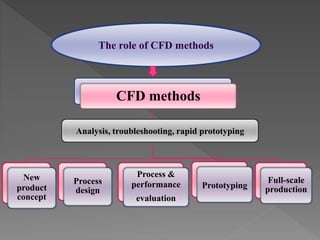
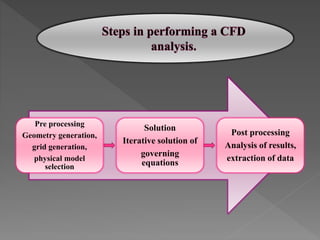
Artificial intelligence has the potential to accelerate drug discovery by generating new molecular structures, automatically designing drug candidates, and using historical data to identify treatments. Companies are using AI techniques like deep learning and generative adversarial networks to analyze vast amounts of data to propose new drug candidates. Robots are also being used in pharmaceutical laboratories and manufacturing to perform repetitive and precise tasks, allowing researchers to focus on higher-level work. Computational fluid dynamics is another tool being used to analyze and optimize pharmaceutical processes.








![ One of the most widespread uses is for re-
purposing drugs — finding new uses for existing
drugs or late-stage drug candidates.
We don’t have to repeat all the phase I testing
and all the toxicology testing, when we take it
into another phase II trial [for] a different
indication, so we can accelerate the process of
medicine development quite dramatically,”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/roboticsppt-180516160941/85/Artificial-Intligence-and-Robotics-ppt-10-320.jpg)