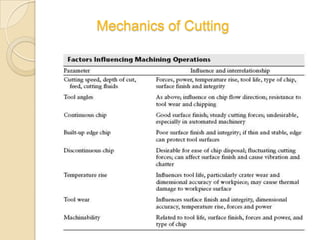
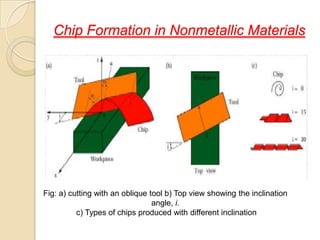
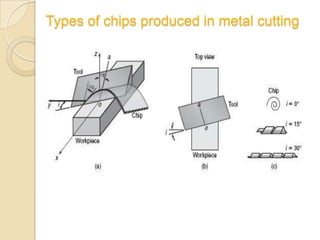
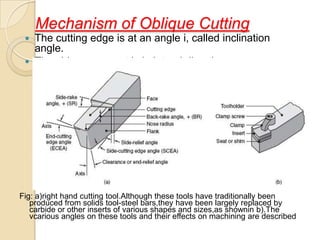
This document discusses oblique machining processes. It begins by defining orthogonal and oblique cutting, with oblique cutting having the cutting edge at an angle other than 90 degrees to the cutting velocity. It describes how in oblique cutting the chip forms in a helical pattern at an inclination angle. The document outlines different methods for determining the chip flow angle in oblique cutting, including observing tool scratches or photographing the process. It also discusses the various rake angles involved in oblique cutting, such as the normal, velocity, and effective rake angles.