Embed presentation
Download to read offline


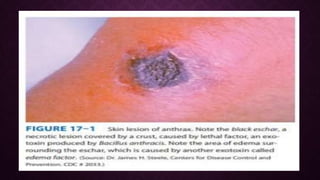








Bacillus anthracis is a gram-positive, spore-forming bacterium that causes anthrax. It forms large, box-car shaped rods arranged in chains. Anthrax presents as cutaneous, pulmonary, or gastrointestinal disease via spore entry through wounds, inhalation, or ingestion. The anthrax toxins, including lethal factor and edema factor, cause necrosis, edema, and hemorrhage. Diagnosis involves culture and antibody testing. Treatment includes antibiotics like penicillin or doxycycline. Vaccines can help prevent infection in at-risk populations.











