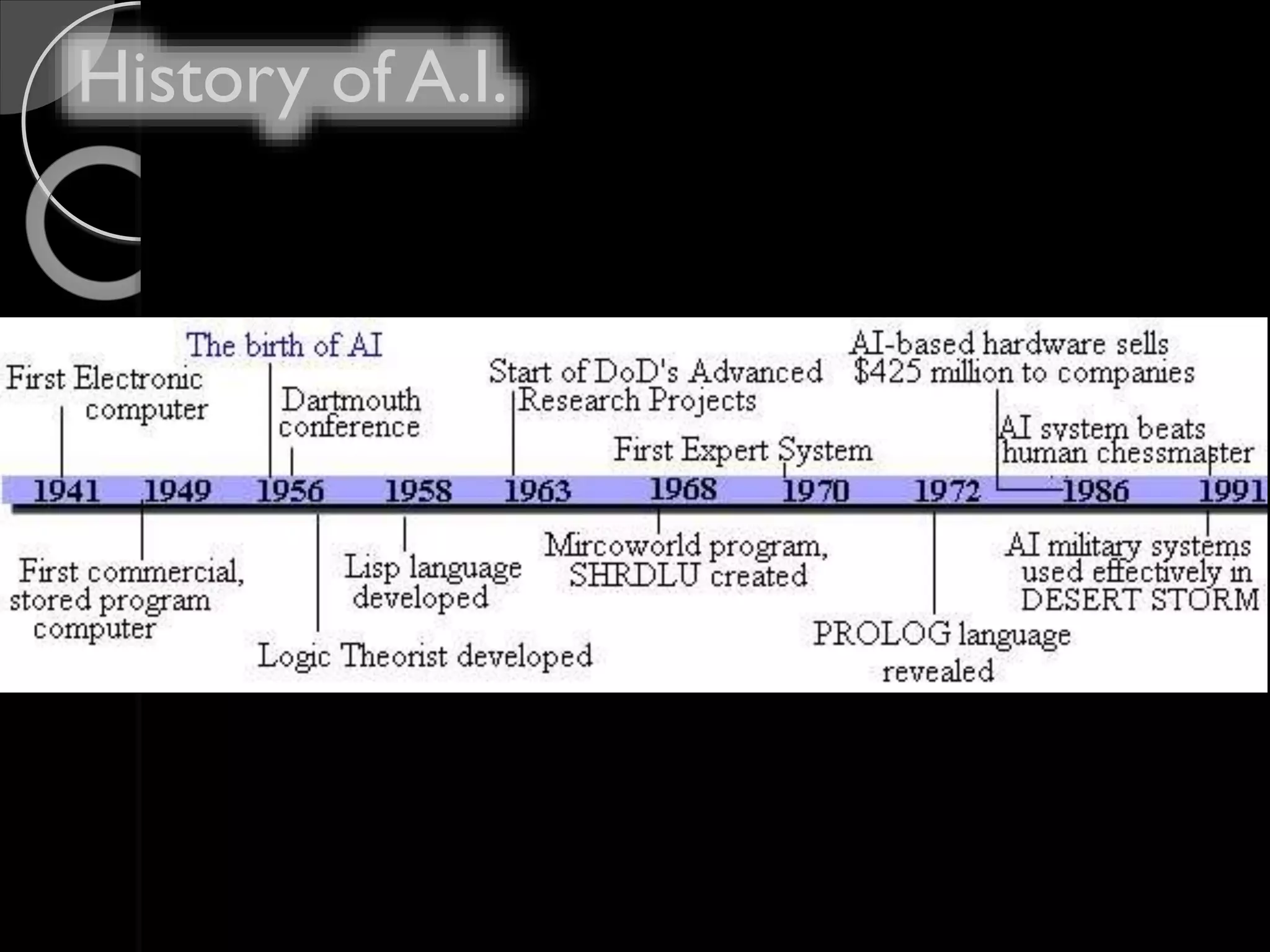
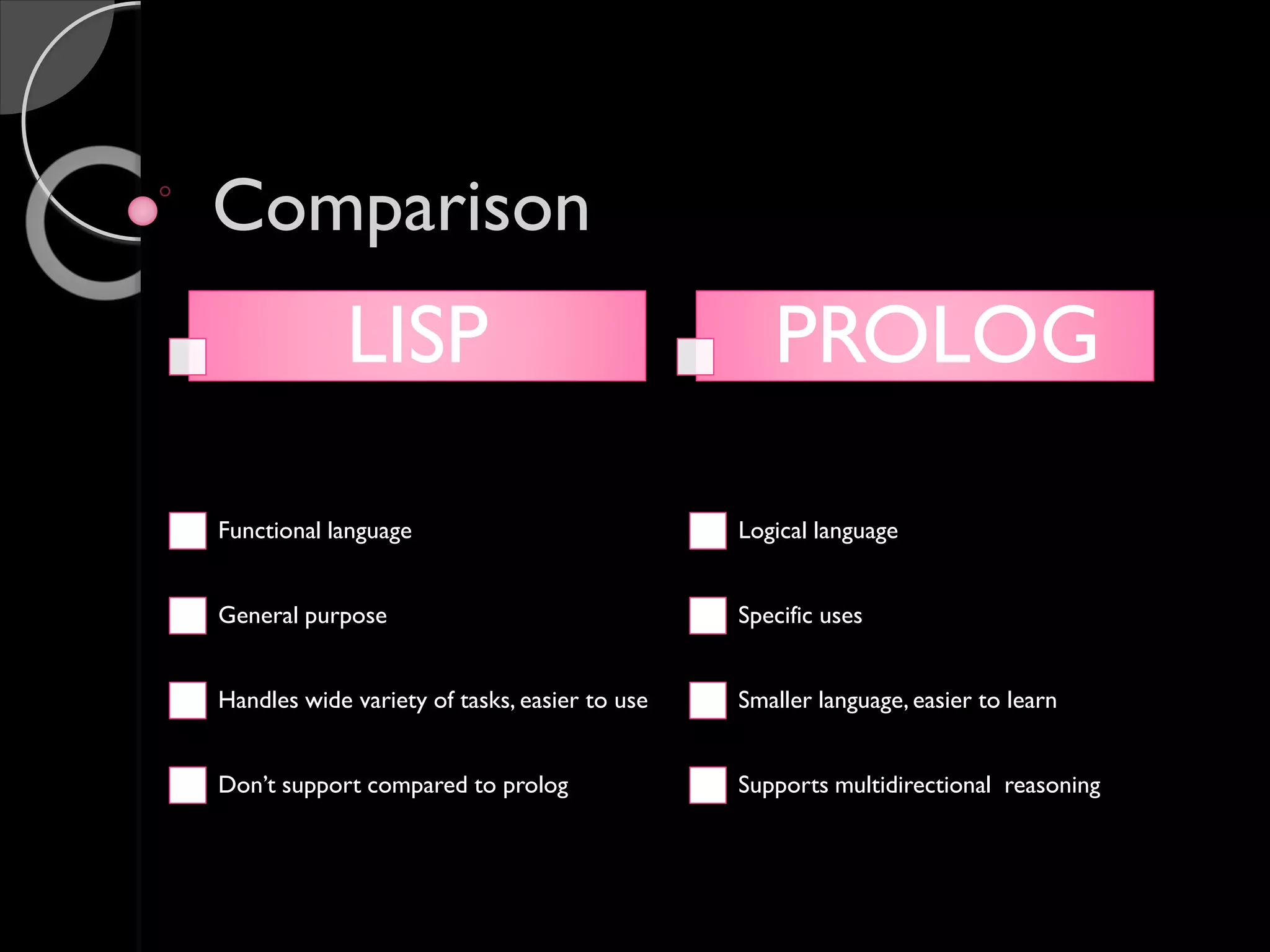
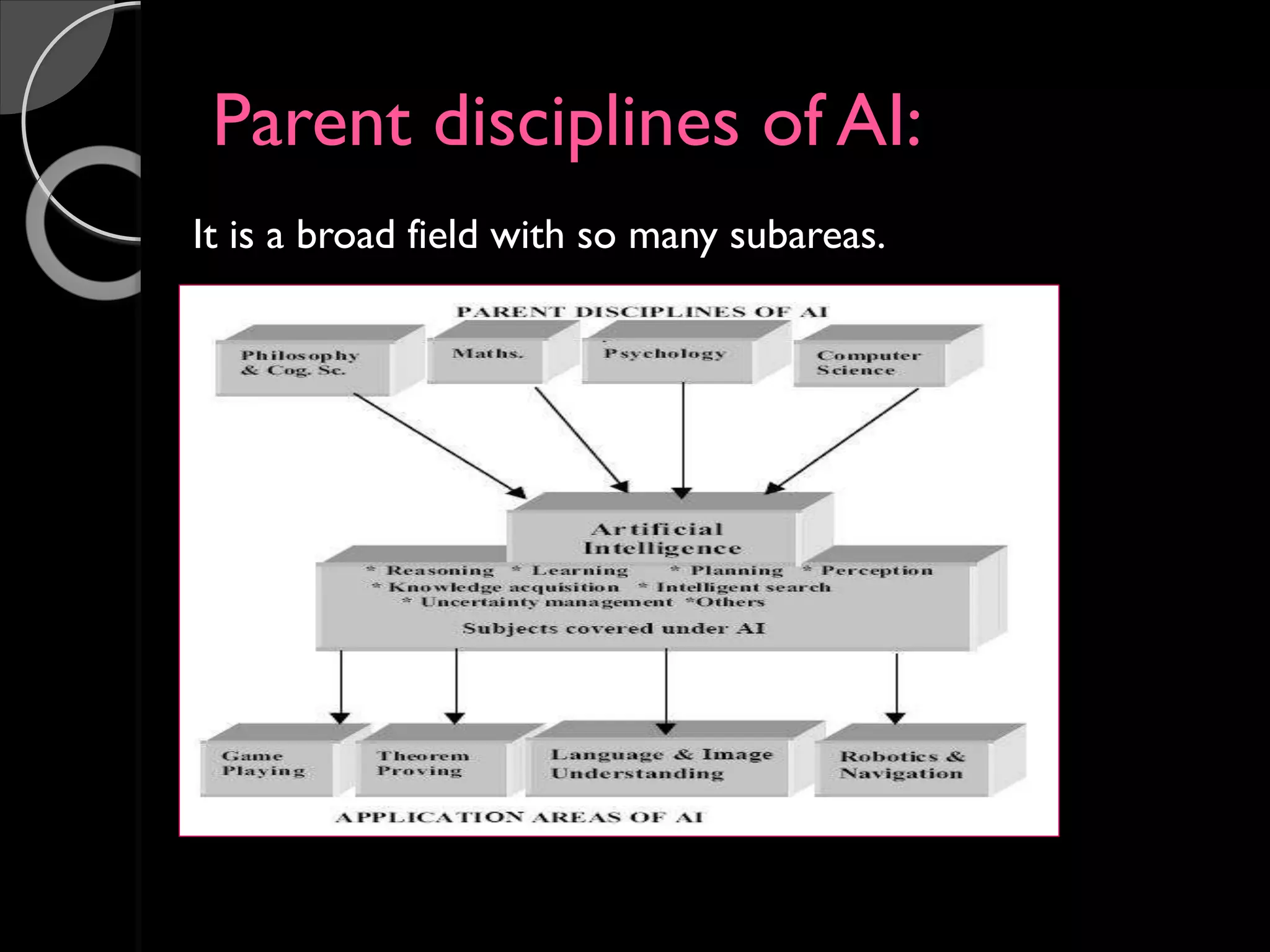
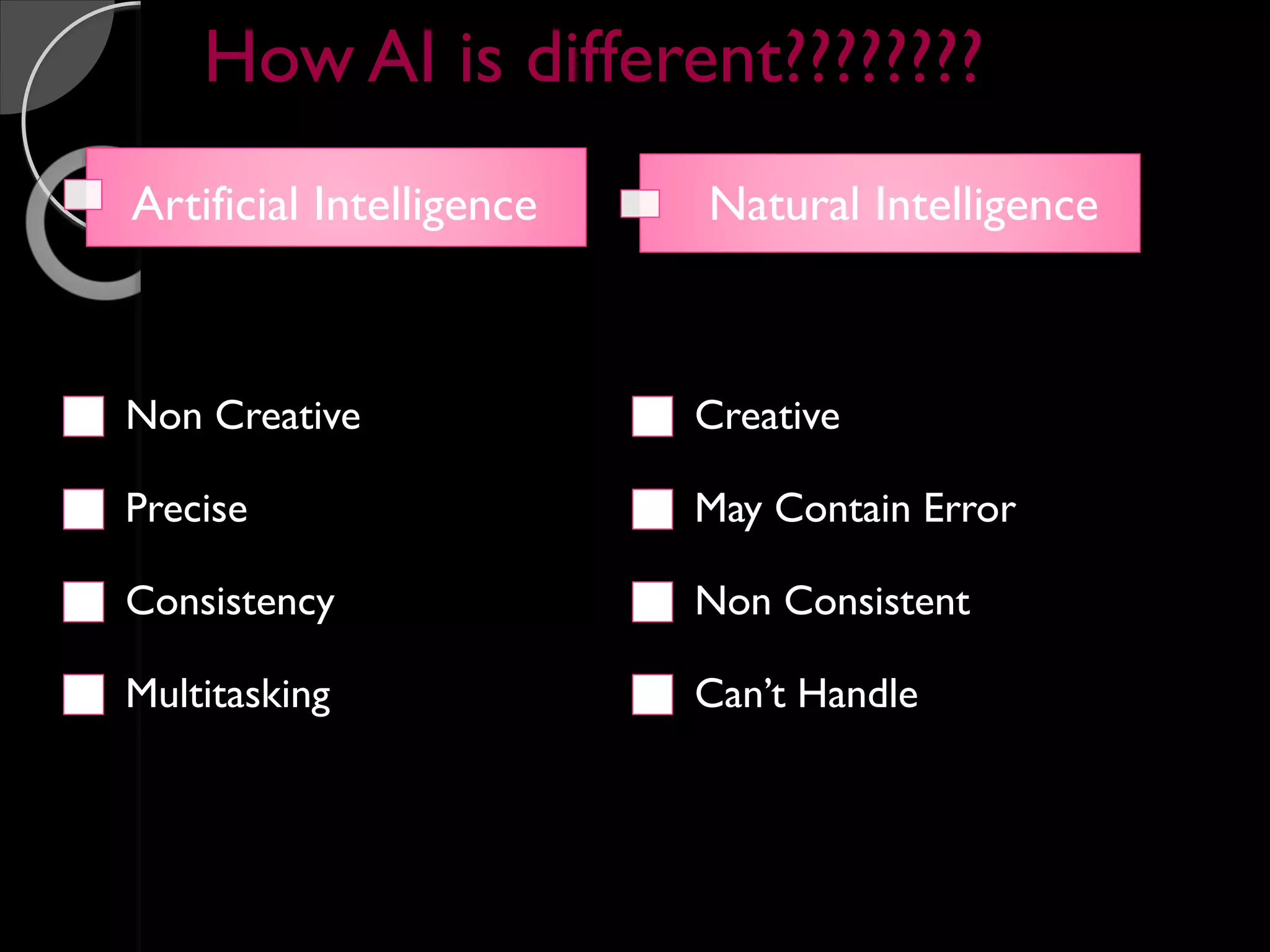
John McCarthy is considered the founder of the field of artificial intelligence. In 1955, he organized the Dartmouth conference which brought together leading researchers and laid the foundation for the field of AI. McCarthy was a professor of computer science at Stanford University. Some of the key programming languages developed for AI include Lisp, Prolog, and STRIPS. The applications of AI include natural language processing, expert systems, planning and robotics, machine learning, and game playing.