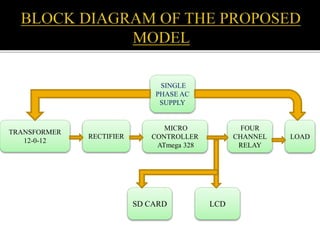
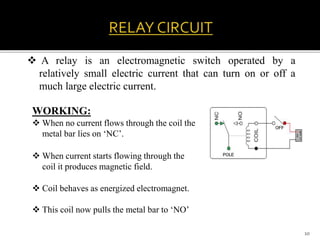
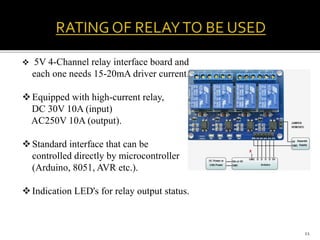
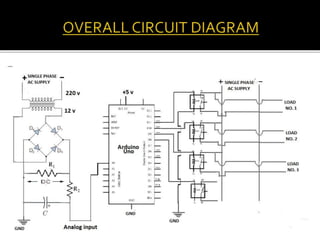
This project aims to automate load shedding in substations using a microcontroller and GSM module, displaying load statuses on an LCD and serial monitor. The system ensures reliable operation and faster response to disturbances, allowing for selected load management without complete blackout. The implementation involves a combination of relays, rectifiers, microcontroller components, and requires skilled maintenance and higher initial investment.