Embed presentation
Download as ODP, PPTX


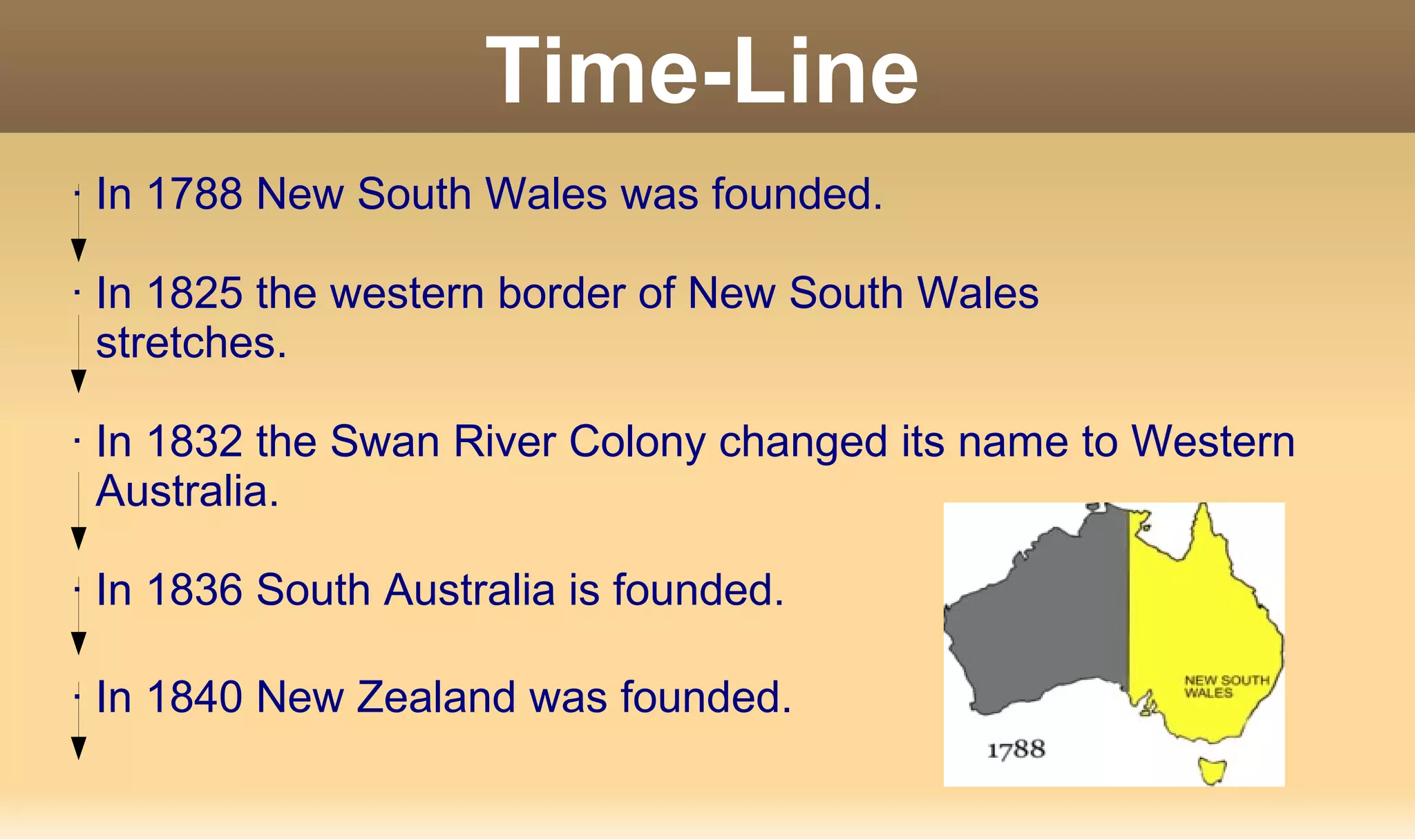





Australian English originated from British English and was first brought to Australia in 1788 when New South Wales was founded. Over subsequent decades, additional Australian states and territories were established including Western Australia, South Australia, Victoria, Tasmania, Queensland, and the Australian Capital Territory. Australian English has developed some distinctive linguistic characteristics such as using "she/her" for inanimate objects and no number distinction for reflexives. It has also incorporated Aboriginal words like "boomerang", "bush", and "kangaroo" into the vocabulary. Migration from Britain and other parts of Europe and Asia have continued to influence the language.
Introduction to Australian English.
Australia is the sixth largest country, covering 7,686,850 km², with British English origins.
Key historical events: founding of states and territories from 1788 to 1911.
Distinctive linguistic traits: pronouns, reflexives, and number pronunciation.
Unique Australian words: Boomerang, Bush, Kangaroo, Battler, Budgerigar, Wallaby.
The history of English in Australia influenced by diverse migrant waves since 1788.







