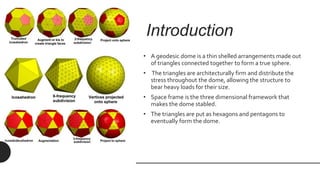
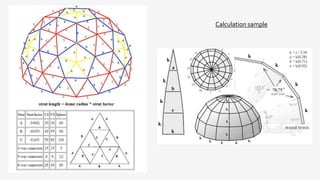
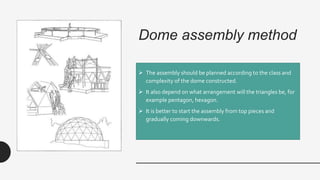
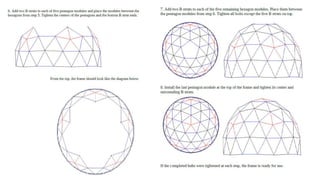
The document provides a comprehensive overview of geodesic domes, covering their structure, history, construction methods, materials used, advantages, disadvantages, and architectural examples. It highlights the development of geodesic domes from early designs by Walter Bauersfeld and R. Buckminster Fuller, emphasizing their strength, efficiency, and quick assembly. Additionally, the document discusses various applications and the challenges faced in their construction.