Embed presentation
Download to read offline

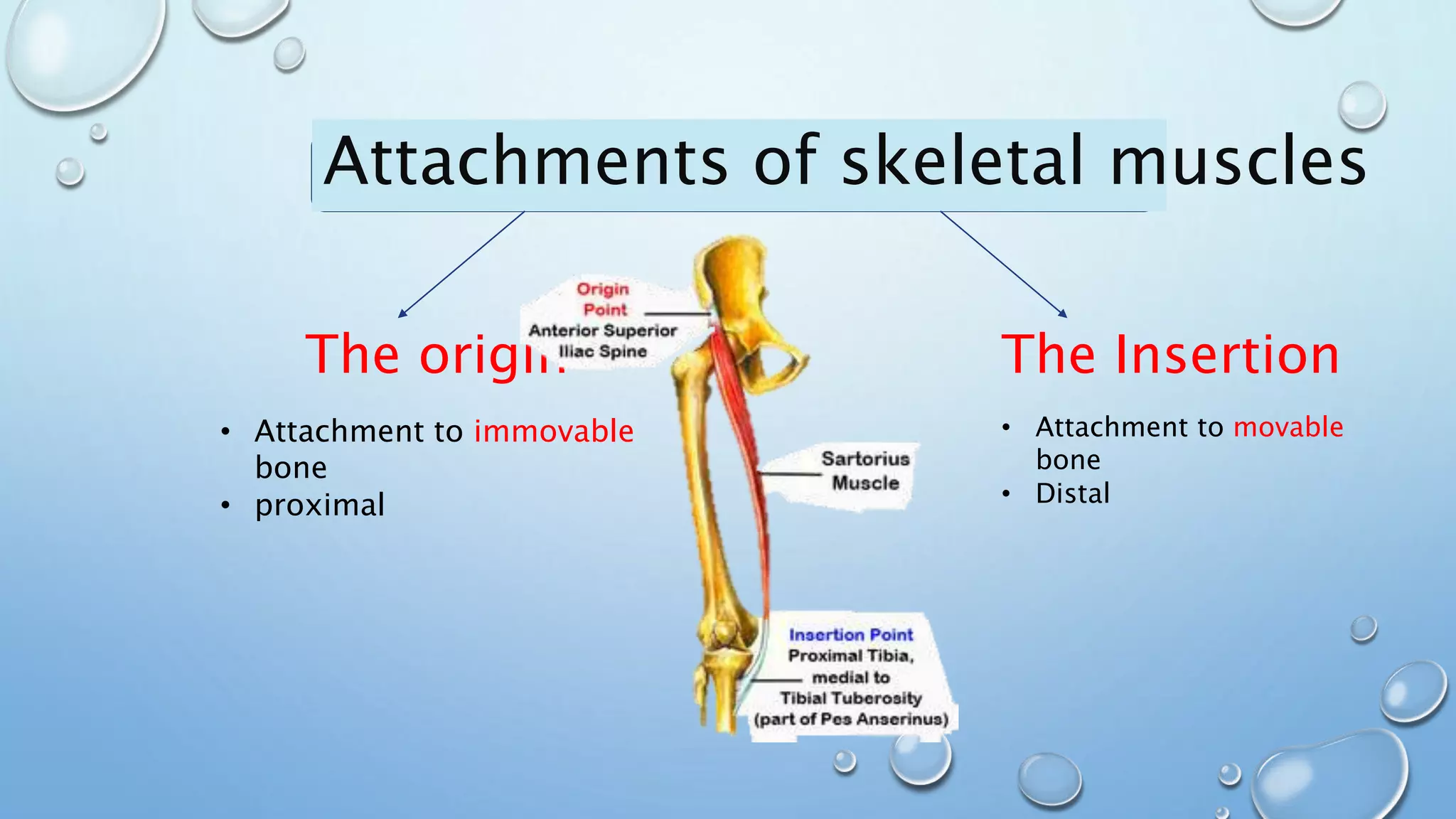
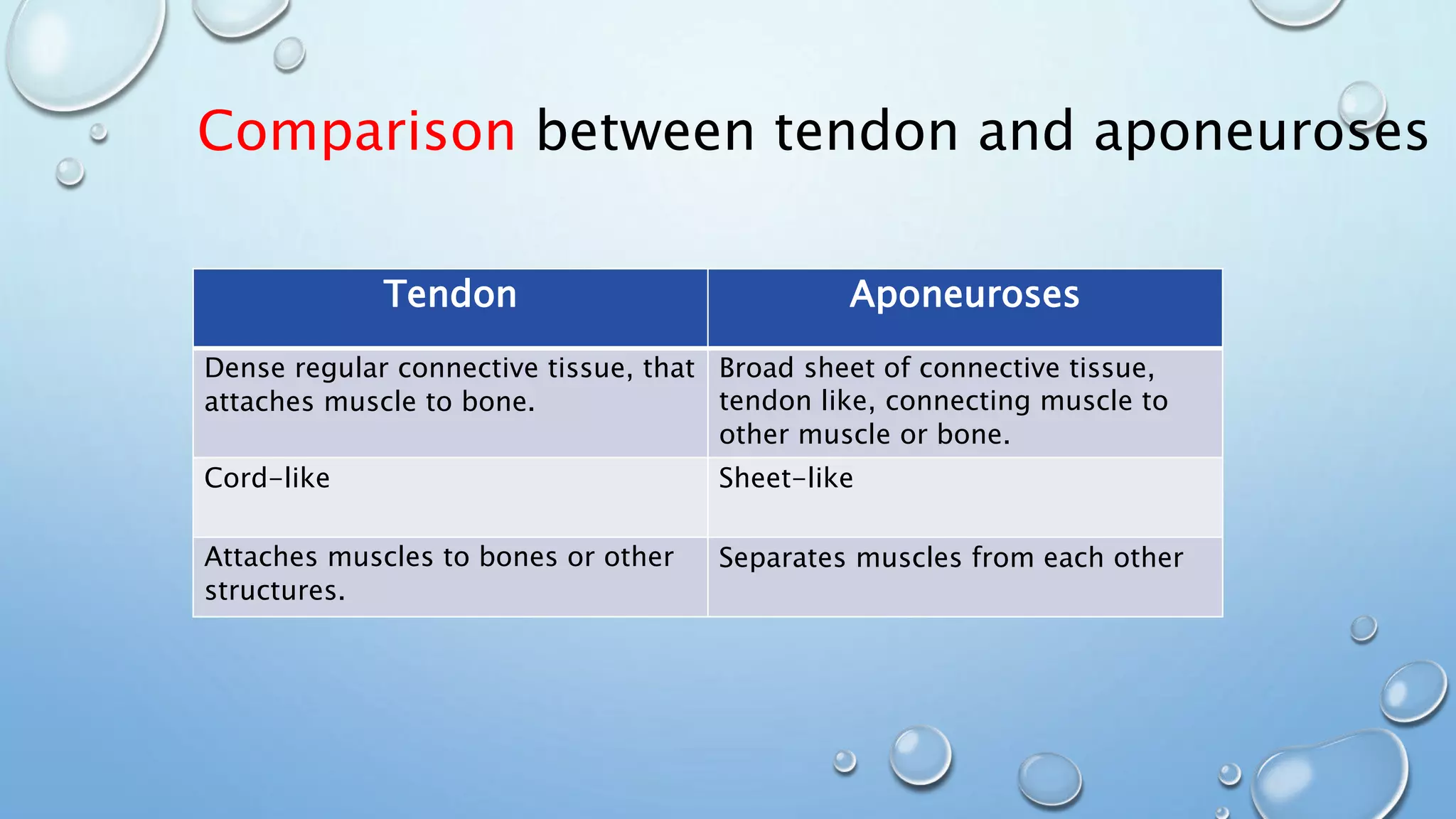
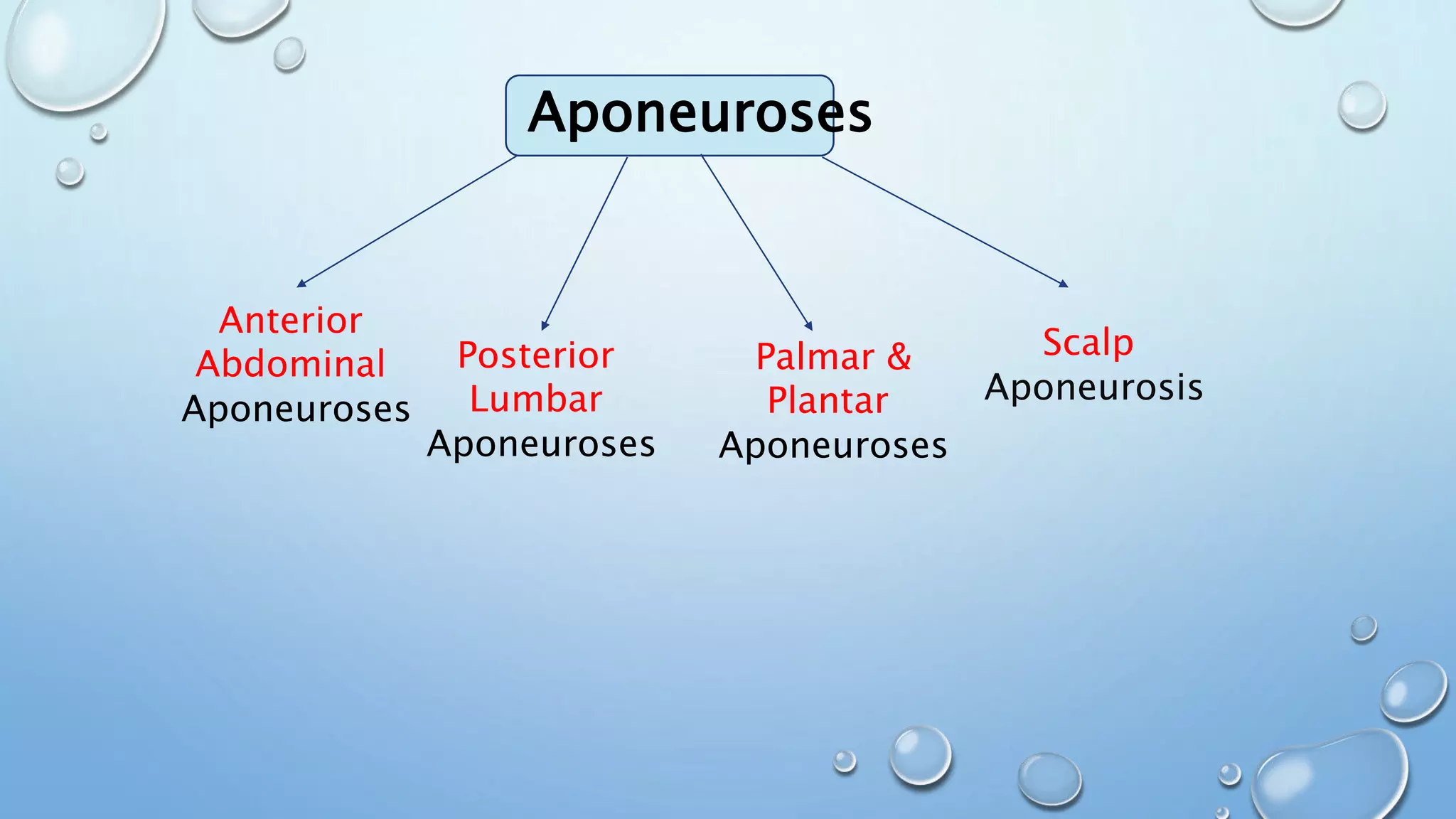
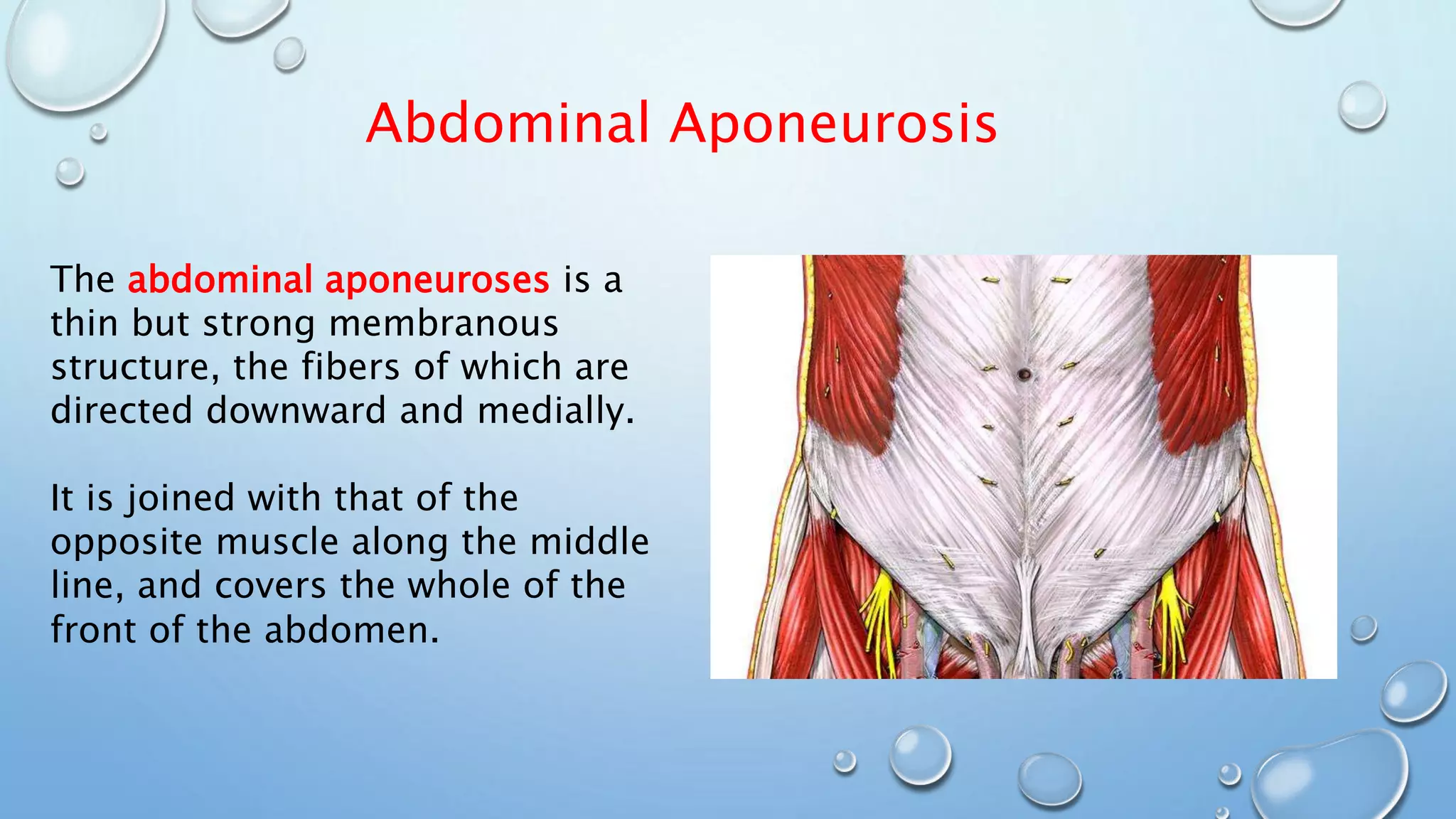
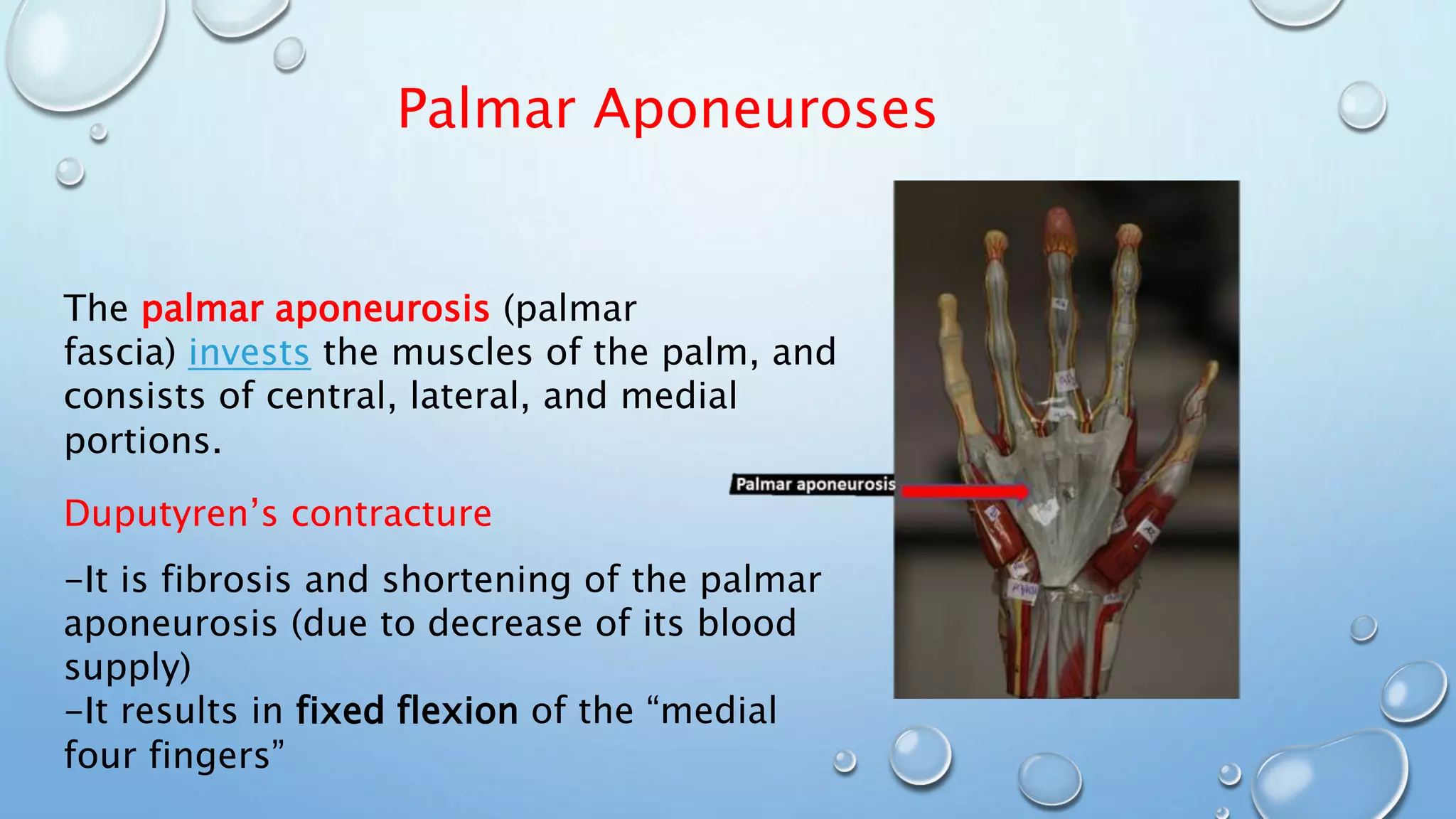
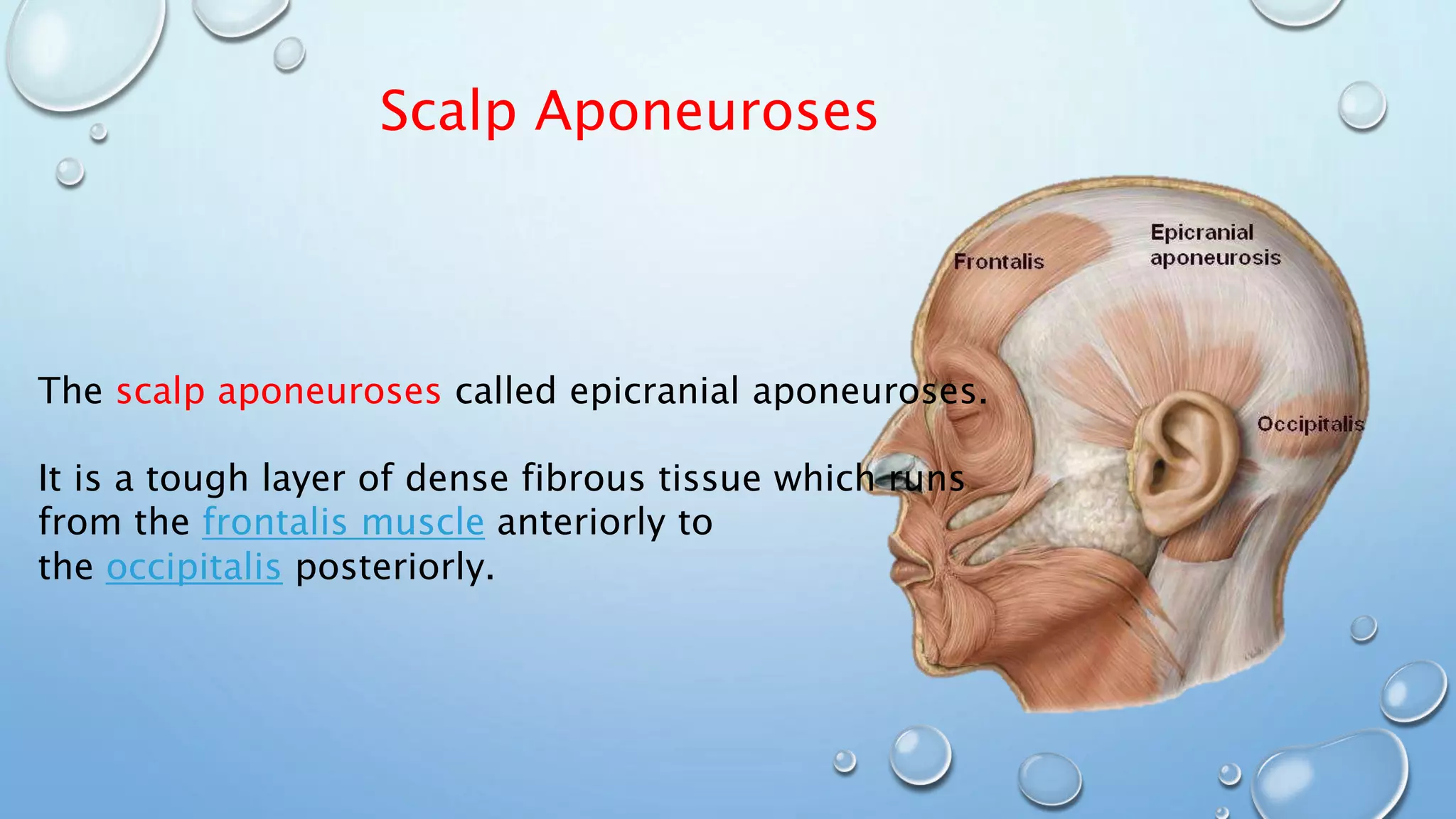

The document discusses attachments of skeletal muscles, comparing tendons and aponeuroses, and detailing specific types including abdominal, palmar, and scalp aponeuroses. It highlights the functions and structures of these connective tissues, including the impact of conditions like Dupuytren's contracture on the palmar aponeurosis. Various aponeuroses serve to connect muscles and bones or separate them within the body.







