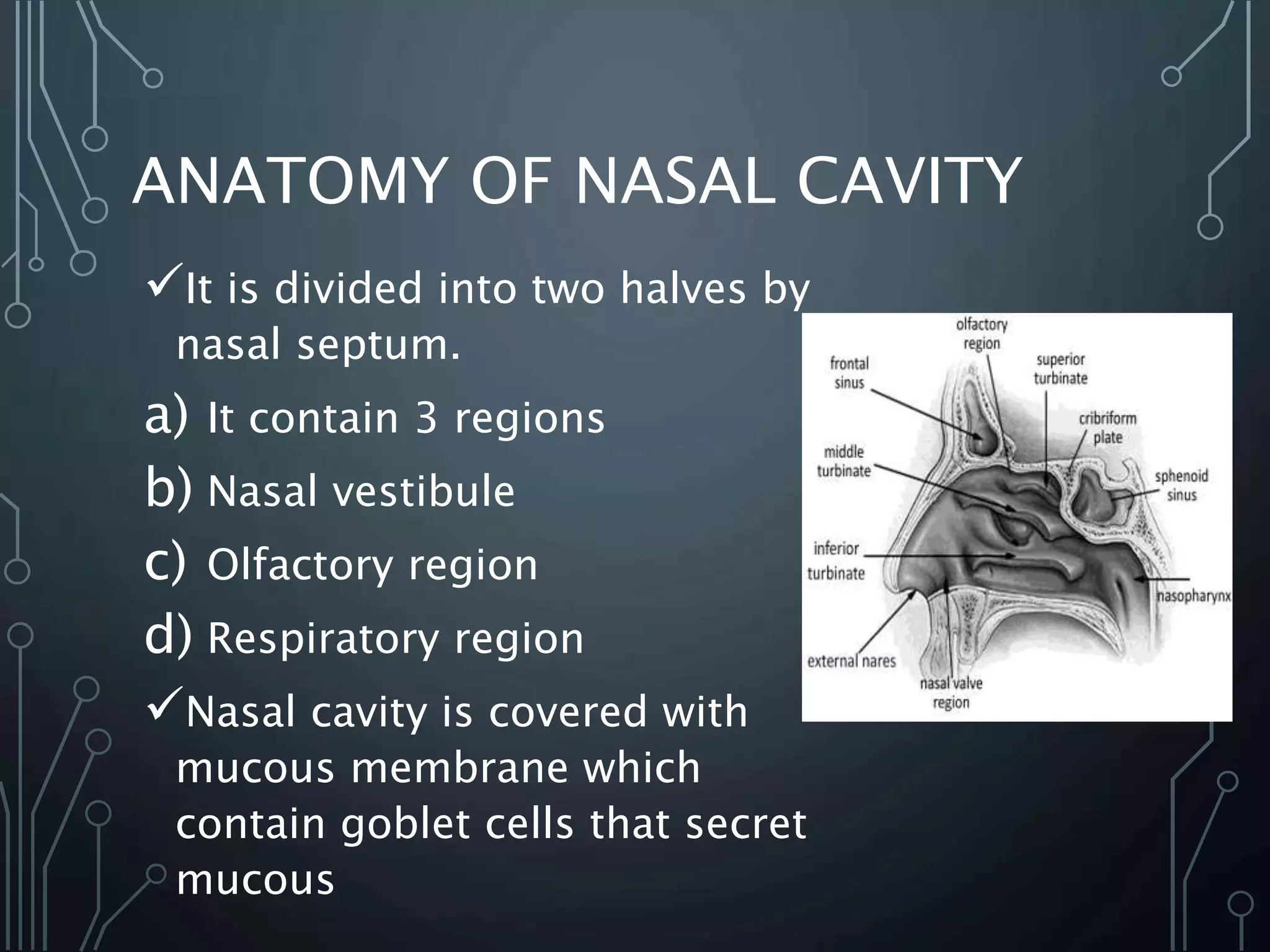
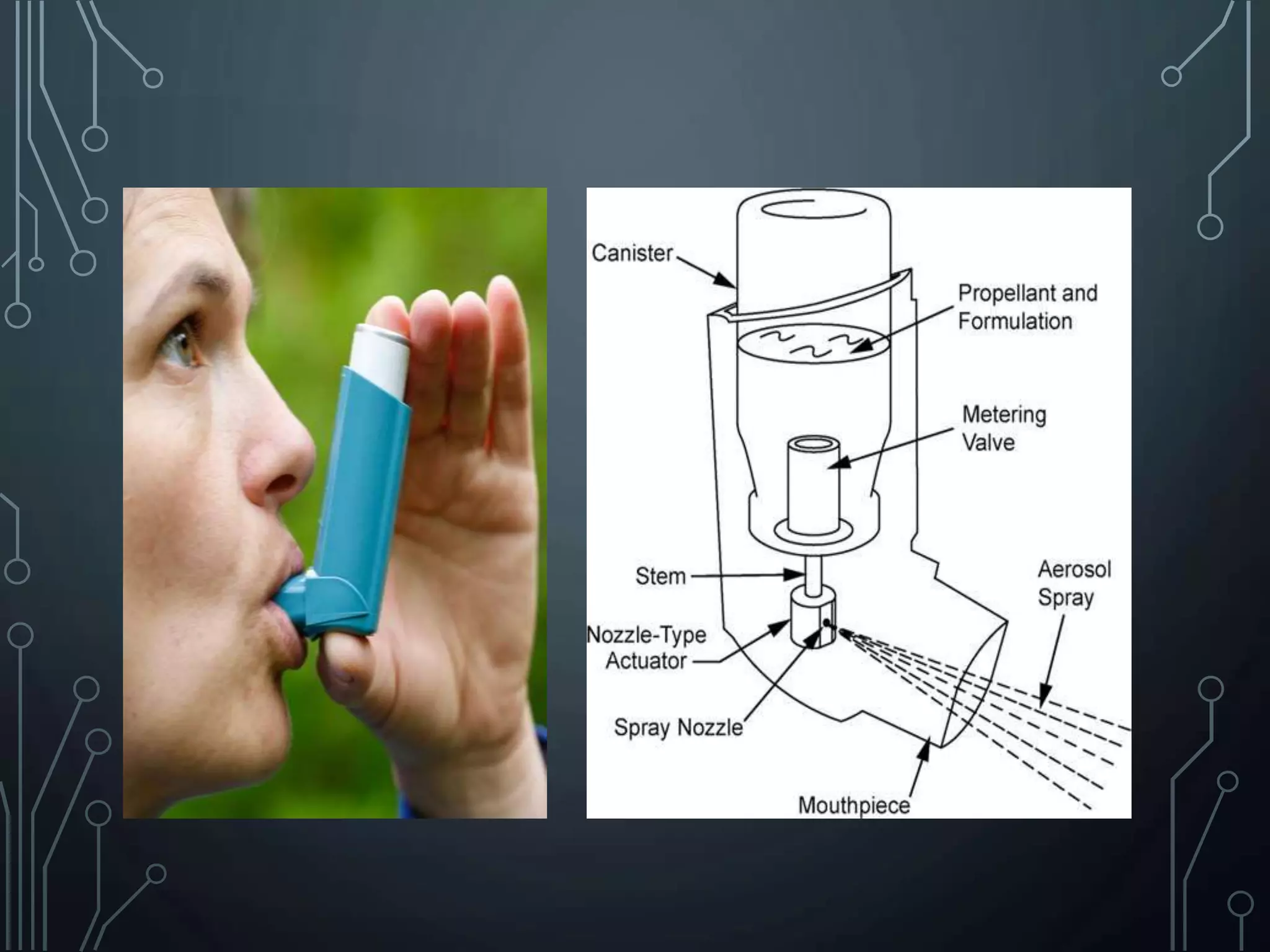
The document discusses nasal drug delivery systems, outlining their definitions, advantages, and disadvantages, as well as the anatomy and physiology of the nasal cavity. It elaborates on the mechanisms of drug absorption, factors affecting bioavailability, and formulation considerations, detailing various types of formulations and devices used for administering drugs. Additionally, it explores applications of nasal drug delivery, including the delivery of non-peptide and peptide pharmaceuticals, targeting the brain, and vaccine delivery.