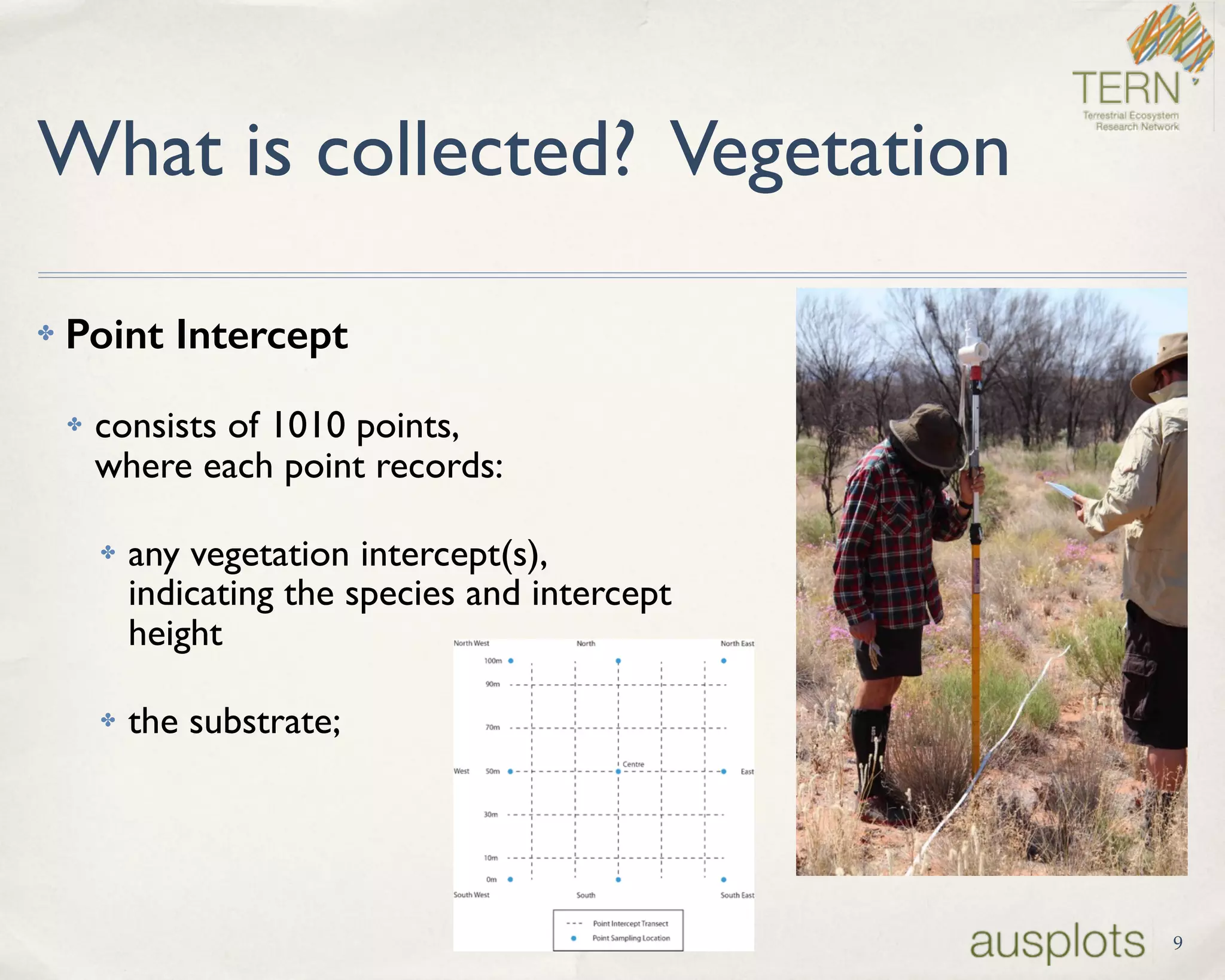
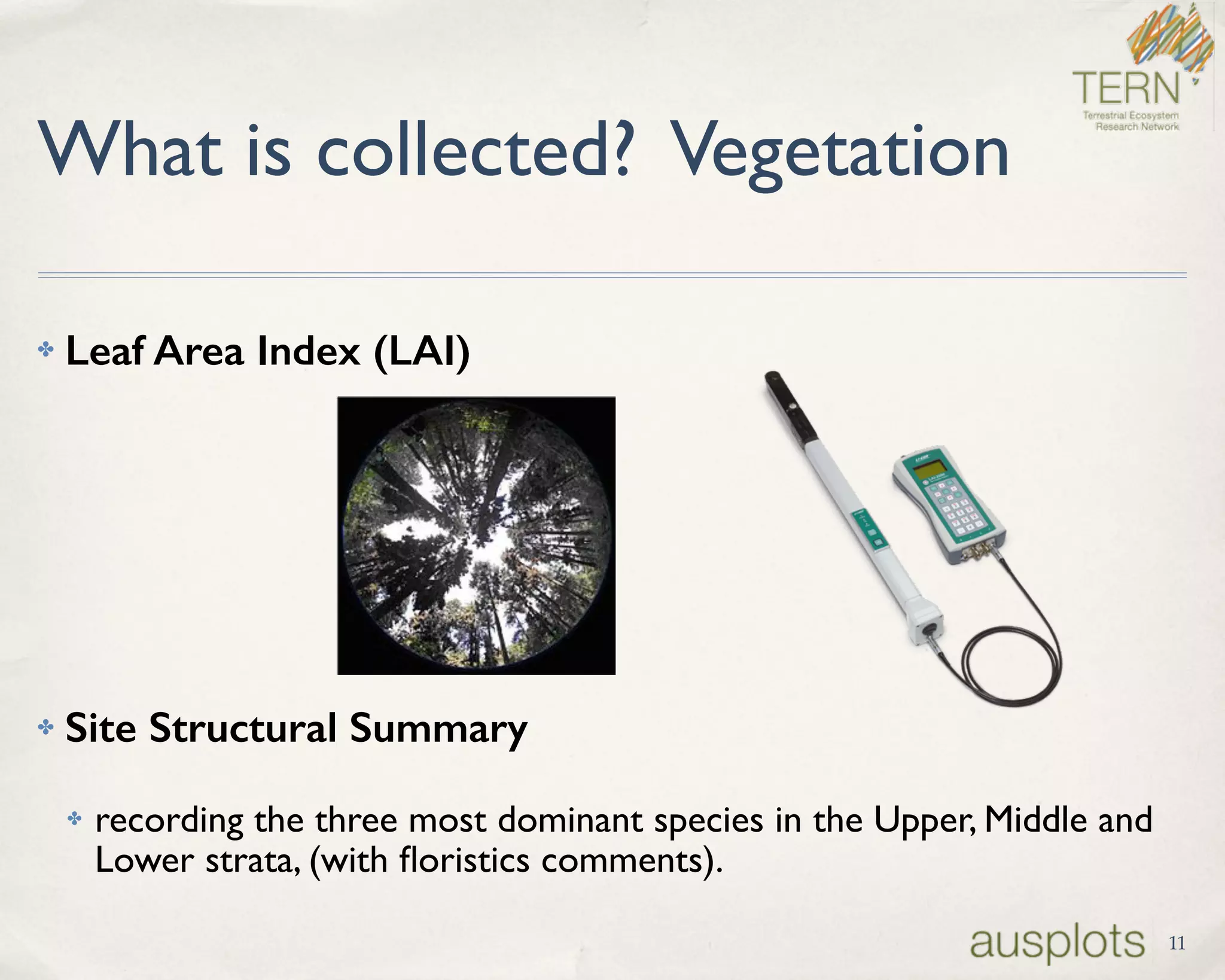
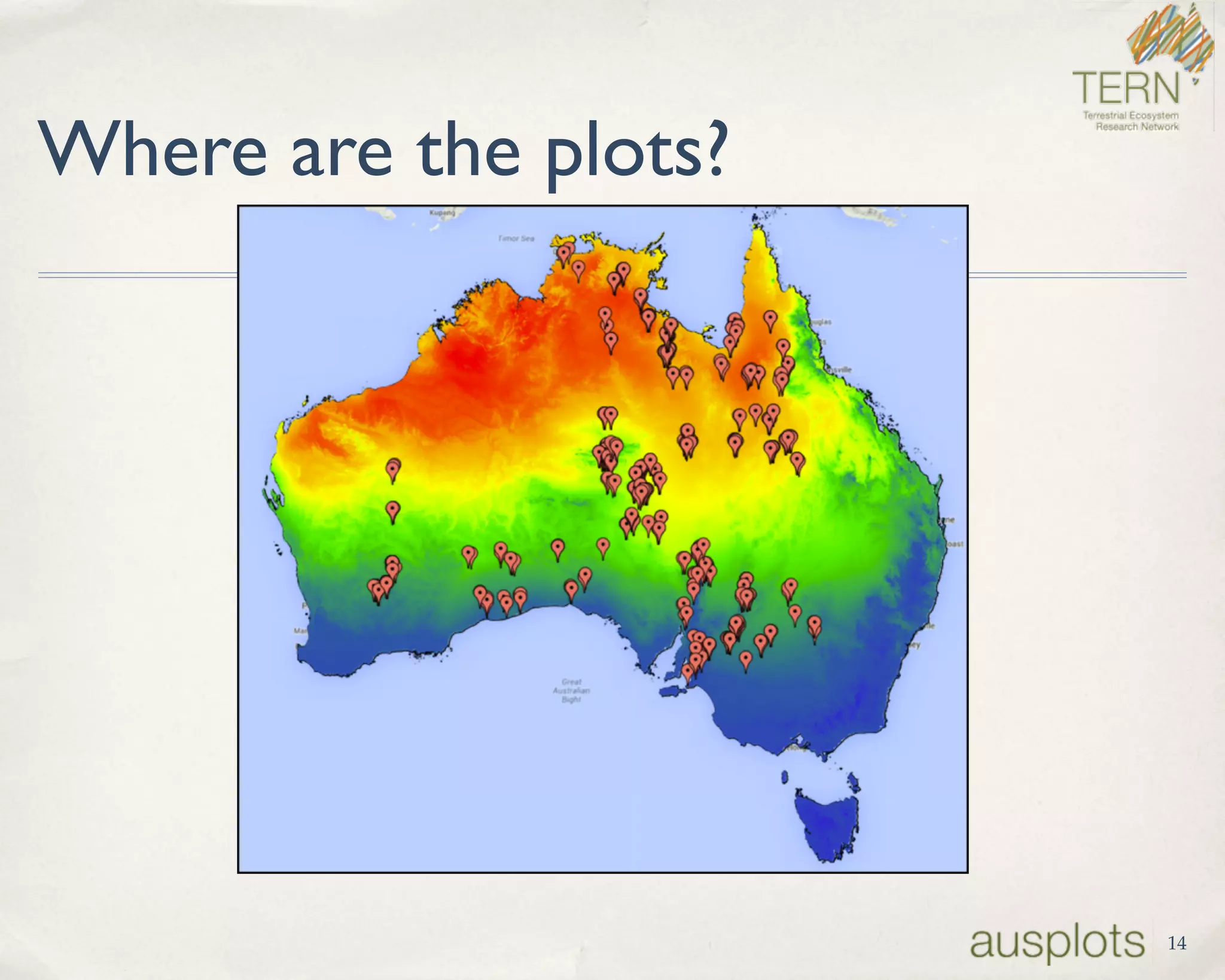
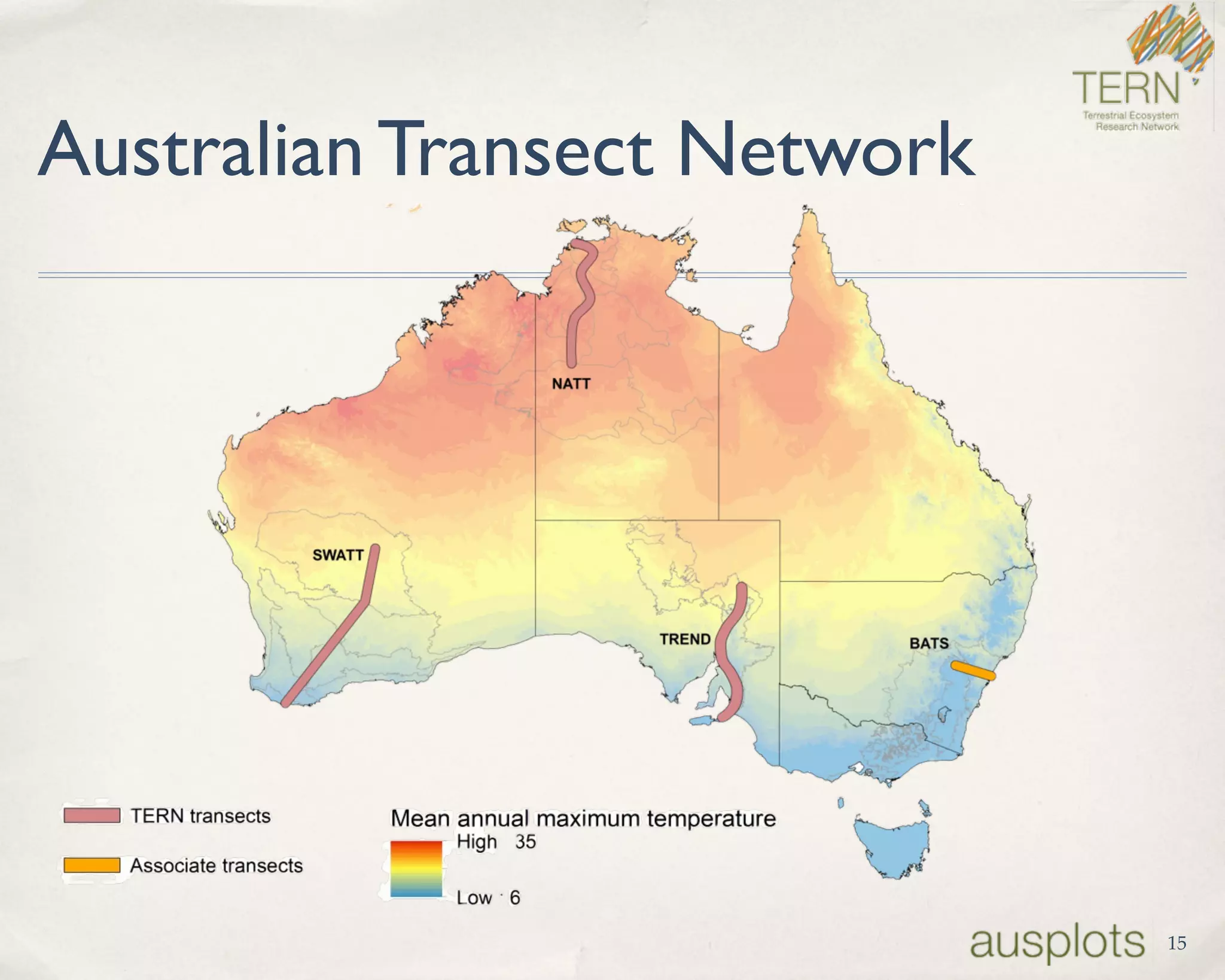
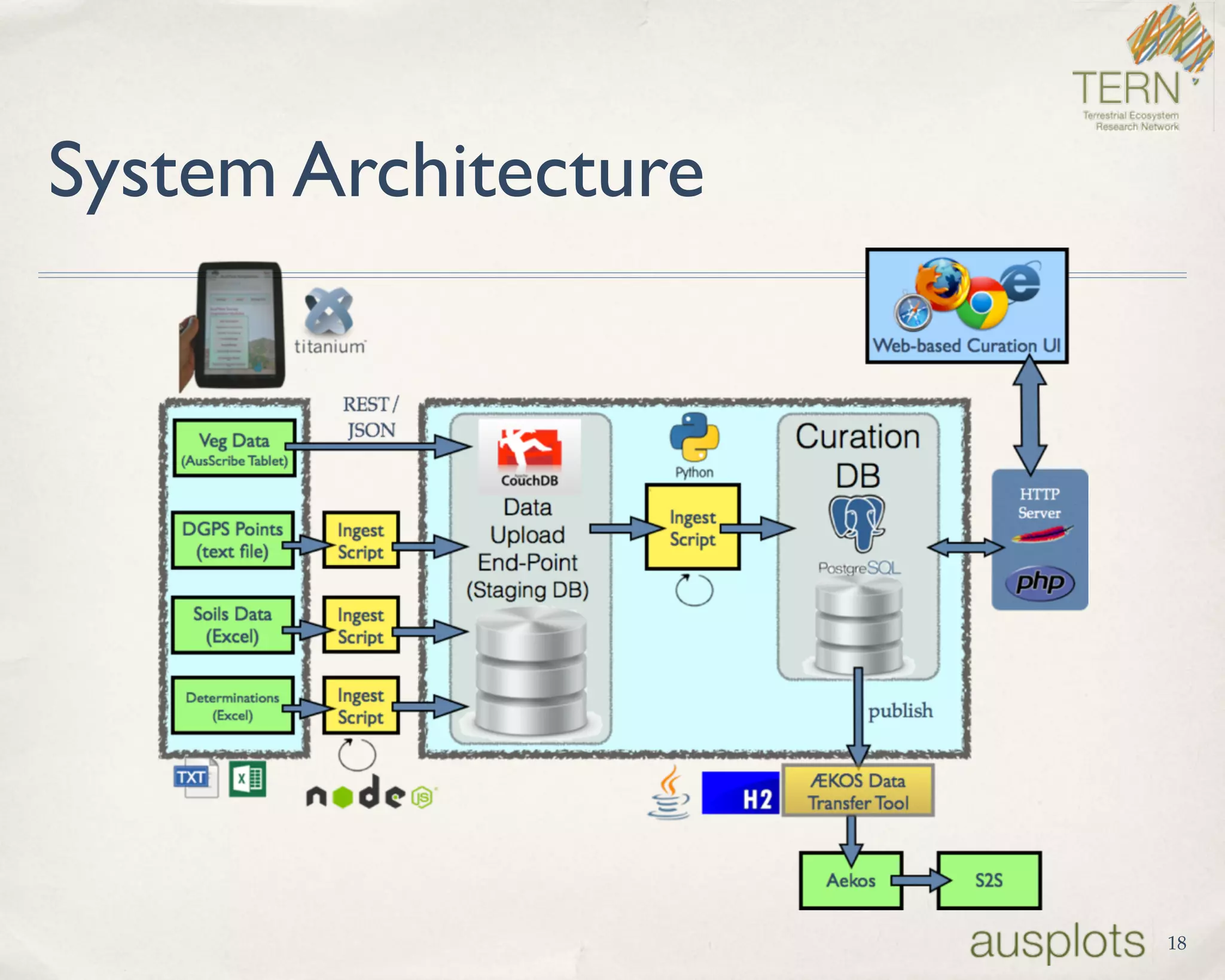
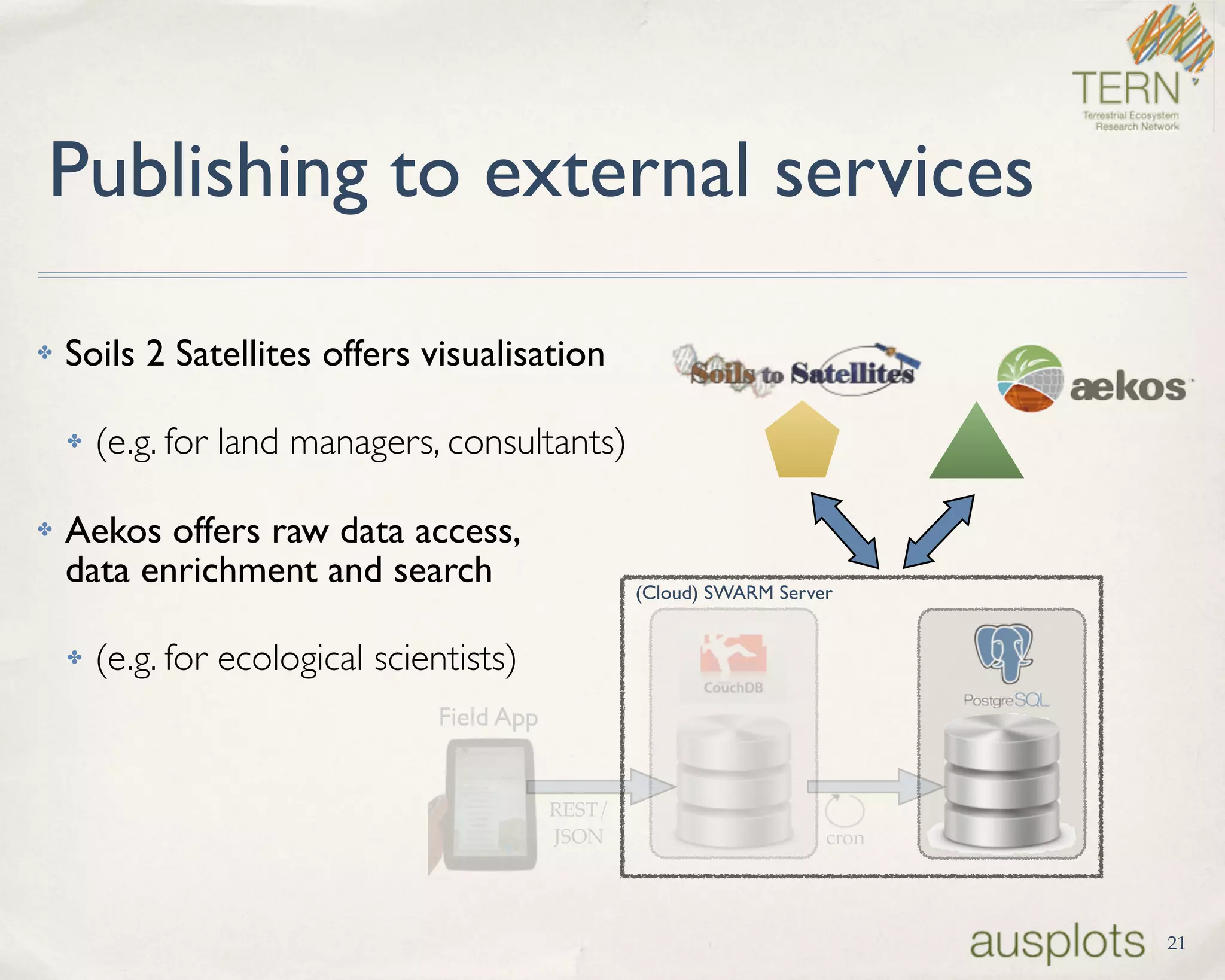
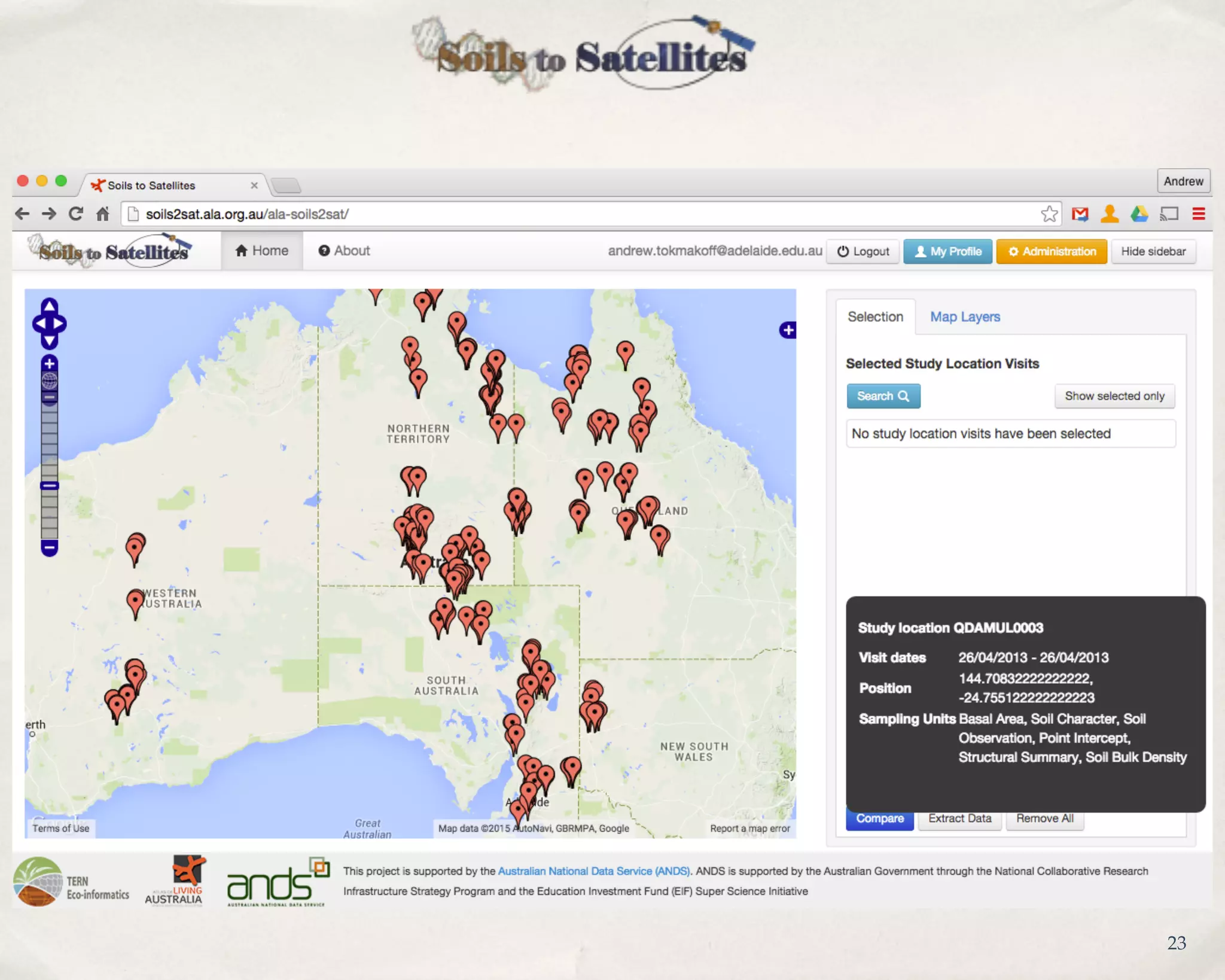
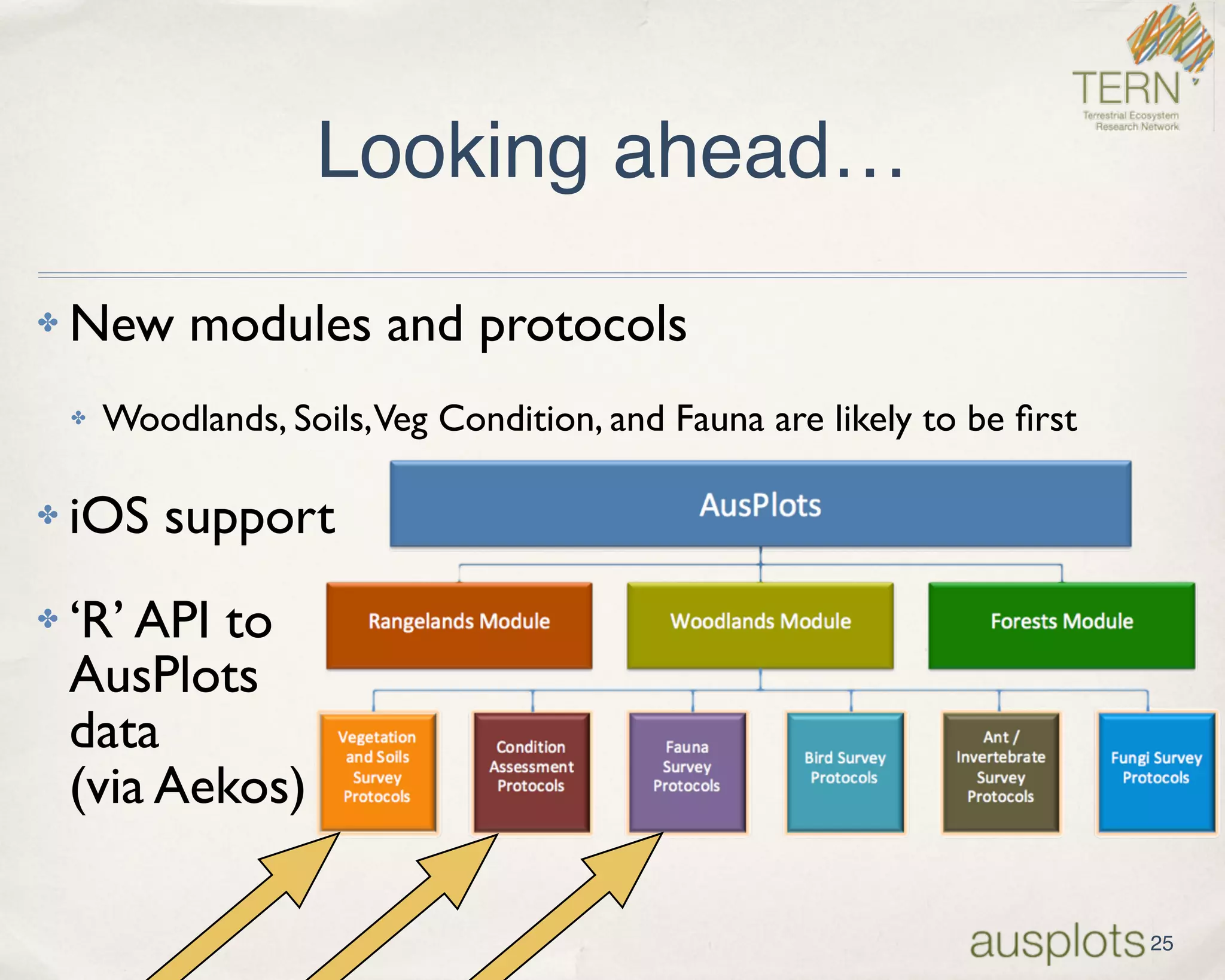
AusPlots collects standardized ecological data from permanent plots across Australian rangelands to facilitate long-term monitoring and decision making. Field data is collected using a custom mobile app, AuScribe, which follows a rigorous protocol. This generates clean integrated data that is easily curated and published through various platforms. The iterative development of AuScribe and a component-based architecture allowed for fast results handling the complex data needs while mobile. The standardized long-term data made available through AusPlots informs ecological research and management.