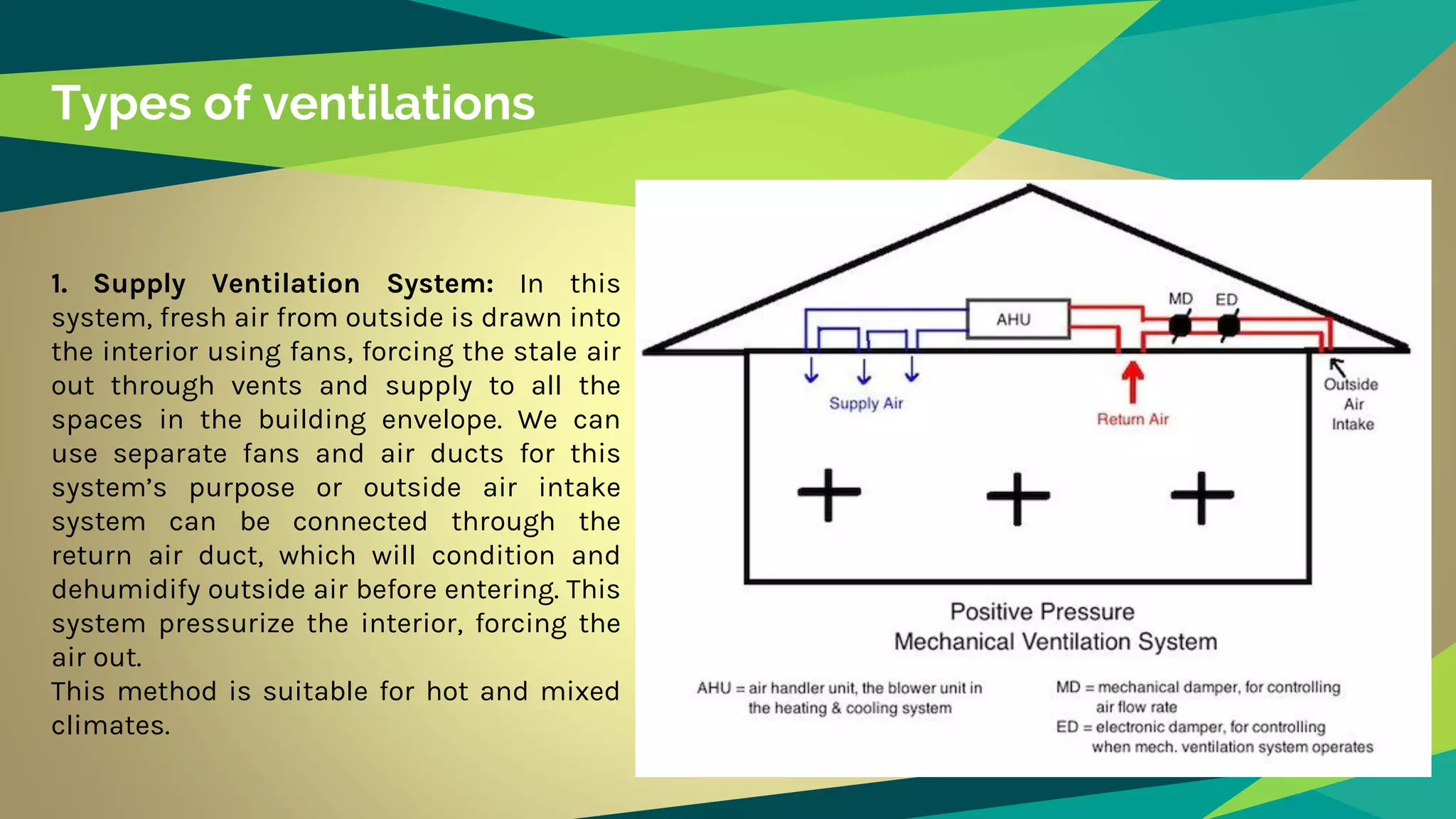
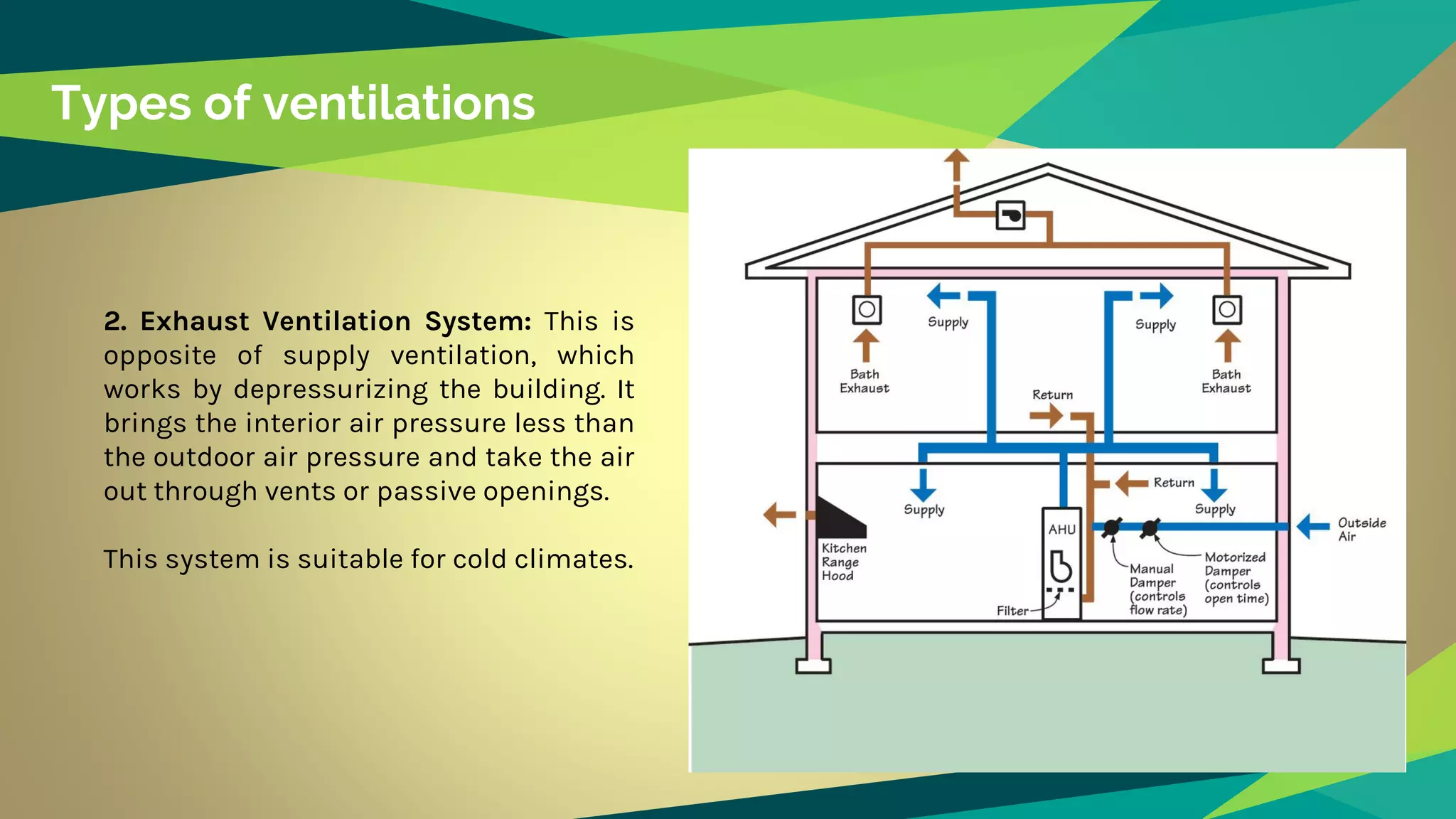
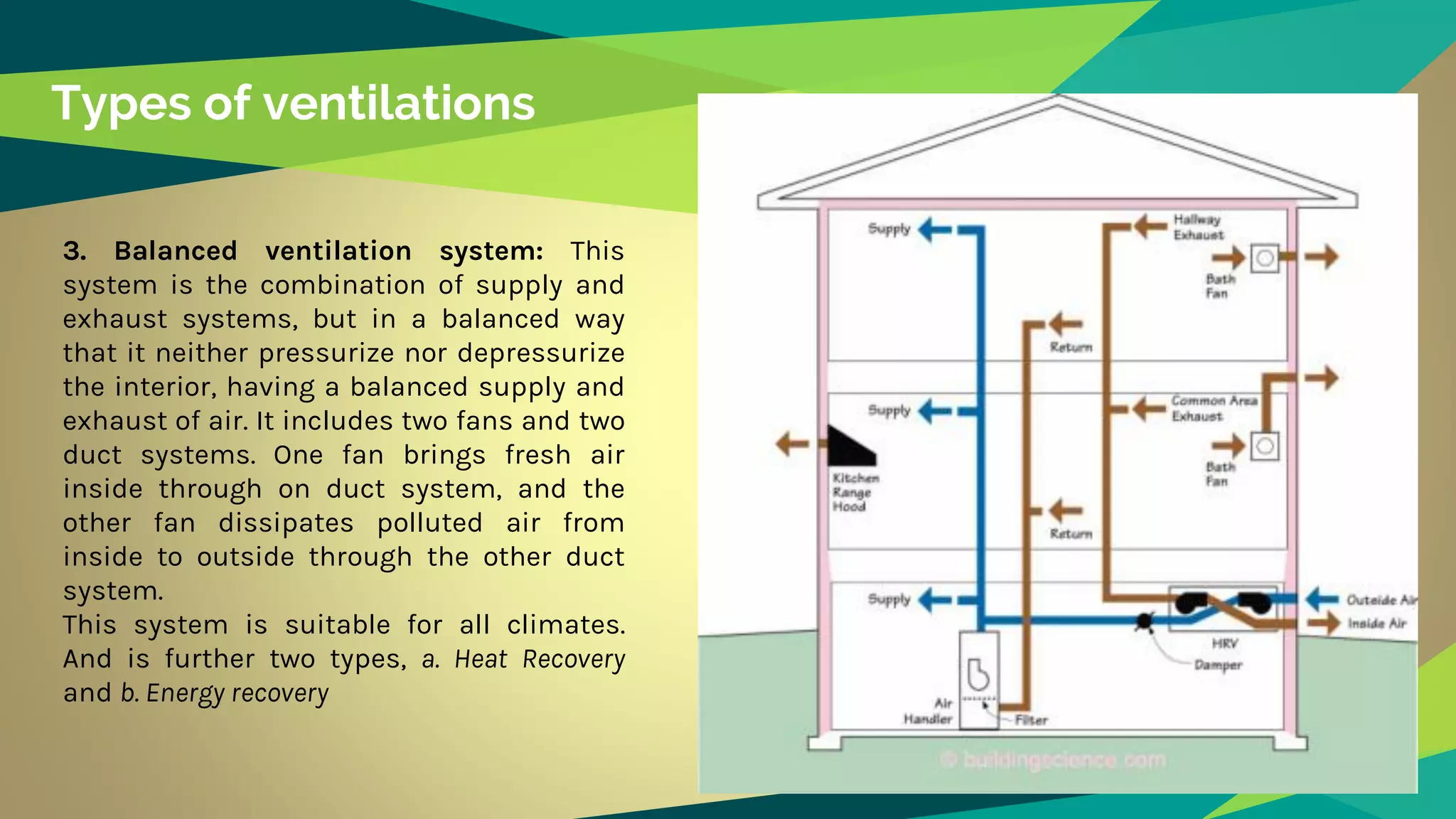
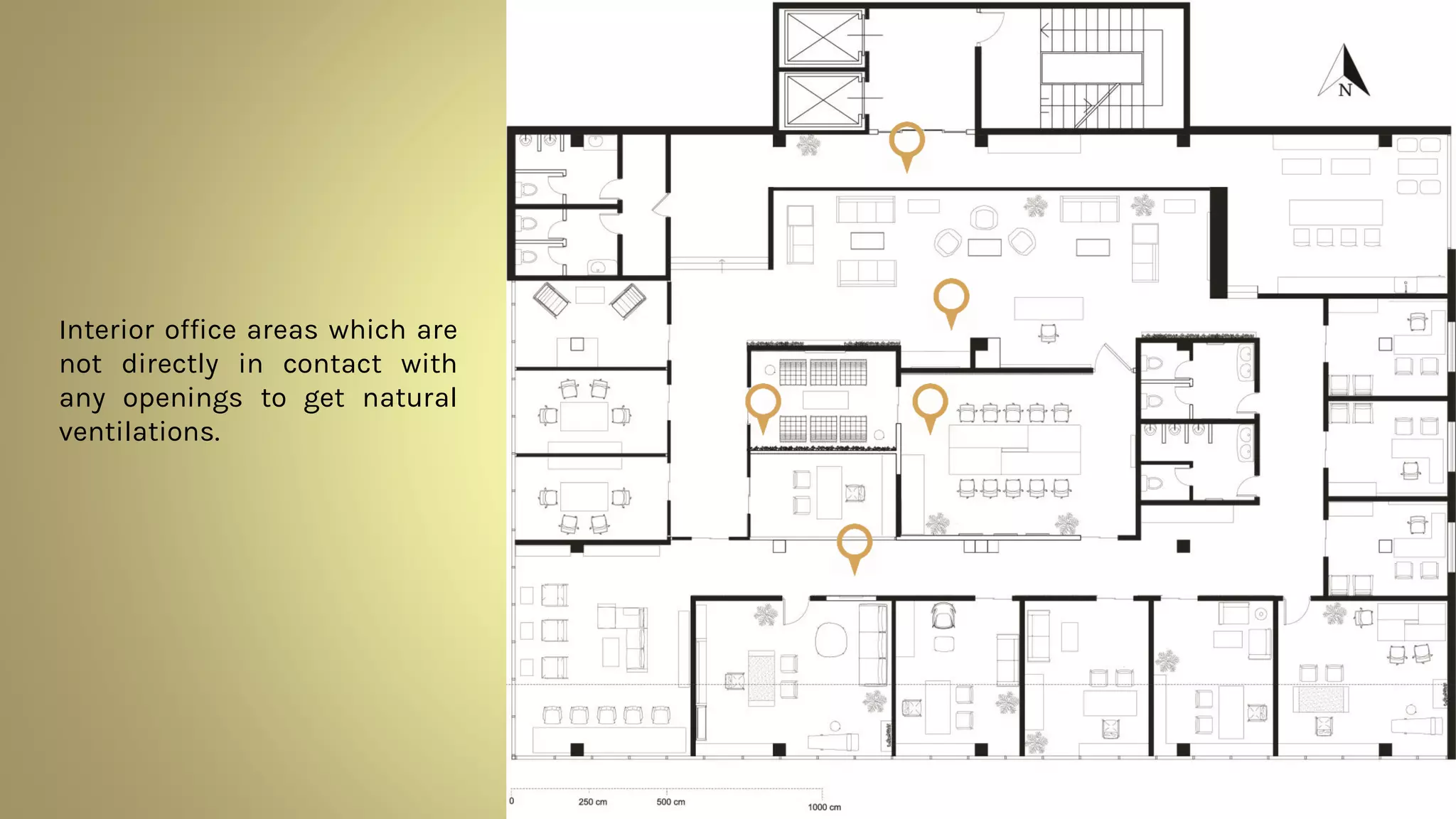
Artificial ventilation involves using mechanical fans and systems to drive stale interior air outside and bring fresh air inside. There are three main types: supply ventilation which pressurizes interior spaces, exhaust ventilation which depressurizes, and balanced ventilation which maintains pressure equilibrium. Balanced ventilation includes heat and energy recovery systems. Artificial ventilation provides controlled air exchange and distribution without introducing outdoor pollutants. However, faulty systems can impact health and quality systems are expensive. A case study of Cundall offices showed how artificial and natural ventilation can be integrated harmoniously in a thermally active building.