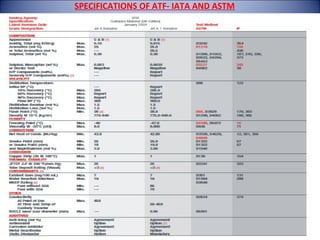
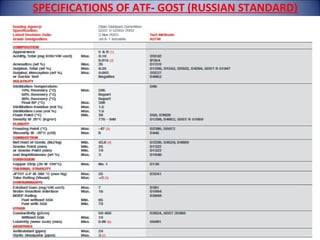
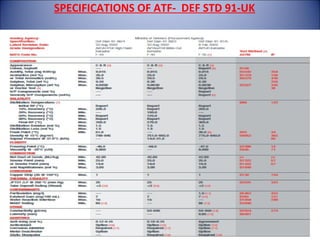
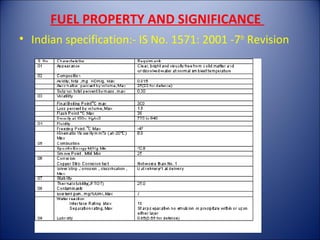
The document provides an overview of aviation turbine fuel (ATF), including its properties, importance, specifications, and the issue of fuel contamination. It highlights various grades of jet fuel, major specifications such as ASTM and DEF STAN, and the critical nature of maintaining fuel quality due to potential contaminants. Quality checks for ATF are also discussed, emphasizing the need for visual inspections and density checks.