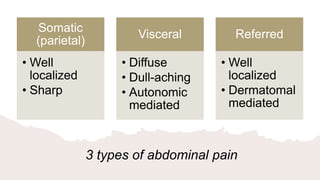
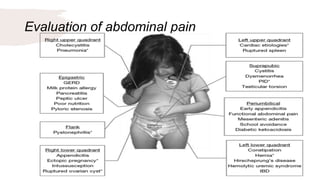
This document provides an overview of the clinical approach and differential diagnosis of acute abdominal pain. It discusses the three types of abdominal pain and lists important factors to consider during evaluation such as associated symptoms. Common and uncommon potential causes of abdominal pain are outlined. For selected differential diagnoses, examples of relevant history, physical exam findings, working diagnoses, and recommended investigations are provided. The goal is to guide clinicians in appropriately evaluating and diagnosing the source of a patient's acute abdominal pain.

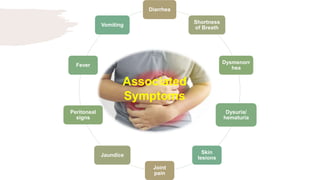
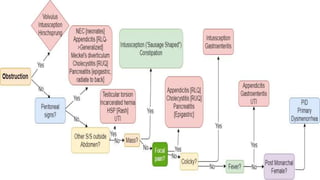
![Differential Diagnosis
Common
Constipation
Acute Appendicitis
Gastroenteritis
Henoch–Schönlein Purpura
Urinary tract infection
Abdominal trauma
Celiac disease
Diabetic ketoacidosis
Cholecystitis
Primary dysmenorrhea
Pneumonia
Functional abdominal pain
Uncommon
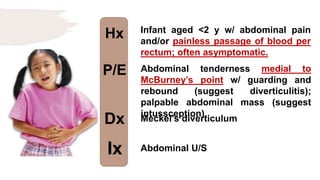
Intussception [Infants]
Meckel’s diverticulum [Infants]
Mesenteric Adenitis
Hirschsprung disease [Infants]
Inflammatory bowel disease
Malrotation [Volvulus] [Neonates]
Necrotizing enterocolitis [Neonates]
Sickle cell crisis [Infants]
Viral hepatitis
Acute pancreatitis
Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome [Infants]
Testicular torsion
Pelvic Inflammatory disease](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pediatricspresentaion-210418144348/85/Pediatrics-Acute-Abdominal-Pain-Workup-6-320.jpg)

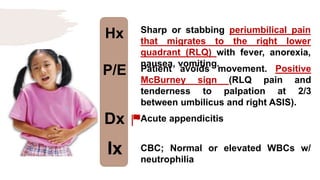
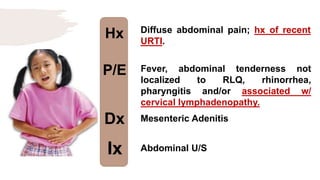
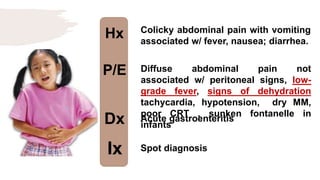
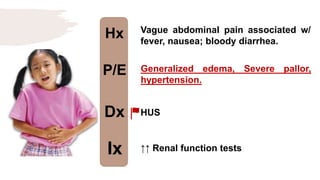
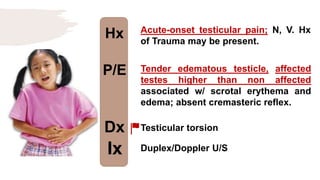
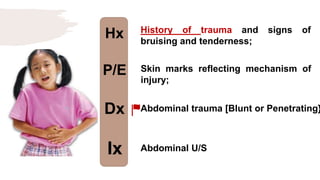
![Hx
P/E
Dx
Ix
Colicky and poorly localized
abdominal pain, sometimes
accompanied by vomiting and bloody
diarrhoea w/ skin rash.
Erythematous, macular trunk-sparing
rash with arthritis/arthralgia
with/without Hematuria, nephrotic
syndrome. [Multiple System
Involvement].
HSP
Spot diagnosis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pediatricspresentaion-210418144348/85/Pediatrics-Acute-Abdominal-Pain-Workup-13-320.jpg)
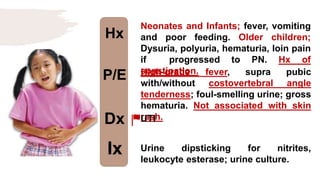
![Hx
P/E
Dx
Ix
Rapid deep breathing, abdominal
pain, vomiting, confusion; IDDM.
Hypothermia, hypotension,
tachycardia, tachypnea [Kaussmaul’s
breathing]
DKA
Urinalysis for ketones](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pediatricspresentaion-210418144348/85/Pediatrics-Acute-Abdominal-Pain-Workup-16-320.jpg)
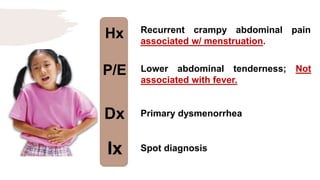
![Hx
P/E
Dx
Ix
Male in early infancy; failure to pass
meconium in the first 36 hours of
life[Bowel Obstruction] with/without
hx of Down $
Abdominal distension in the LLQ;
palpable fecal mass; absence of
peritonitis, guarding or rebound
tenderness; dysmorphic features of
Down $
Hirschsprung disease
Abdominal X-ray](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pediatricspresentaion-210418144348/85/Pediatrics-Acute-Abdominal-Pain-Workup-19-320.jpg)
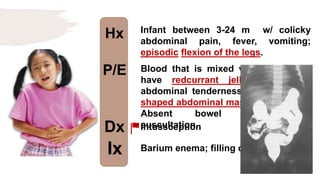
![Hx
P/E
Dx
Ix
Early infancy age group; Hx of bilious
vomiting
Diffuse abdominal and tenderness;
absent bowel sounds [obstruction],
guarding, rebound tenderness [+ve
peritoneal signs] associated w/ low
grade fever and hematochezia.
Malrotation volvulus
Upper GI contrast study; bird beak
sign of stricture.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pediatricspresentaion-210418144348/85/Pediatrics-Acute-Abdominal-Pain-Workup-20-320.jpg)
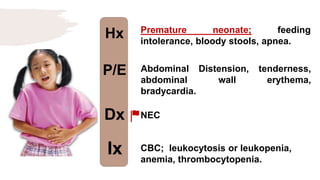
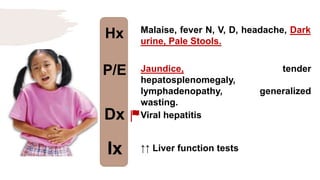
![Hx
P/E
Dx
Ix
Recurrent episodic RUQ colicky pain
occurs after eating fatty foods
radiating to the back; with referred
pain to the rt shoulder.
Right subcostal region tenderness;
+ve murphy’s sign during palpation.
[+ve peritoneal signs].
Acute Cholecystitis
RUQ U/S](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pediatricspresentaion-210418144348/85/Pediatrics-Acute-Abdominal-Pain-Workup-23-320.jpg)
![Hx
P/E
Dx
Ix
N, V, epigastric colicky pain radiating
to back.
Epigastric tenderness; tachycardia
and tenderness in severe cases; +ve
Cullen sign [Discoloration around
umbilicus] or +ve Grey-Turner sign
[Discoloration around flanks]
Acute Pancreatitis
↑↑ Serum Amylase](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pediatricspresentaion-210418144348/85/Pediatrics-Acute-Abdominal-Pain-Workup-24-320.jpg)