The document discusses the different types of audits conducted by the Commission on Audit of the Philippines - financial, compliance, and performance audits. It explains that a financial audit aims to determine if financial statements are properly prepared, while a compliance audit checks for compliance with laws and regulations and a performance audit assesses economy, efficiency and effectiveness.
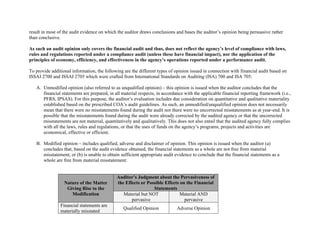
The document also summarizes the different types of audit opinions that can be issued for a financial audit. An unmodified or unqualified opinion means the financial statements are properly prepared, while a modified opinion (qualified, adverse, or disclaimer) means there are material misstatements or the auditor could not obtain sufficient evidence.
Finally, the document emphasizes that an audit opinion only relates to the financial