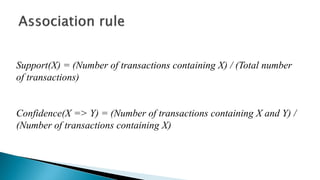
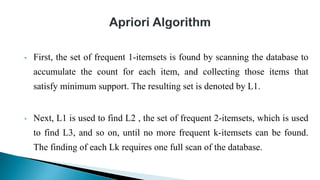
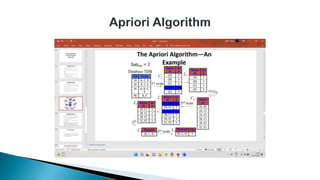
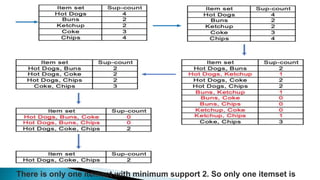
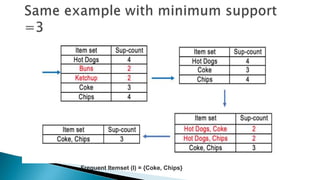
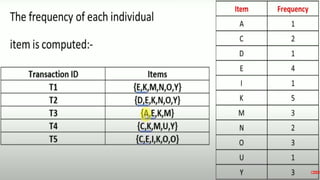
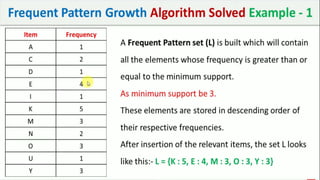
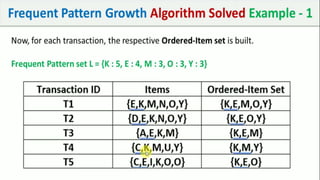
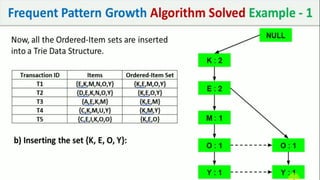
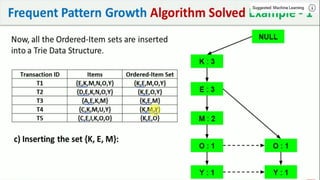
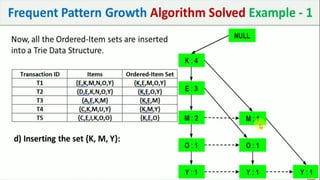
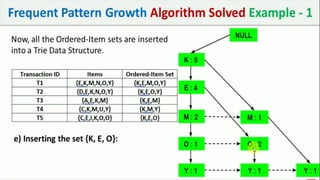
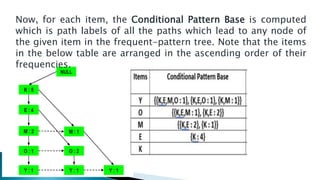
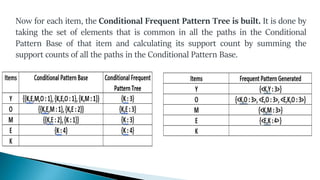
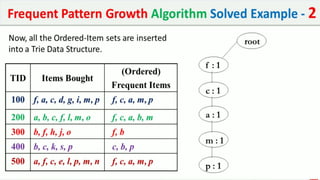
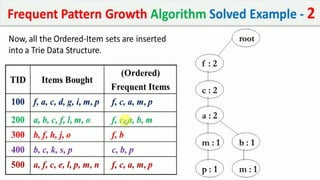
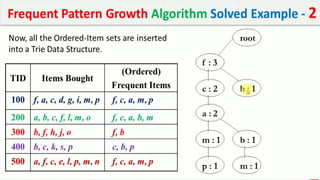
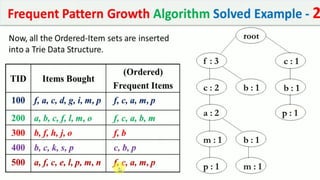
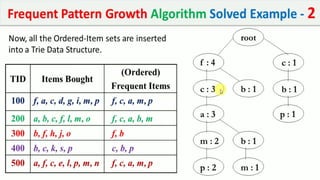
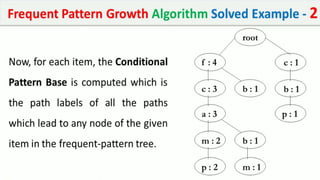
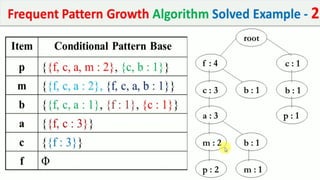
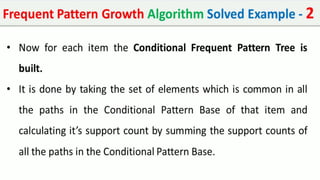
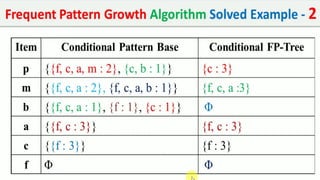
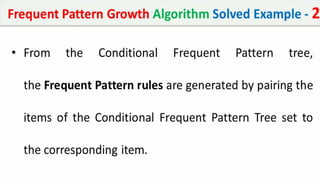
The document discusses data mining, particularly focusing on the process of knowledge discovery, including preprocessing, data mining, and postprocessing. It highlights frequent itemset mining techniques such as the Apriori and FP-Growth algorithms, explaining their functionality, advantages, and applications in various fields like market basket analysis and fraud detection. Additionally, it delineates the concepts of association rules, support, and confidence, emphasizing their significance in understanding relationships among items in datasets.







![ Typical representation formats for association rules:
◦ Green Tea Honey[0.5%, 60%]
◦ buys: Green Tea buys: Honey [0.5%, 60%]
◦ Green Tea and Honey are bought together in 0.5% of the rows
in the database."
◦ "IF buys Green Tea , THEN buys Honey in 60% of the cases.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit4updated-240604145335-924af87f/85/Association-and-Correlation-analysis-10-320.jpg)
![Green Tea Honey [0.5%, 60%]
1 Antecedent, left-hand side (LHS), body
2 Consequent, right-hand side (RHS), head
3 Support, frequency ("in how big part of the data the things
in left- and right-hand sides occur together")
4 Confidence, strength ("if the left-hand side occurs, how
likely the right-hand side occurs")
"IF buys Green Tea ,
THEN buys Honey
in 60% of the cases
in 0.5% of the rows"
1 2 3 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit4updated-240604145335-924af87f/85/Association-and-Correlation-analysis-11-320.jpg)