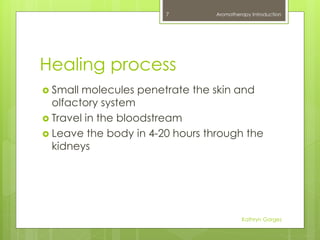
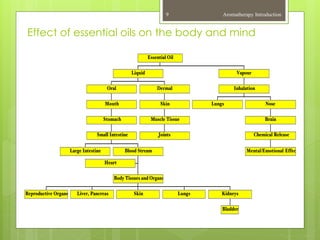
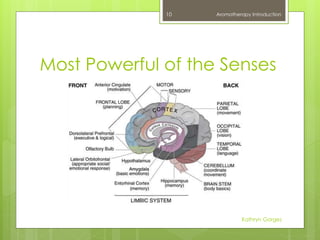
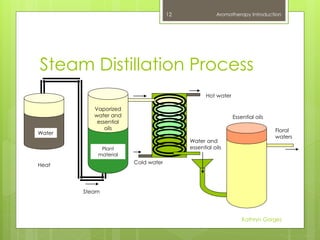
This document provides an introduction to aromatherapy, including definitions, types of oils used, methods of extraction, historical uses, applications for common ailments, and examples of essential oils. Aromatherapy is defined as the holistic treatment of diseases or disorders using aromatic essential oils from plants. The document outlines the healing properties of essential oils, their effects on the body and mind, and how they are derived from plants through various extraction methods like distillation. A brief history of aromatherapy in ancient cultures is also presented, along with common applications and essential oil examples.