Embed presentation
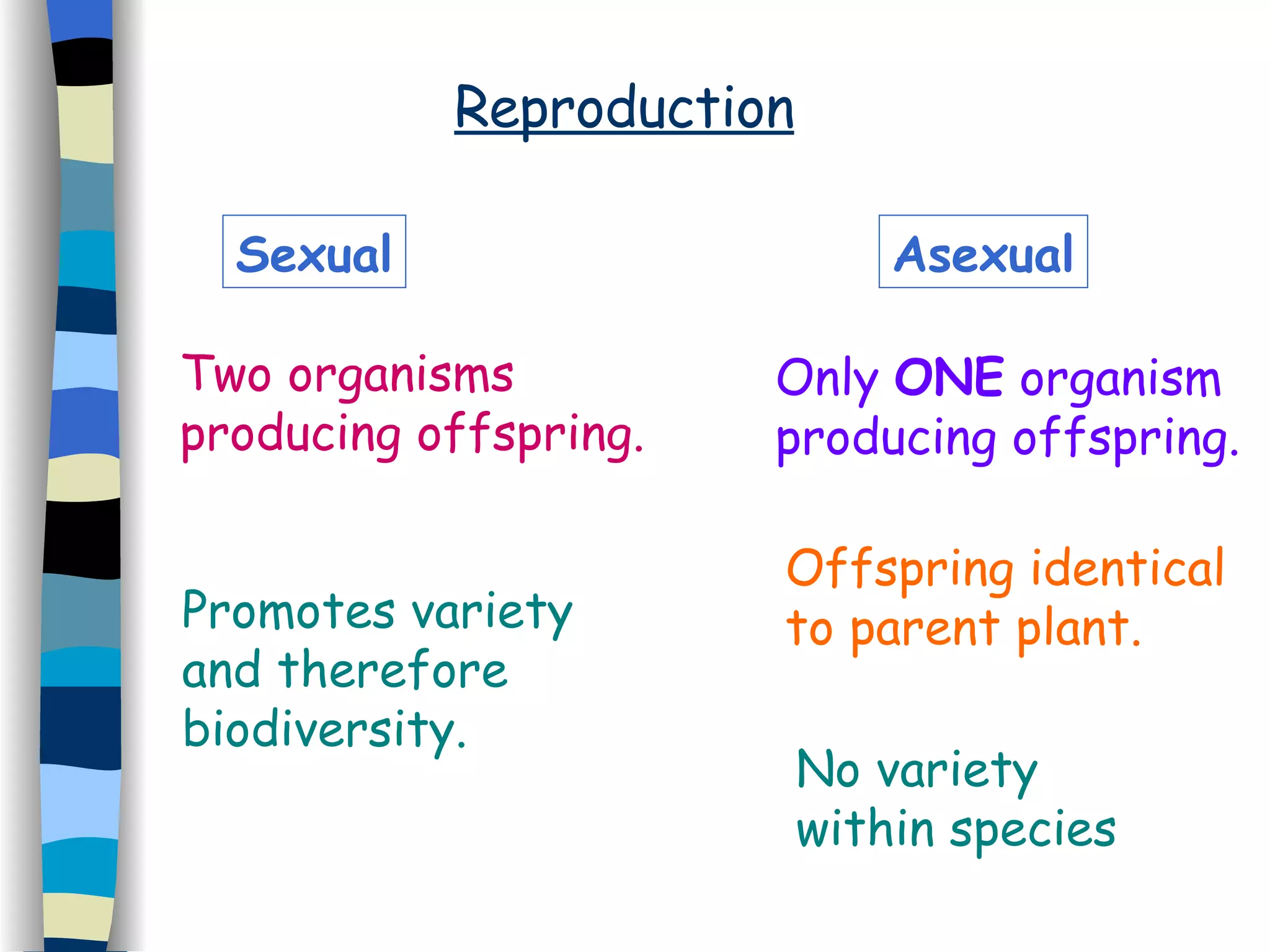
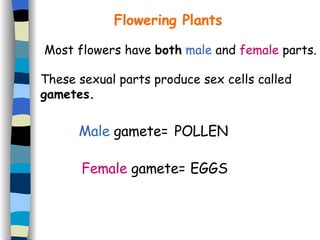
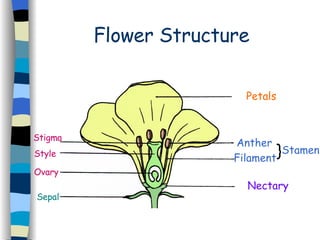
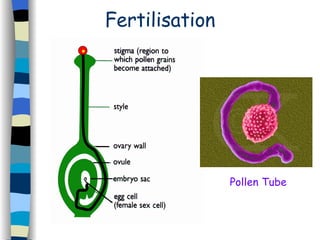



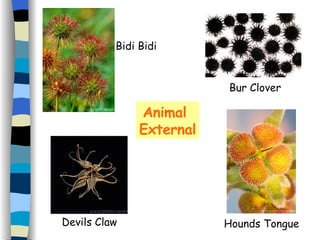



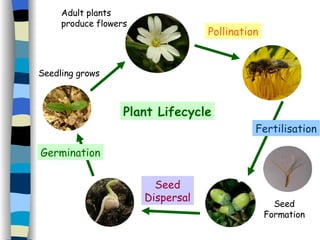

Reproduction can occur asexually through one organism producing offspring that are identical to the parent, or sexually through two organisms producing offspring that promote greater variety. Most flowering plants have both male and female reproductive parts that produce gametes - pollen grains and eggs. After fertilization of the egg by pollen, a seed forms which contains a new plant that will disperse and germinate, continuing the plant lifecycle. Seeds use various dispersal methods like wind, water, or animals to spread to new areas away from the parent plant.













