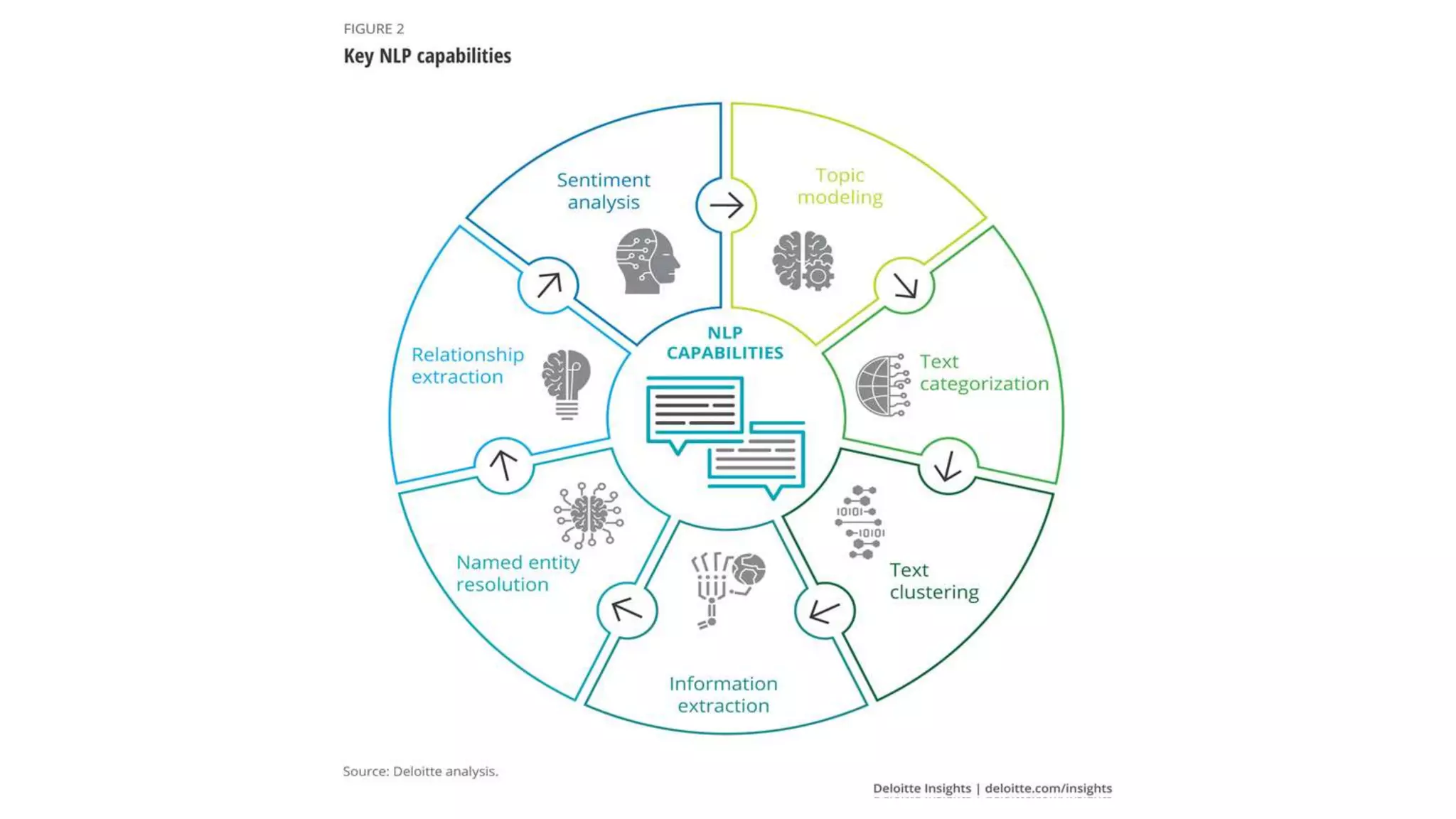
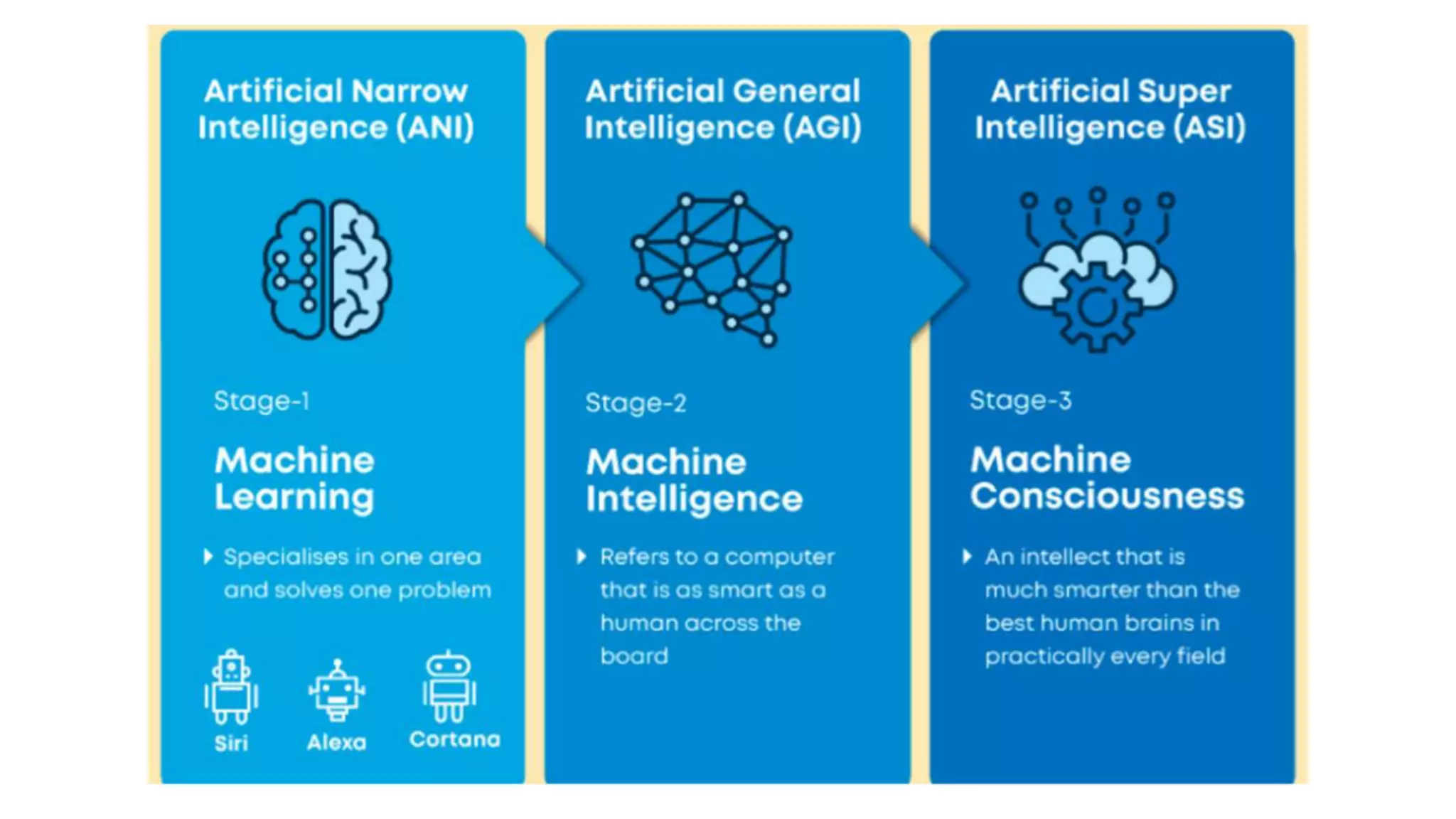
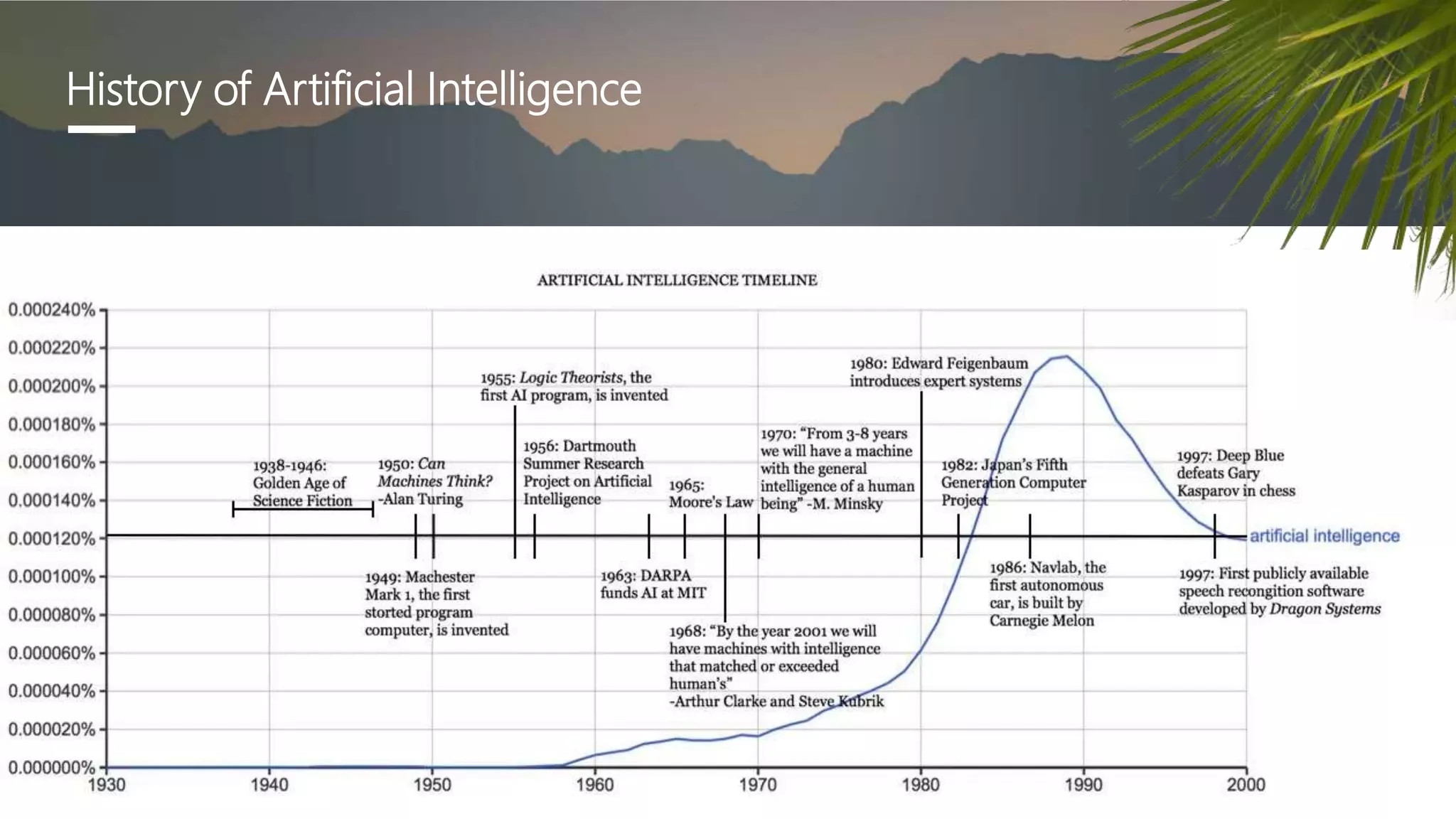
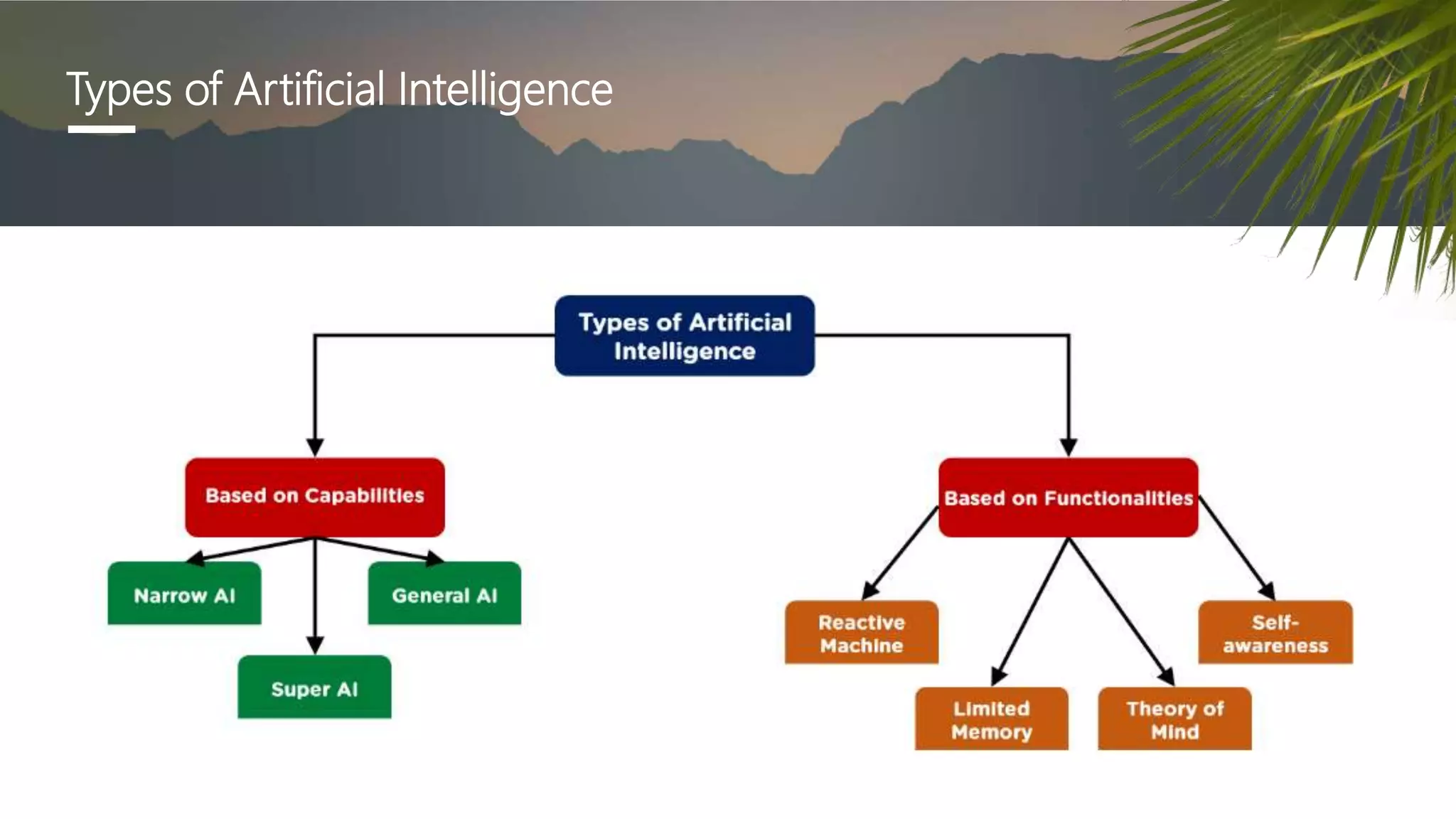
The document provides a comprehensive overview of artificial intelligence (AI), including its definition, history, types, applications across various sectors such as agriculture, health, and business, and underlying technologies like machine learning and natural language processing. It also discusses the evolution of AI from its inception in the 1950s to current advancements like self-driving cars and smart assistants, highlighting notable milestones and frameworks used in AI development. The importance and impact of AI on efficiency, automation, and decision-making processes in numerous industries are emphasized throughout the document.















![AI in Detecting Floods – Natural Calamities
In the flood-prone region of Patna in northern India, the waters were
rising. But thanks in part to an artificial intelligence system, residents of
the region received early warnings on their phones. A flood forecasting
system that Google developed for India’s Central Water Commission is
making a difference! But it can do more than forecast high waters. It’s
also smart enough to avoid false alarms.
Sella Nevo, the head of the flood forecasting unit and a software
engineering manager at Google, notes that “For our high-risk alerts, we
had less than 10 percent false positives [down to regions measuring 64
by 64 meters] ... That’s highly accurate.” The trick is training the system’s
accuracy so that unnecessary evacuations are avoided, and trust can be
built for the alert system.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artificialintelligence-module3-220105050340/75/Artificial-Intelligence-26-2048.jpg)