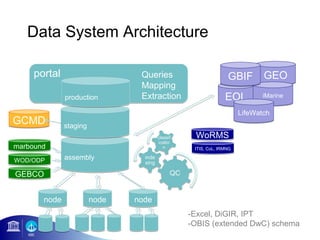
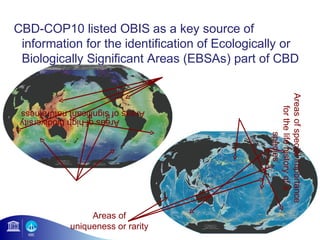
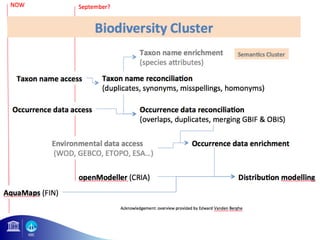
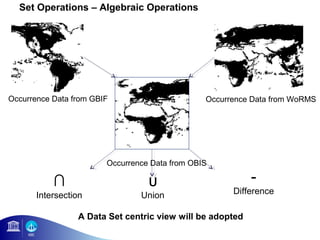
1) OBIS aims to make biogeographic data freely available to support ocean management and conservation.
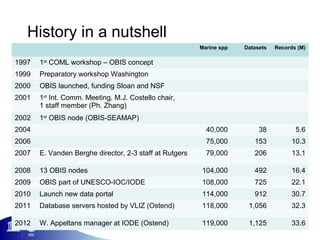
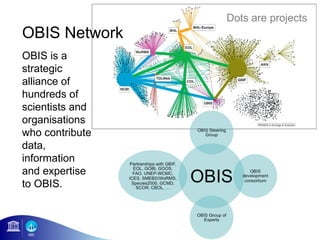
2) It has grown from 1 staff member in 2001 to include hundreds of contributing partners by 2012.
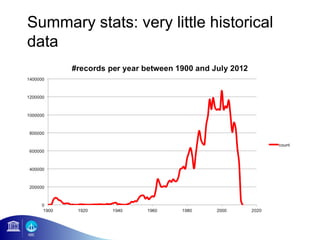
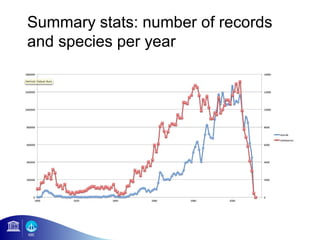
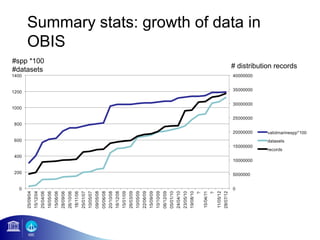
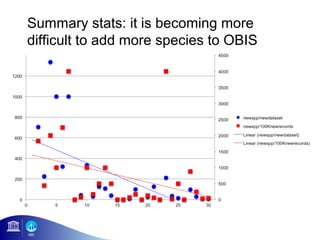
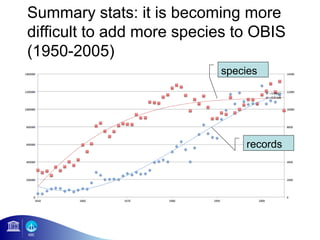
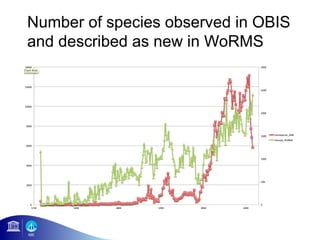
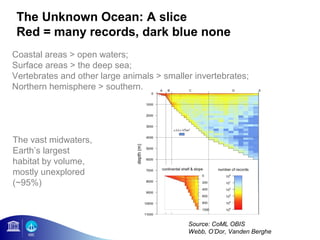
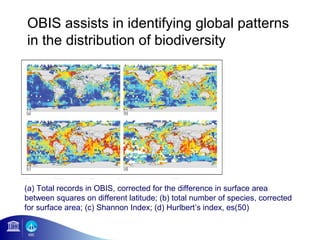
3) The number of species, datasets, and records in OBIS has increased dramatically over time but significant data gaps still remain, especially in understudied areas like the deep sea.