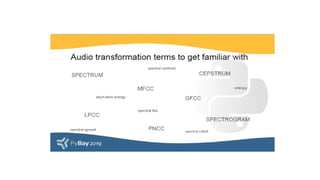
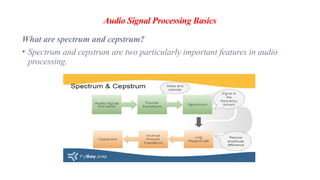
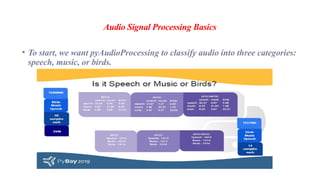
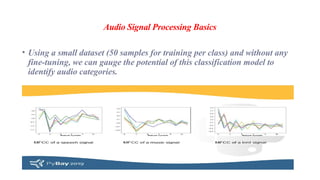
The document covers the fundamentals of audio signal processing, detailing the characteristics of audio data, various file formats, and essential features like spectrum and cepstrum. It also discusses applications of audio analysis, including speech, voice, music, and environmental sound recognition, as well as tools and technologies utilized in these processes. MATLAB's Mirtoolbox and Voicebox are highlighted as resources for audio processing, with insights into voice recognition efficiencies and challenges.