Bioawk is a tool that extends GNU awk to facilitate working with biological file formats like FASTA, FASTQ, SAM, BED, GFF, and VCF. It directly reads gzipped files and treats spanning sequences as single records. Some key functions added in Bioawk include calculating GC content, reversing/reverse complementing sequences, and working with quality values. Bioawk allows for convenient parsing, manipulation and statistical analysis of genomic data.



![Examples
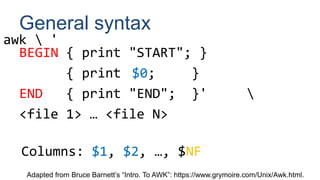
BEGIN { FS=OFS="t"; }
{ print $1,$2,$3; }
FNR > 1 { }
grep -v 'chr[mM]' <f> | awk '{print
$1,$2,$3}' | sed 's/chr//;'
awk '$1 !~ /chr[mM]/ {sub(/chr/, "");
print $1,$2,$3}' <f>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2020-12-02viner-tech-awkandbioawk-210126180923/85/Awk-primer-and-Bioawk-5-320.jpg)
![Examples: two files
awk 'FNR==NR{a[$1]=$2; next}
{print $1,$2,a[$2]; }'
<file 1> <file 2>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2020-12-02viner-tech-awkandbioawk-210126180923/85/Awk-primer-and-Bioawk-6-320.jpg)







![Bioawk - examples - VCF files
bioawk -c vcf '{
freq[$filter]++
total++
}
END {
for(val in freq)
printf "%st%dt%dn",
val, freq[val], freq[val]*100/total
}'
From sahilseth's flowr Bioawk tips, itself adapted from Stephen Turner's "Bioinformatics one-liners".
Assess pipeline—
sequence filter statistics:
• filter (e.g. LowQual)
• number of filter
occurrences
• percentage of total filters](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2020-12-02viner-tech-awkandbioawk-210126180923/85/Awk-primer-and-Bioawk-14-320.jpg)

