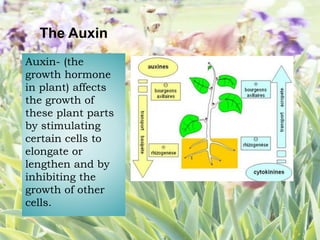
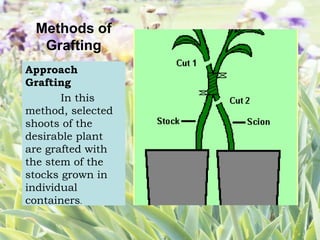
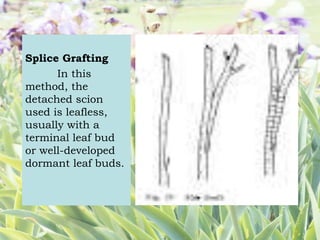
The document explains asexual plant propagation through grafting, highlighting key concepts such as the cambium layer, auxin's role in growth, and the definition and characteristics of grafting. It details the selection of scions, required tools, materials, advantages of grafting, and methods like approach grafting and cleft grafting. Specific steps for performing cleft grafting are also outlined, emphasizing the importance of ensuring proper contact between the cambium layers.