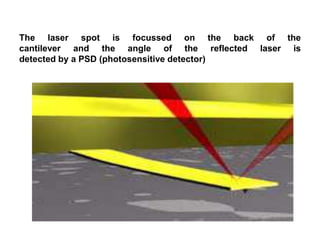
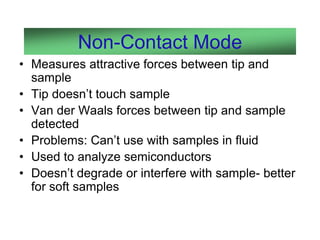
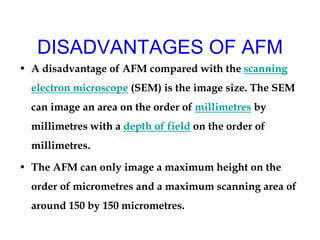
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) is a type of scanning probe microscopy with very high resolution. It uses a sharp tip at the end of a flexible cantilever to scan the surface of a sample and measure forces. As the tip scans the surface, a laser detects how the cantilever bends from surface forces. This allows creating 3D images of surfaces with resolutions down to fractions of a nanometer. AFM can image in various modes including contact, non-contact, and tapping and has applications in biology, materials science, and nanotechnology.