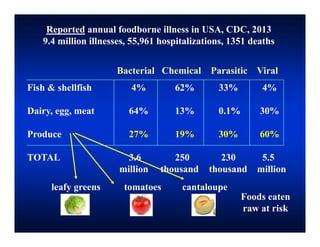
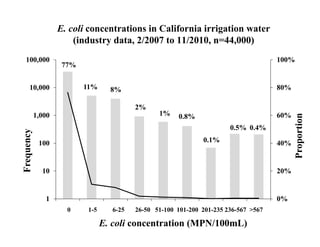
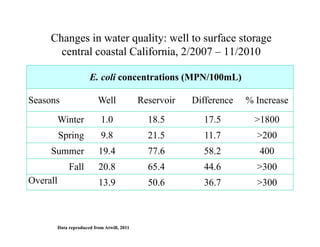
The document discusses the relationship between conservation practices and food safety in California, highlighting annual foodborne illness statistics and the role of irrigation water in pathogen transmission. It details the prevalence of E. coli and other pathogens in various sources, emphasizing the need for improved management strategies such as fencing, habitat modification, and various agricultural practices to mitigate risks. Evidence from field trials and studies illustrates the impact of wildlife on food safety, particularly in produce contamination incidents.