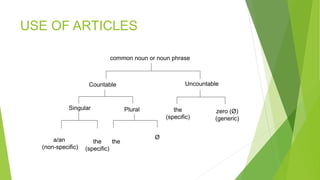
This document discusses English grammar and the use of articles. It explains that articles are words used to modify nouns, including the indefinite articles "a" and "an" and the definite article "the". The indefinite article refers to any nonspecific person, place or thing, while the definite article refers to a specific noun. The document provides examples of when to use each type of article with both countable and uncountable nouns in different contexts.