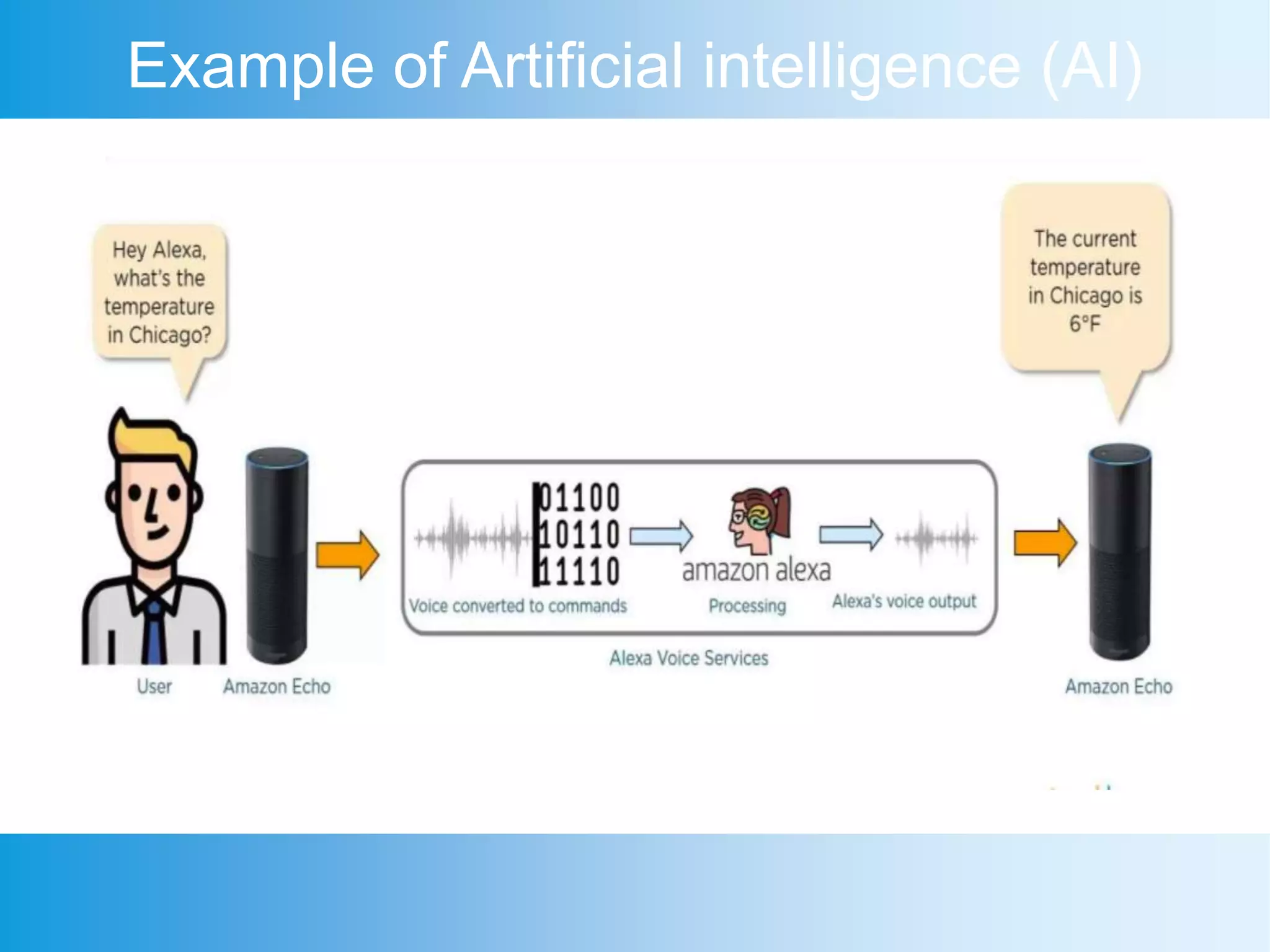
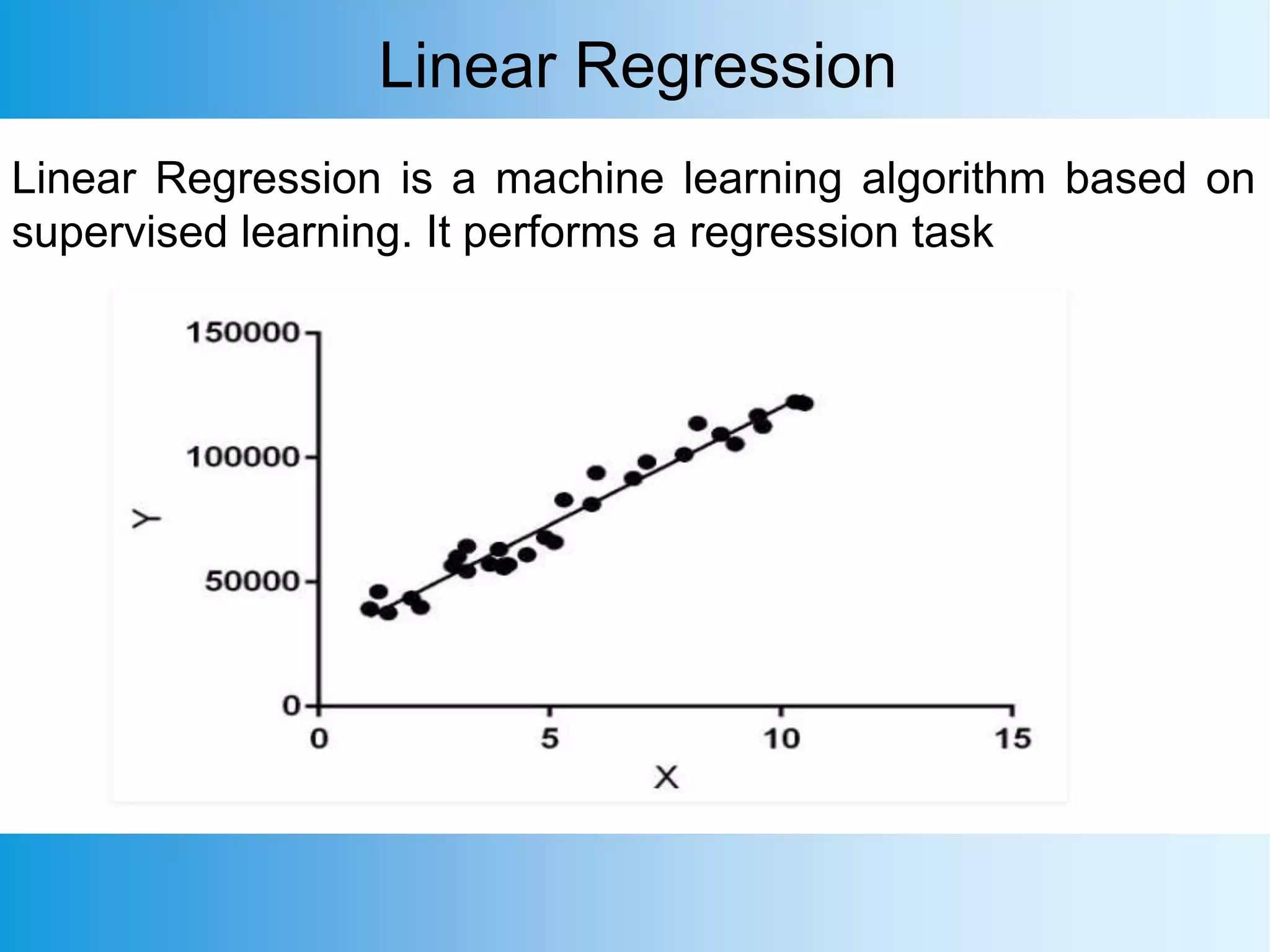
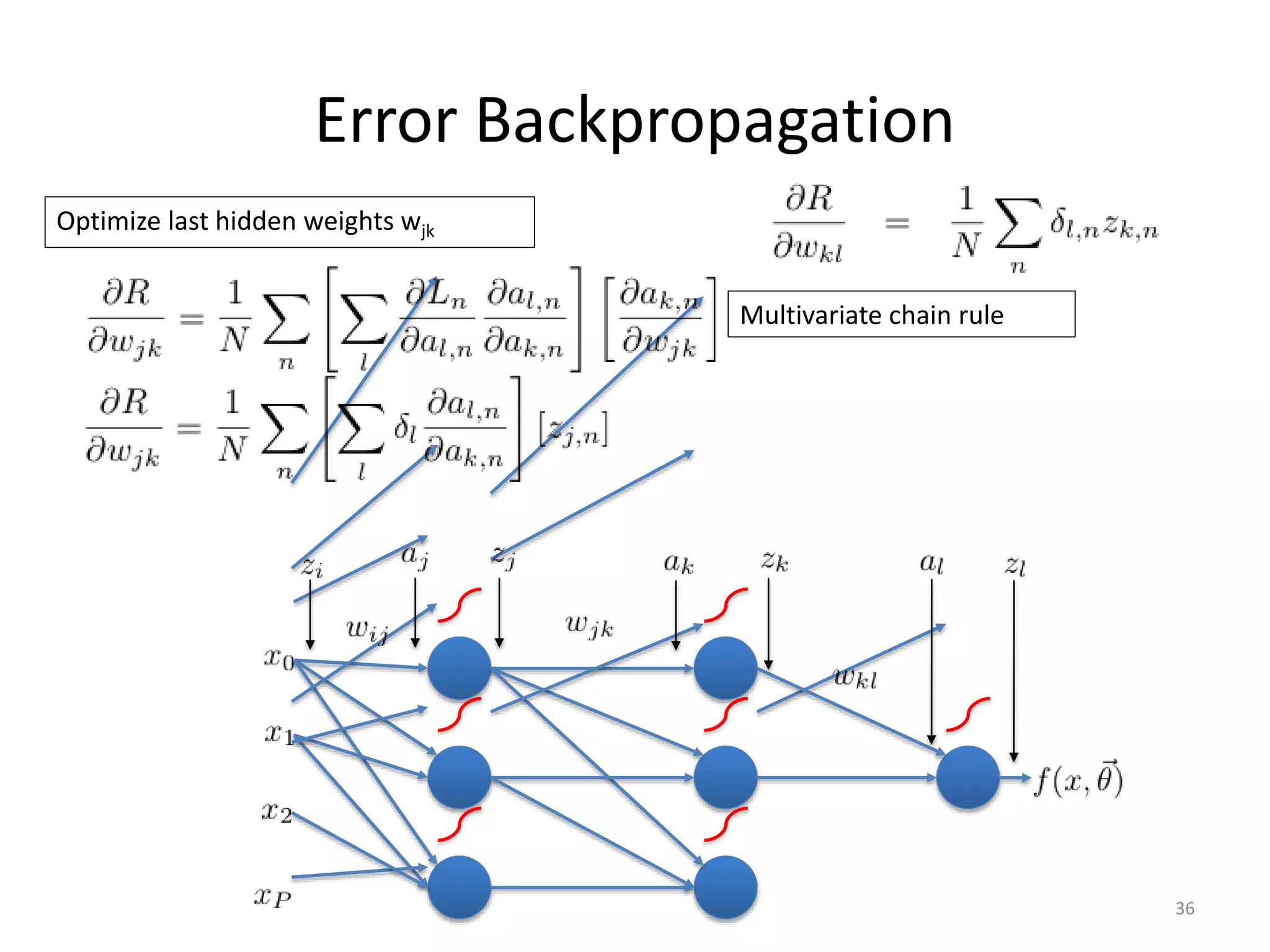
The document provides an overview of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and deep learning, outlining key definitions, types, and algorithms used in these fields. It distinguishes between machine learning and deep learning, particularly in how data is structured and processed within different types of algorithms like linear regression and convolutional neural networks. Additionally, it covers practical applications of deep learning in various domains such as robotics, facial recognition, and autonomous vehicles.