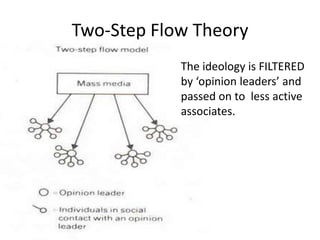
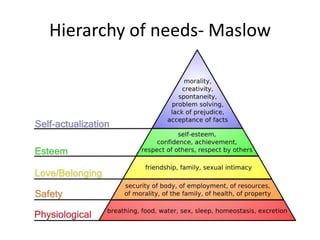
This document explores various audience theories that can be applied to coursework, including: the hypodermic needle theory which views audiences as passive receivers; two-step flow theory where opinion leaders filter messages; uses and gratifications theory focusing on why audiences use media; hierarchy of needs; readings by Stuart Hall; Laura Mulvey's male gaze; and objectification frameworks by Martha Nussbaum and Rae Langton. It aims to help students prepare for an exam question on audience theory.