Embed presentation
Downloaded 23 times





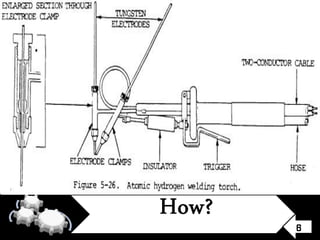







This document discusses atomic hydrogen welding. It explains that atomic hydrogen welding uses an arc generated between two tungsten electrodes inside a hydrogen atmosphere. The arc is maintained separately from the workpiece and reaches temperatures of 11,000°F. This causes the diatomic hydrogen molecules to break down and recombine when hitting the workpiece, releasing energy. Annular nozzles around the electrodes carry the hydrogen gas. The process has advantages like concentrating an intense flame, less distortion, faster welding without needing separate flux or shielding gas. However, its cost is slightly higher than other processes and it is limited to flat positions. Atomic hydrogen welding is used for applications requiring rapid welding of stainless steels and special alloys.












