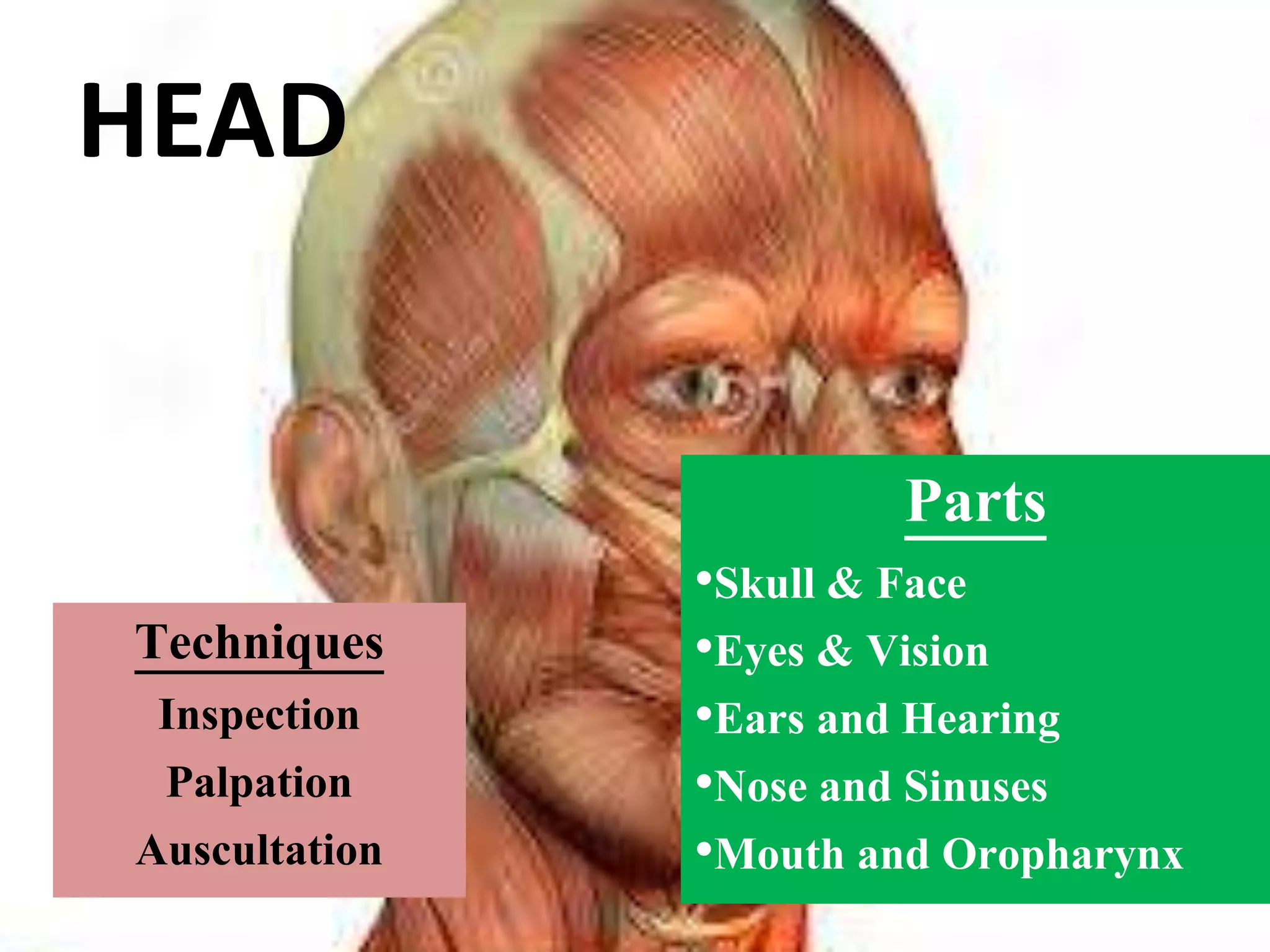
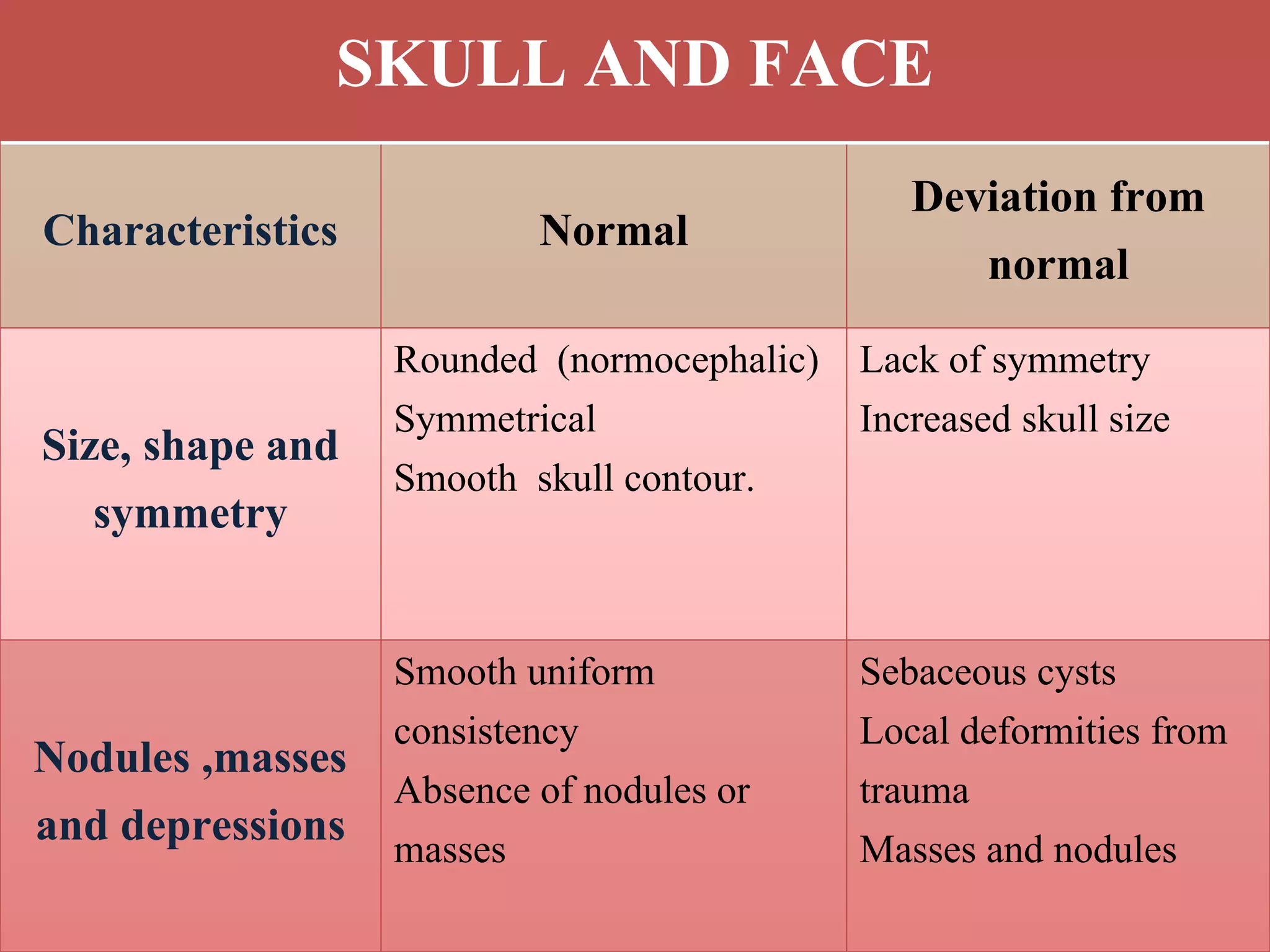
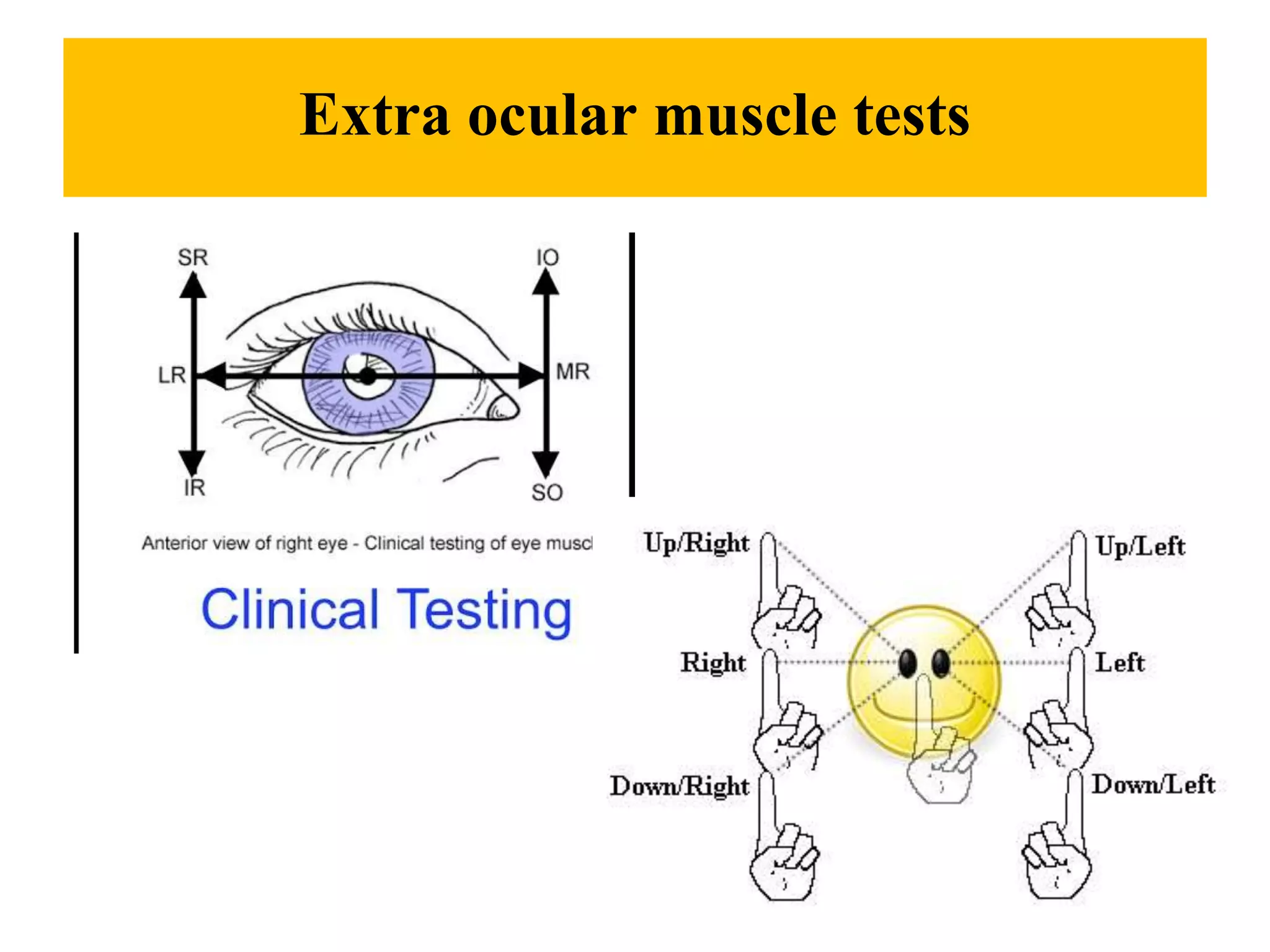
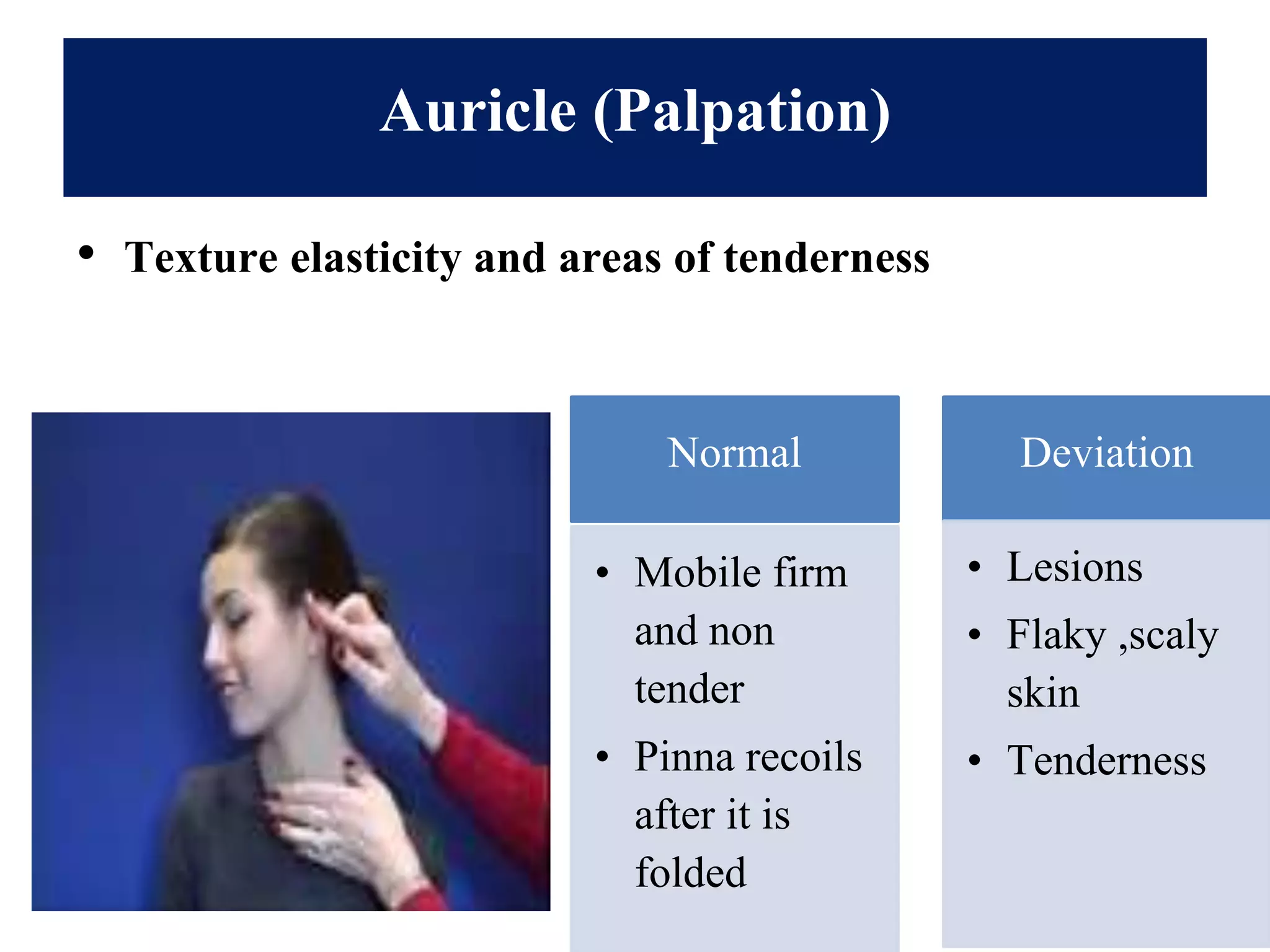
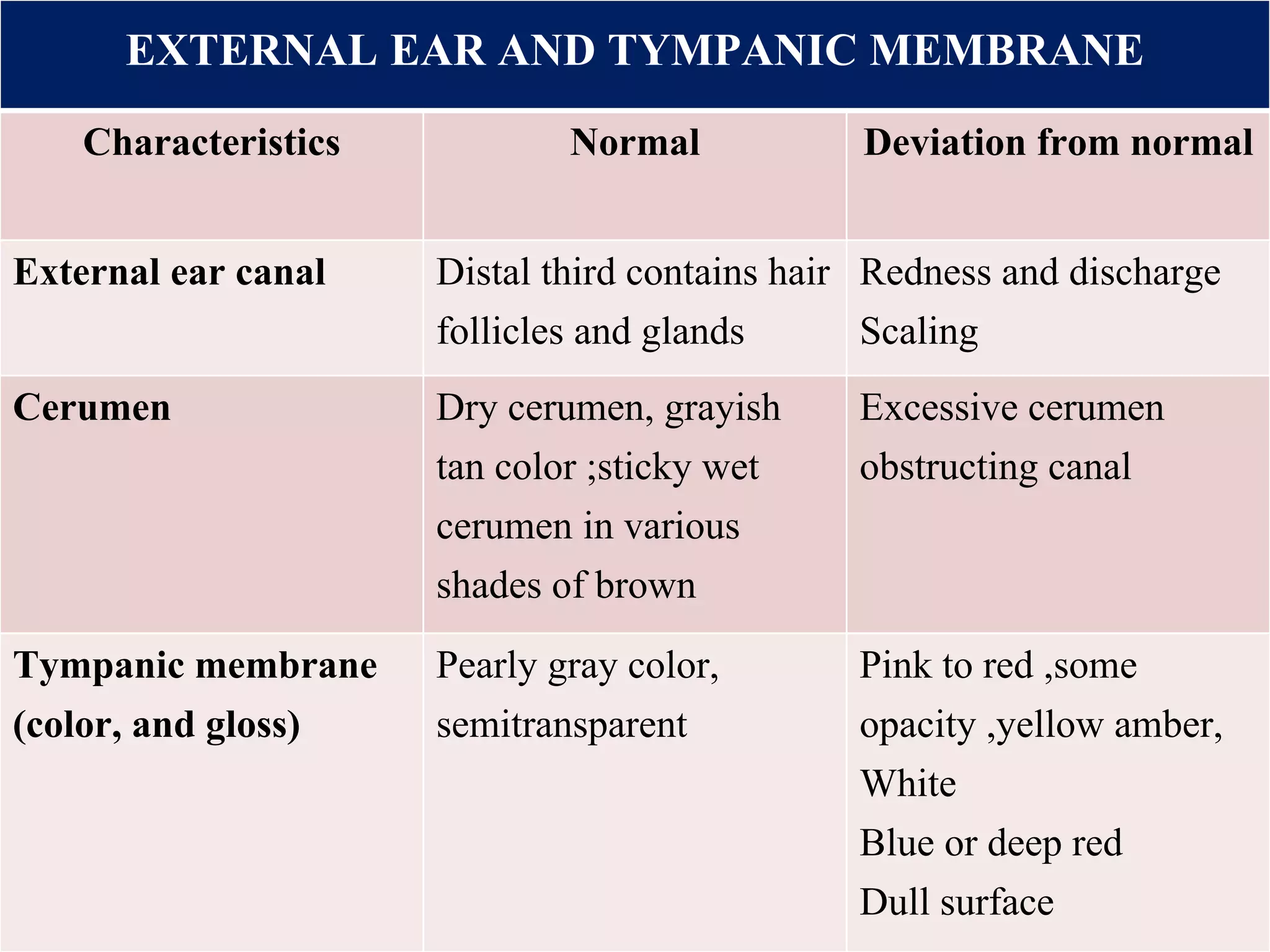
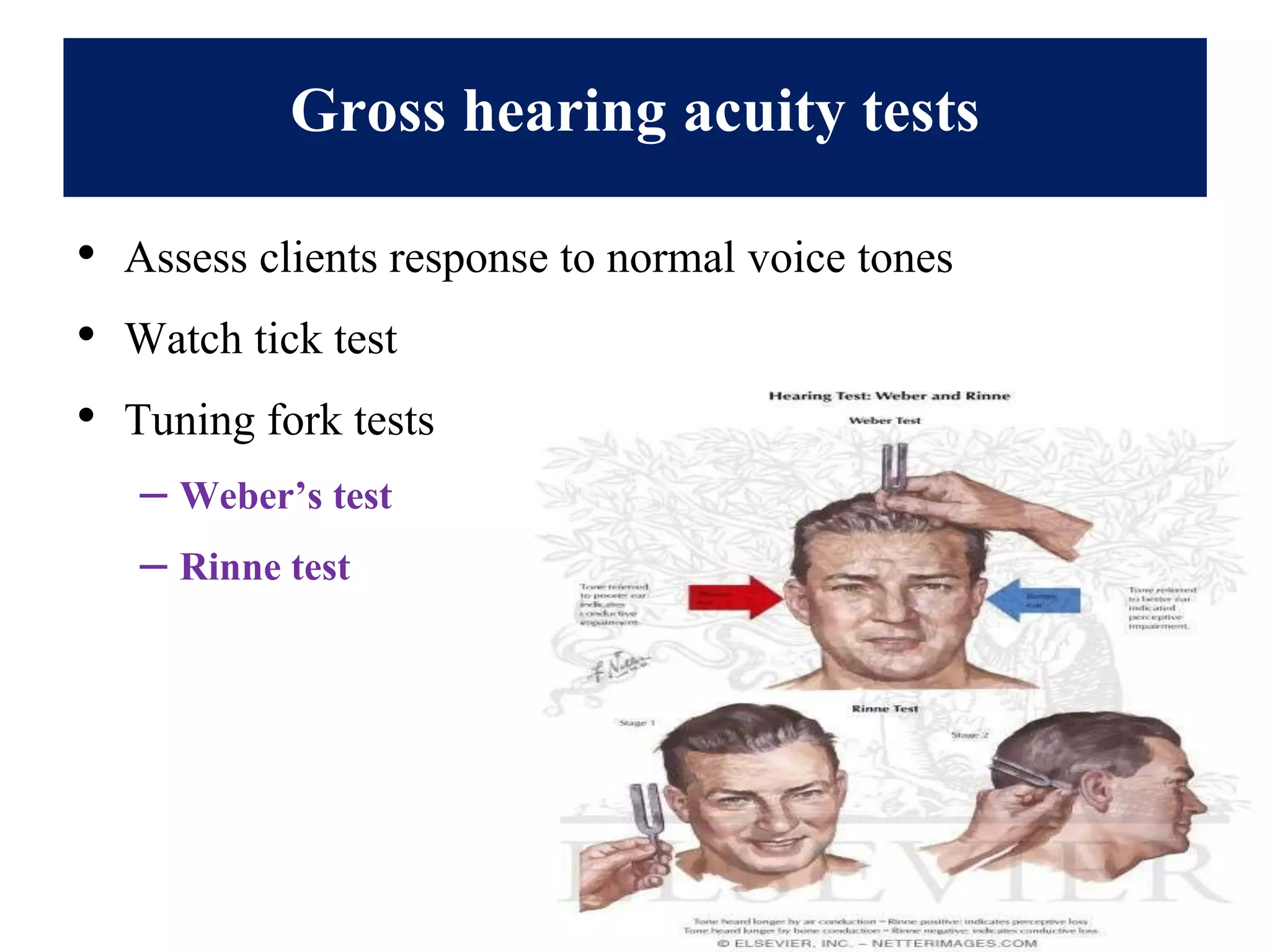
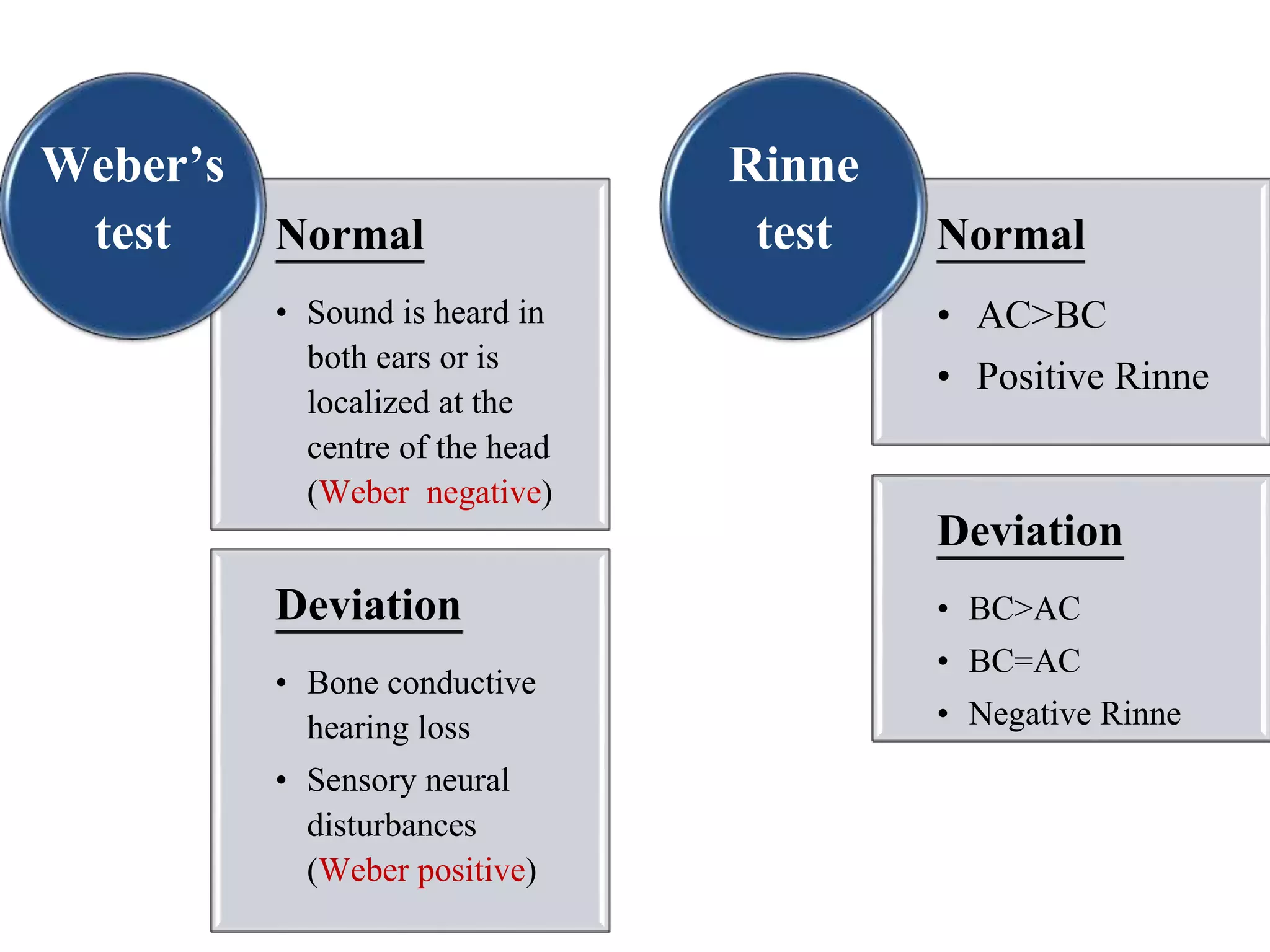
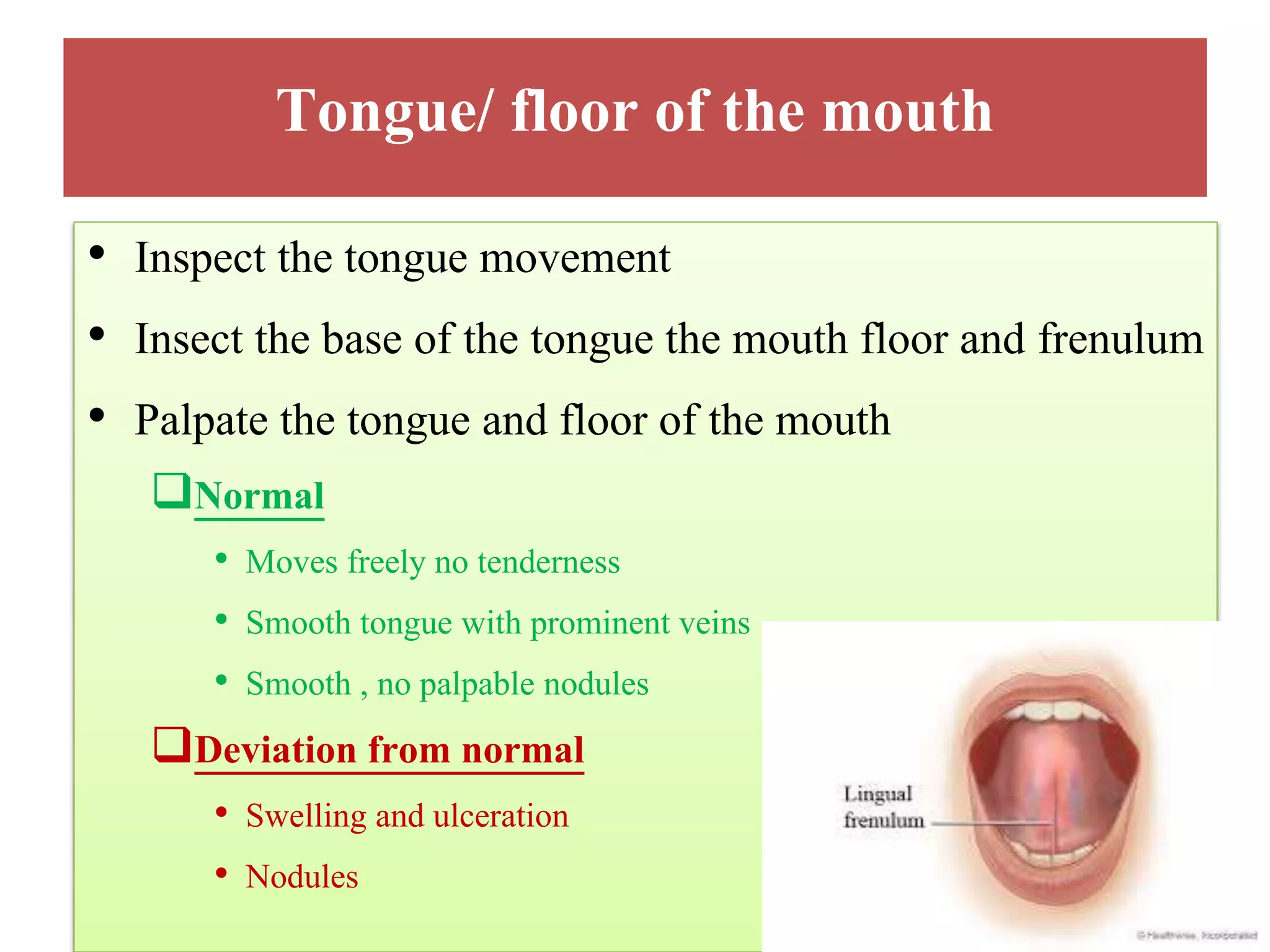
This document provides information on performing a physical examination of the head, including techniques, parts, characteristics, and deviations from normal. It describes examining the skull and face, eyes and vision, ears and hearing, nose and sinuses, mouth and oropharynx, neck, and thyroid gland. Inspection, palpation, and auscultation are used. The summary examines the head, eyes, ears, nose, mouth, and neck, noting key assessment areas and normal versus abnormal findings for each.