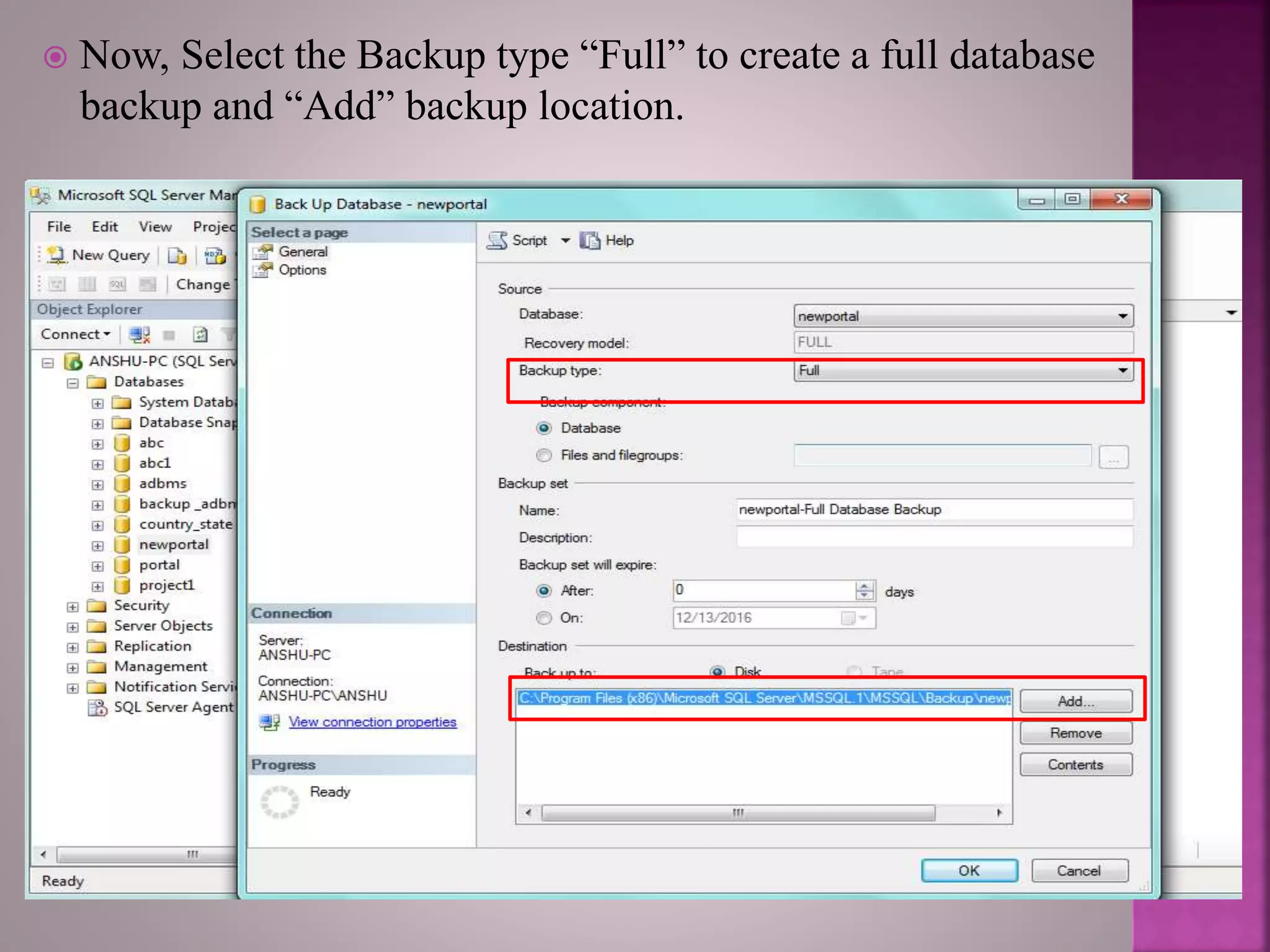
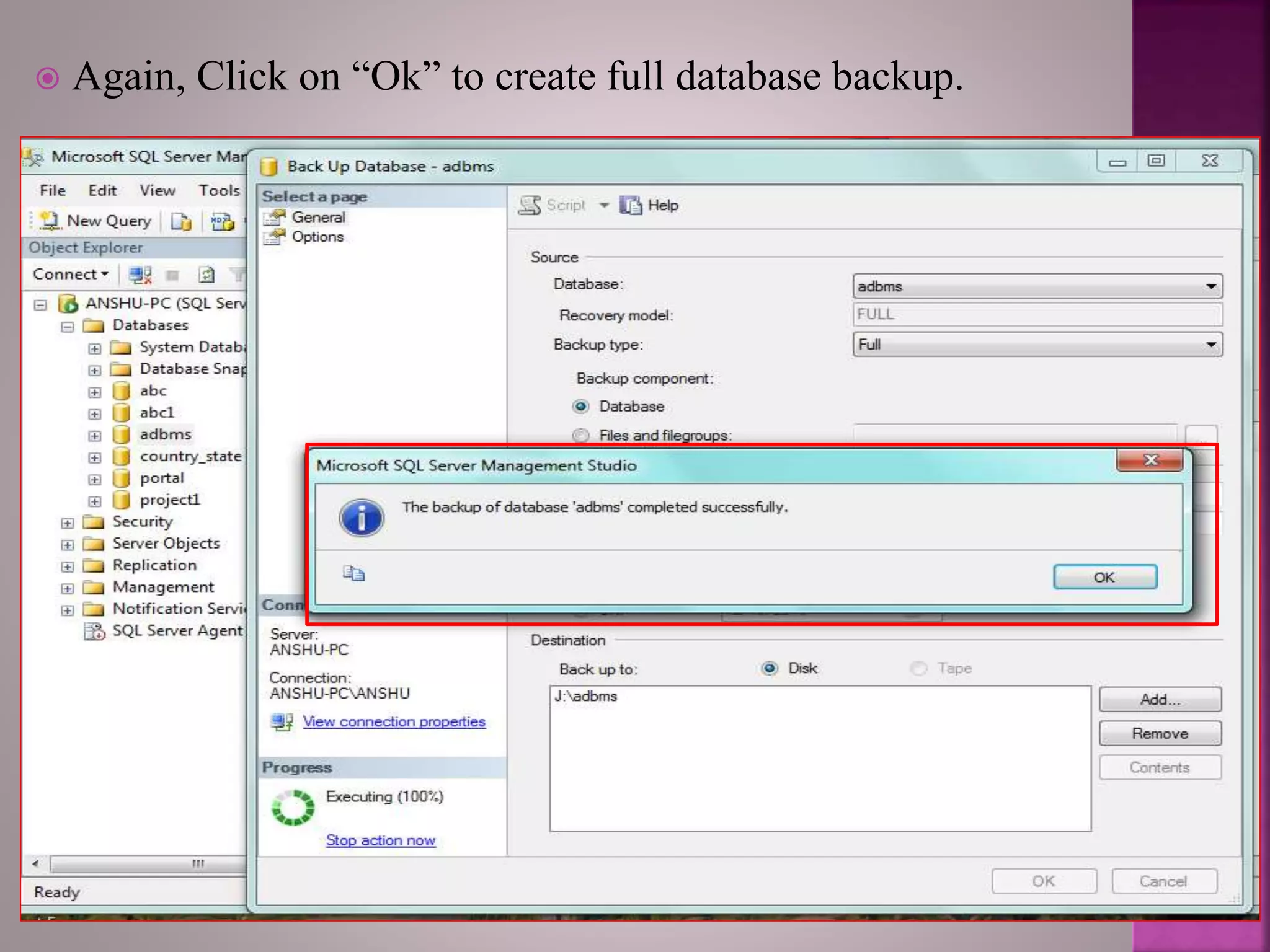
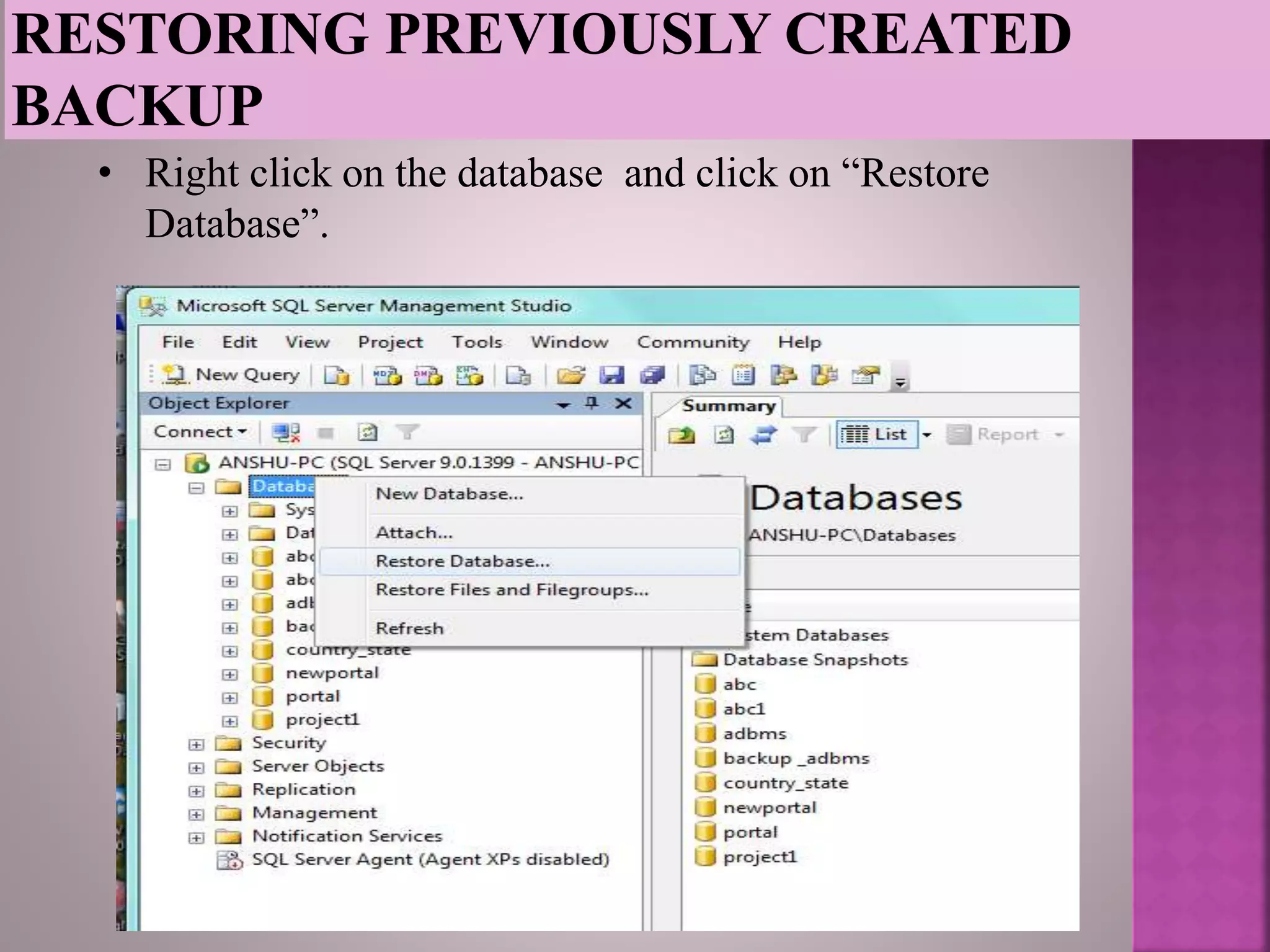
The document discusses the backup and recovery of SQL Server databases, detailing methods for creating full, differential, and transaction log backups. It outlines the process of backing up and restoring databases, emphasizes the importance of backups for data protection against failures, and notes the challenges related to storage space and version compatibility. The conclusion highlights the critical role of database administrators in managing backups and responding to data loss events.