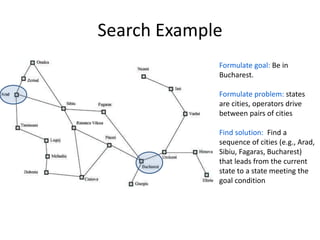
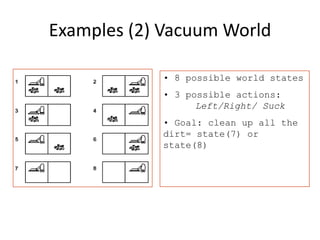
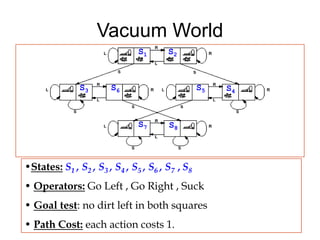
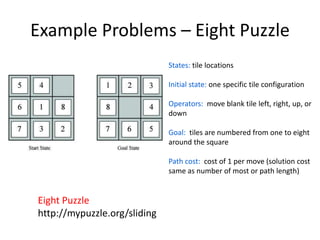
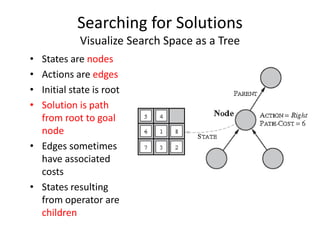
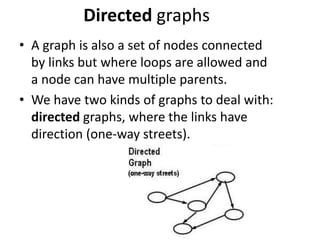
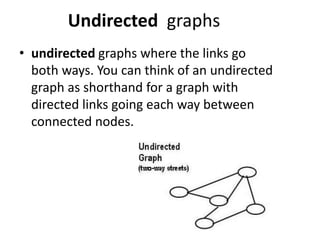
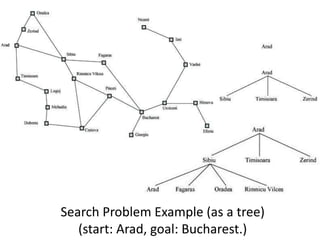
The document discusses problem solving agents and search algorithms. It defines a search problem as having an initial state, possible actions or operators that change states, a goal test to determine if a state is the goal state, and a path cost function. Search algorithms take a problem as input and systematically examine states by considering sequences of actions to find a lowest cost path from the start to a goal state. Different search techniques include methods that find any solution path, the lowest cost path, or methods that consider an opponent. Examples of search problems discussed are finding parking, the vacuum world problem, and the eight puzzle problem.