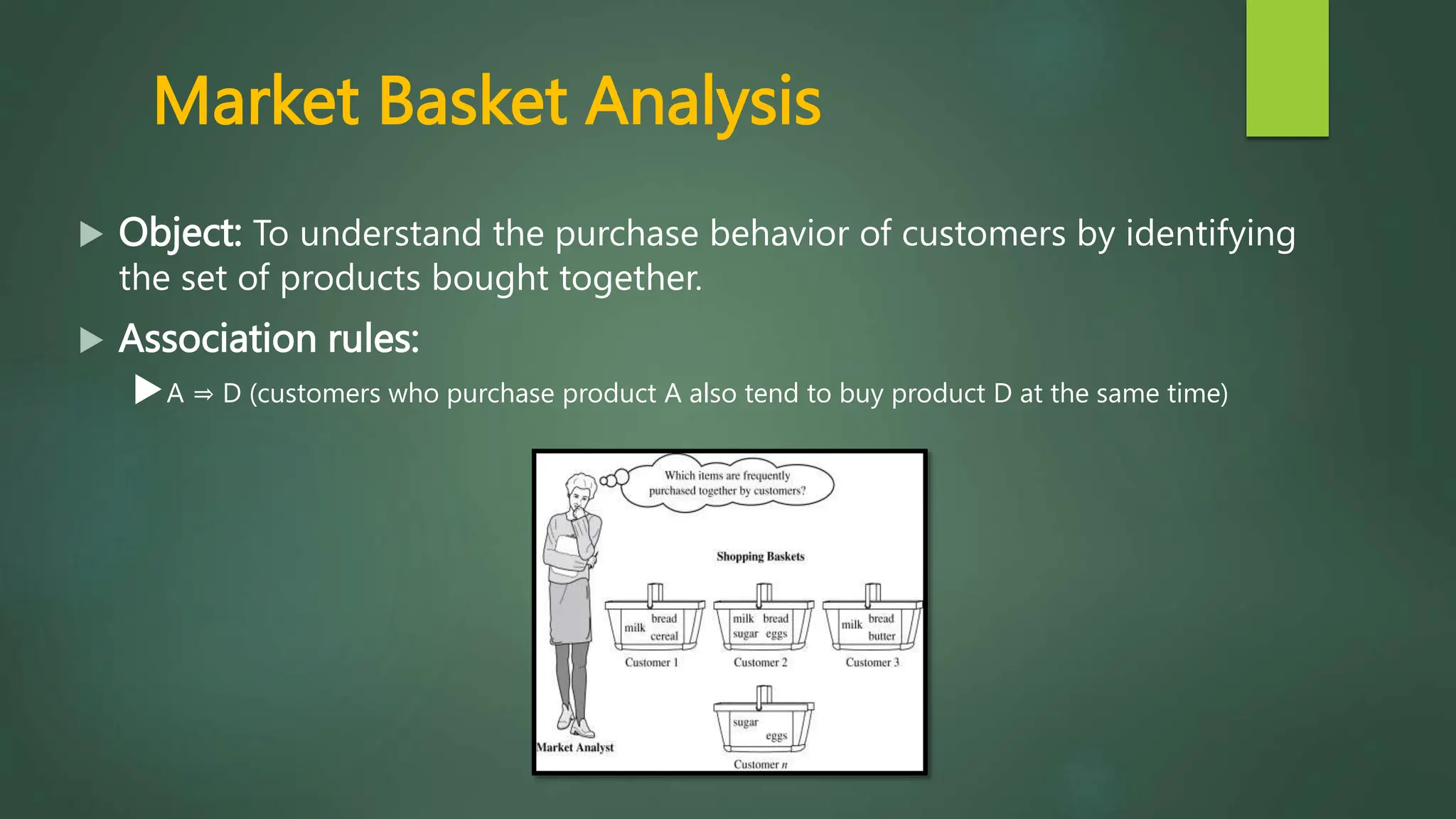
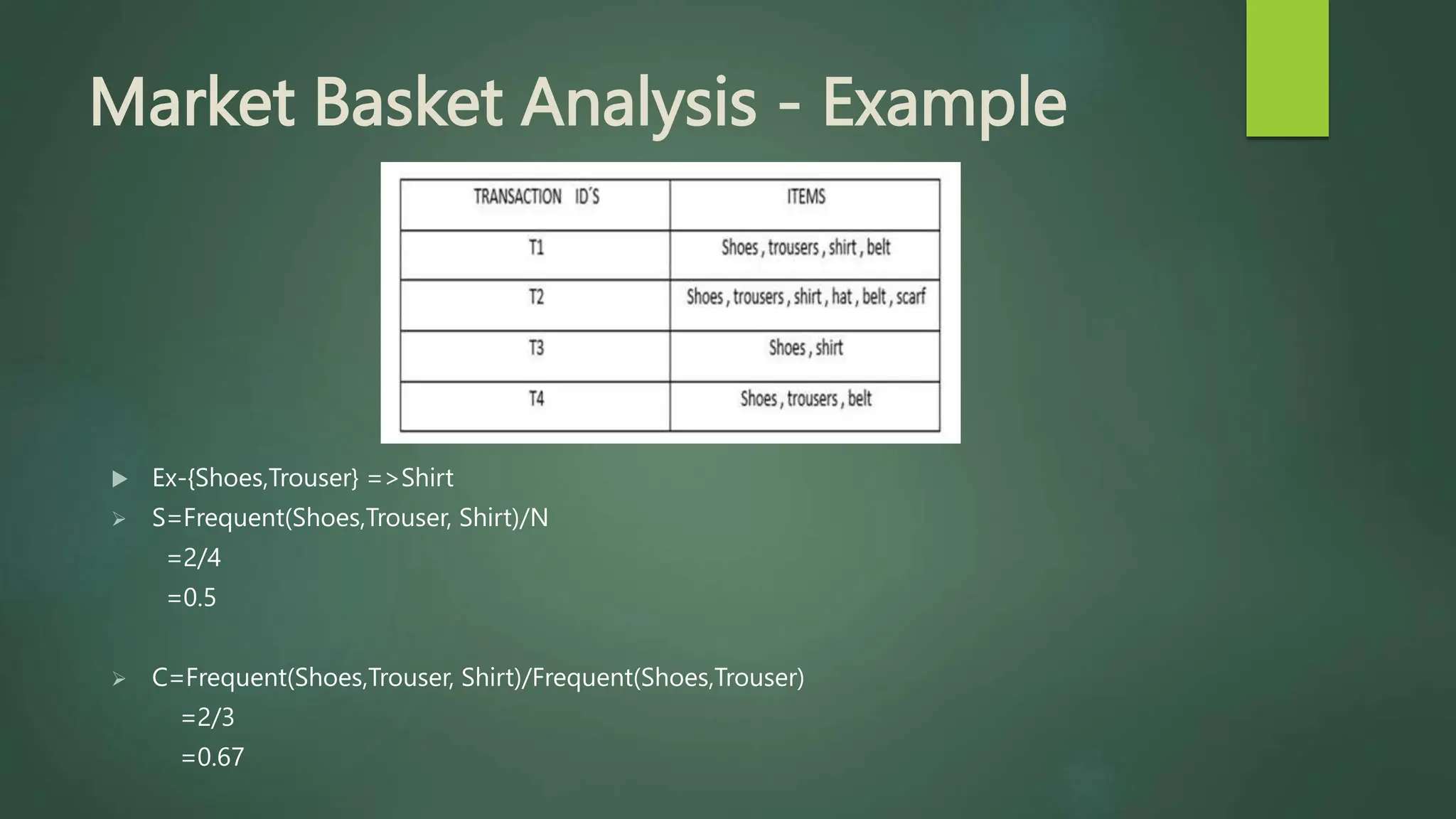
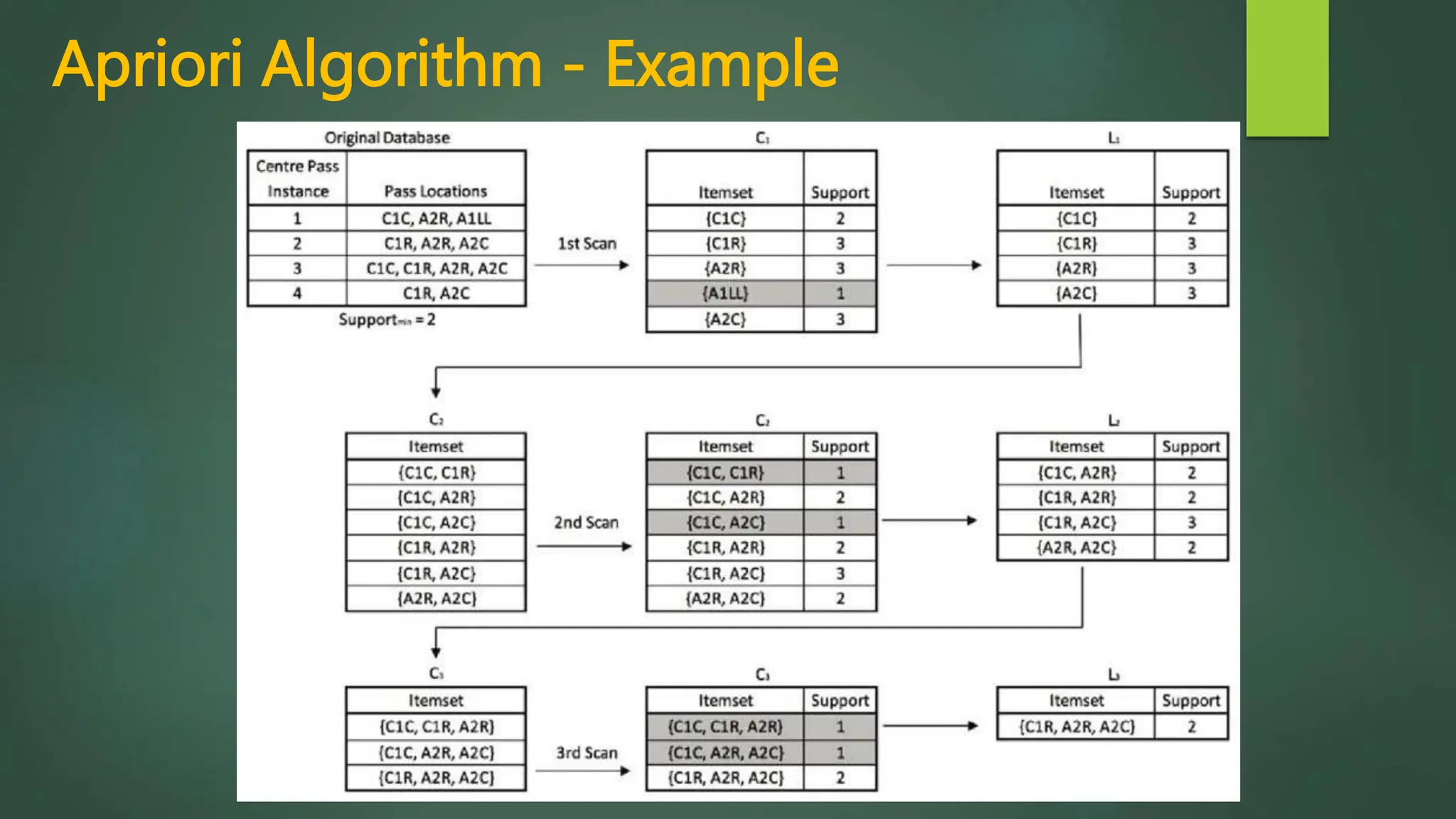
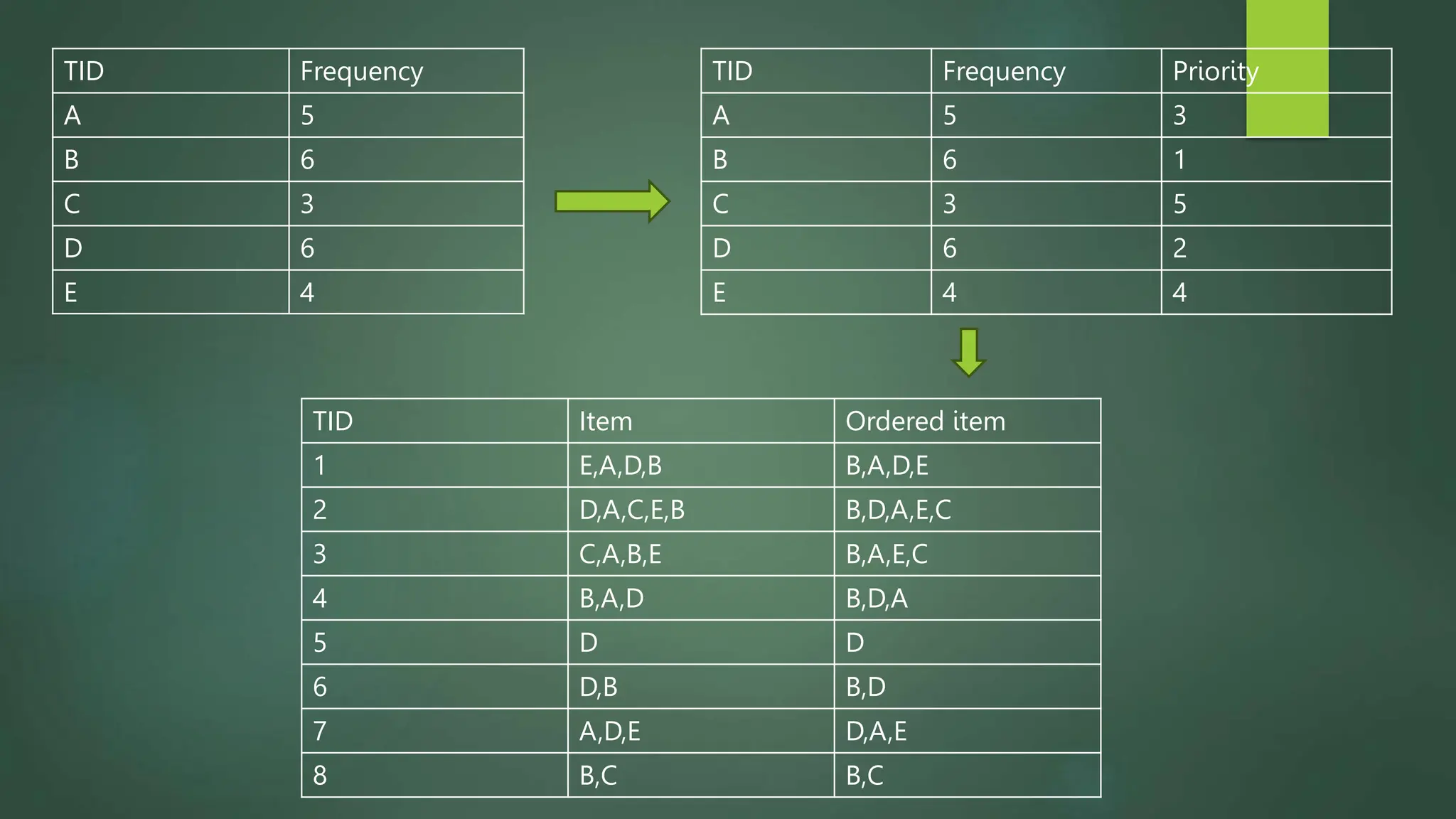
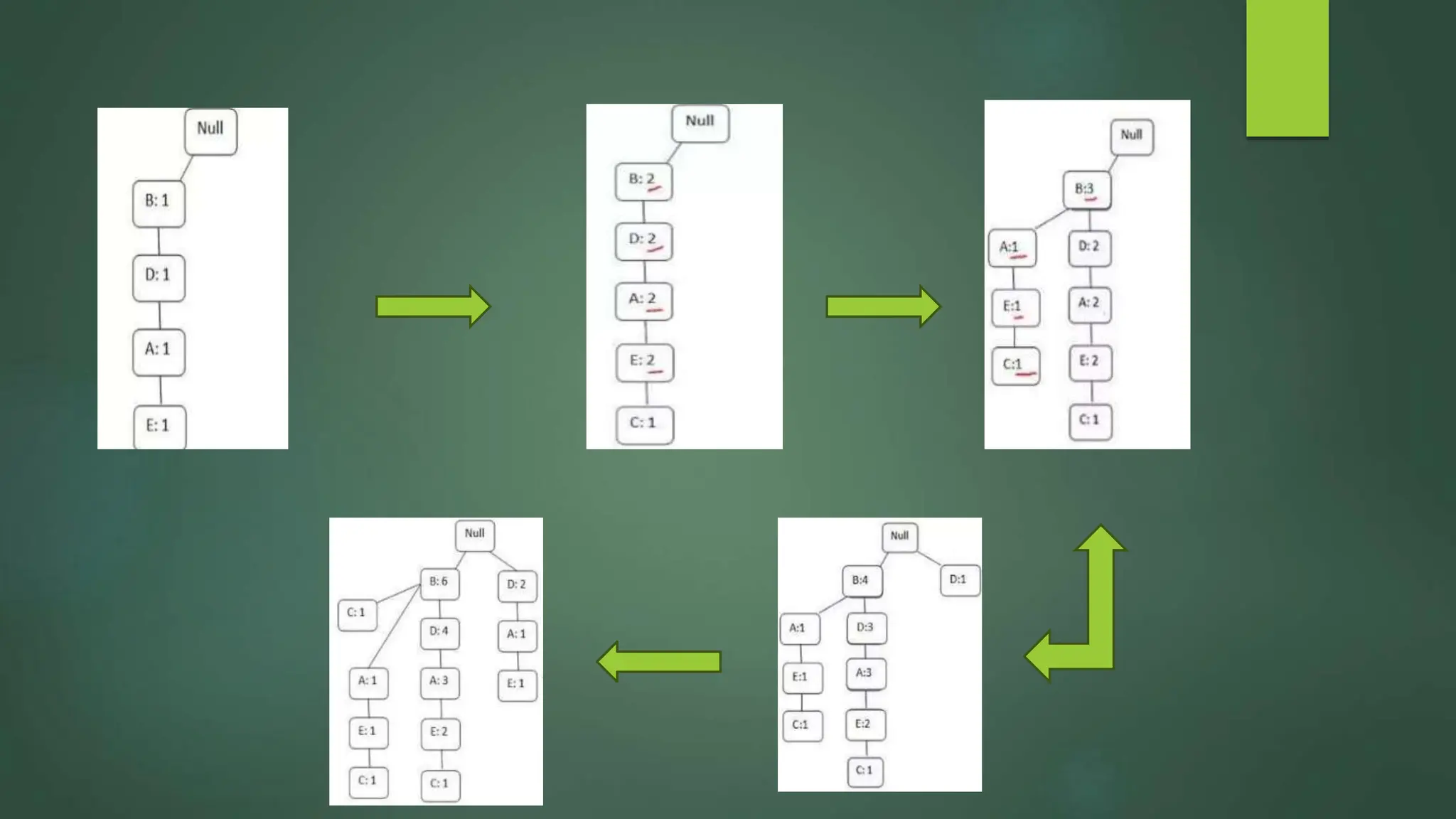
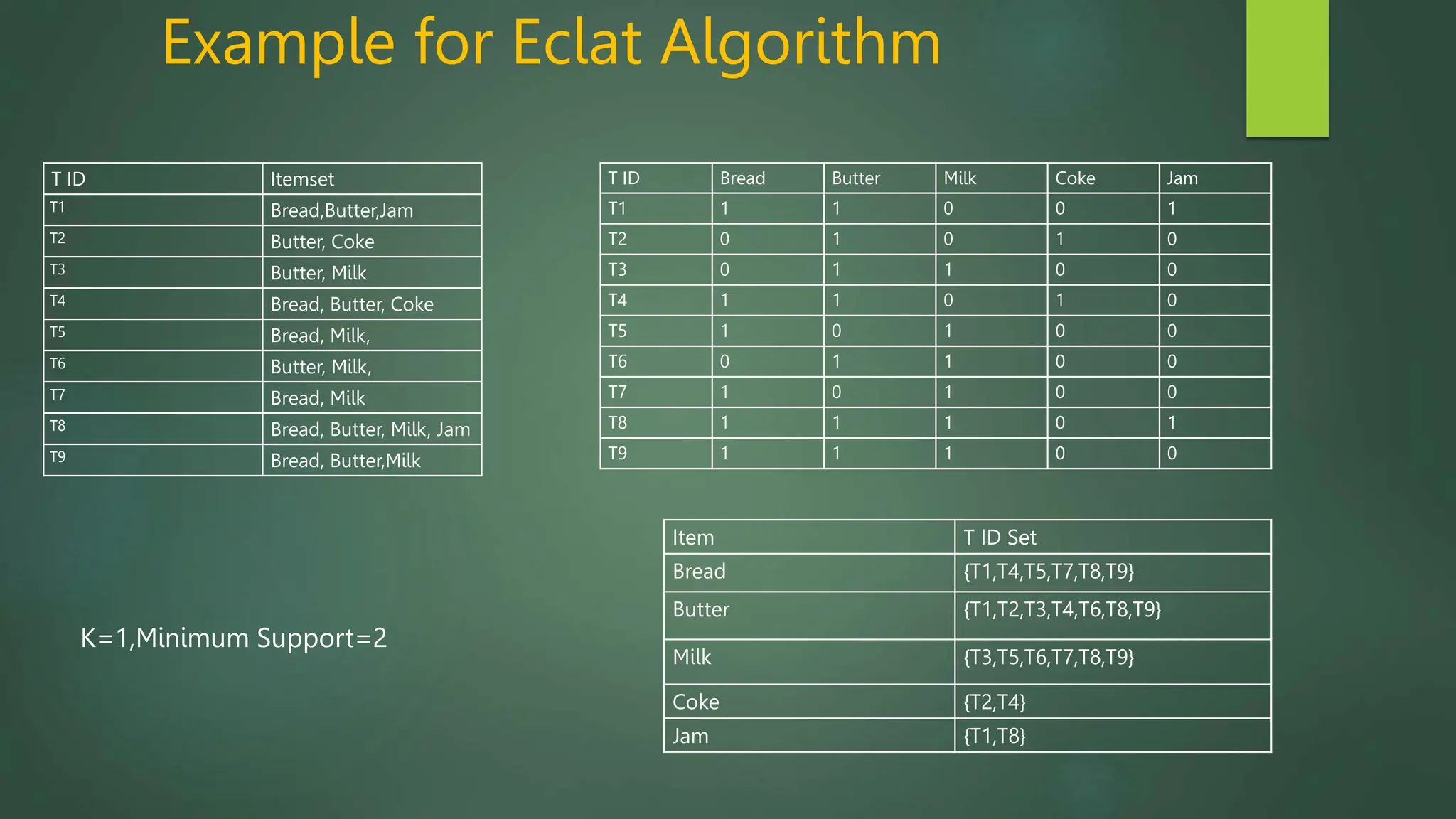
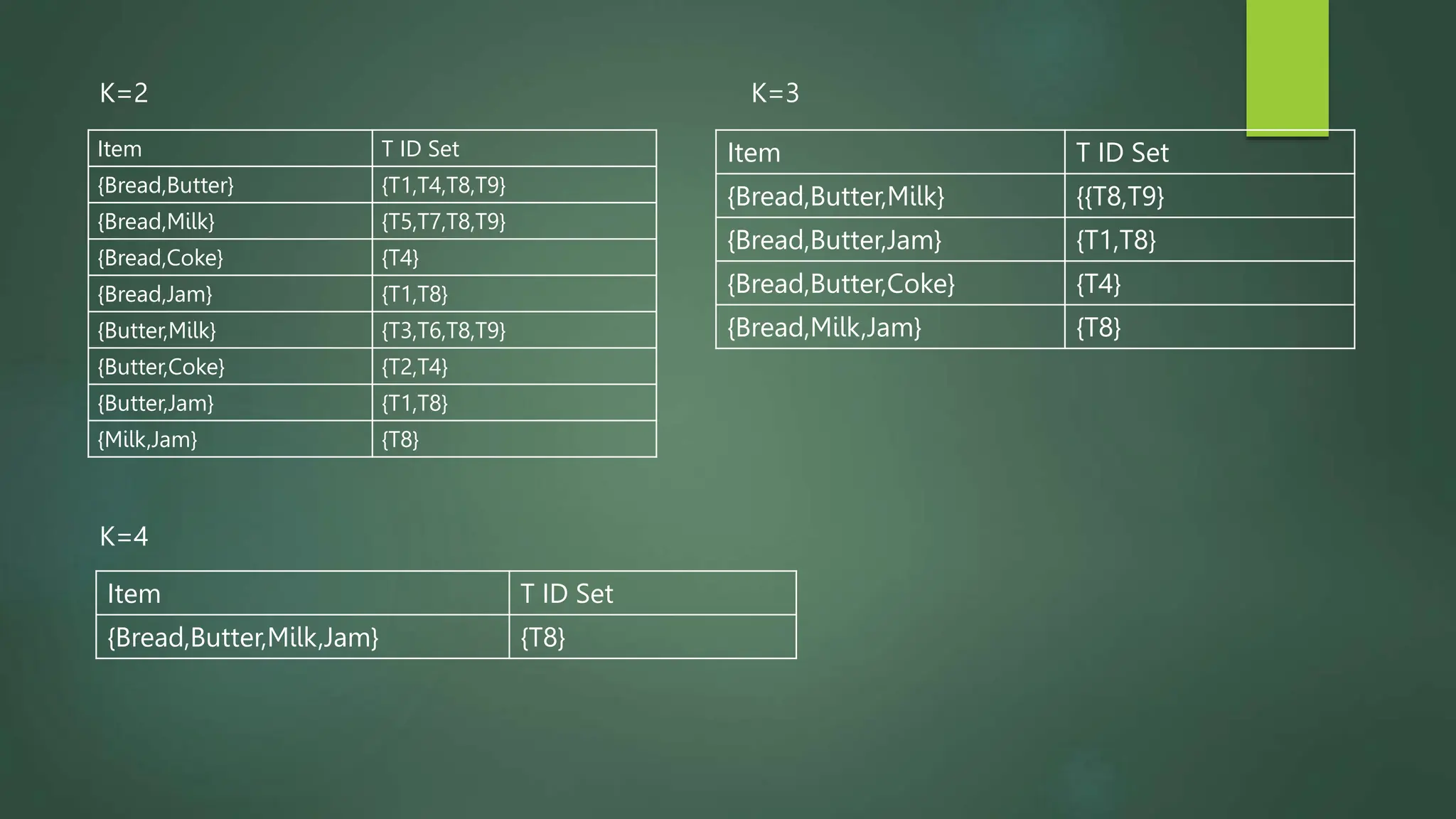
Association rule mining is a technique used to discover relationships between variables in large datasets. It identifies patterns and correlations among items. The key concepts are itemsets, support, and confidence. The Apriori algorithm and FP-Growth approach are two common algorithms used. Apriori generates candidate itemsets in multiple passes over the data, while FP-Growth avoids candidate generation by building a tree structure. The Eclat algorithm also finds frequent itemsets but uses a vertical database format and depth-first search. These algorithms are applied to market basket analysis to understand customer purchasing behaviors.