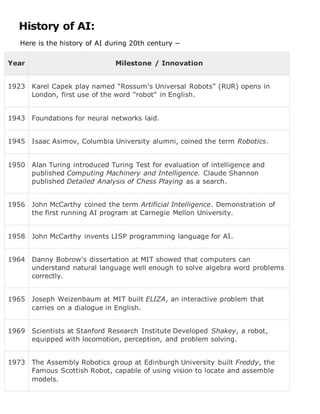
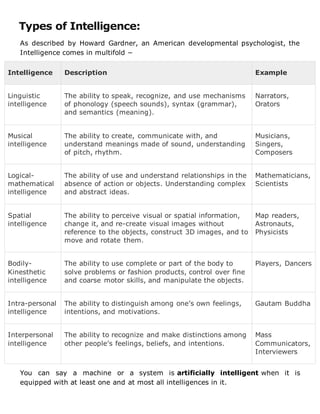
This report provides an overview of artificial intelligence including its goals, techniques, applications, and history. It defines AI as the science of creating intelligent machines and programs that mimic human intelligence. The report discusses how AI programming differs from traditional programming by being able to absorb new information without affecting its structure. It also outlines various AI techniques used to organize vast amounts of knowledge and several real-world applications of AI in areas like gaming, natural language processing, and robotics. Finally, the report compares human and artificial intelligence in terms of perception, memory, and problem-solving abilities.