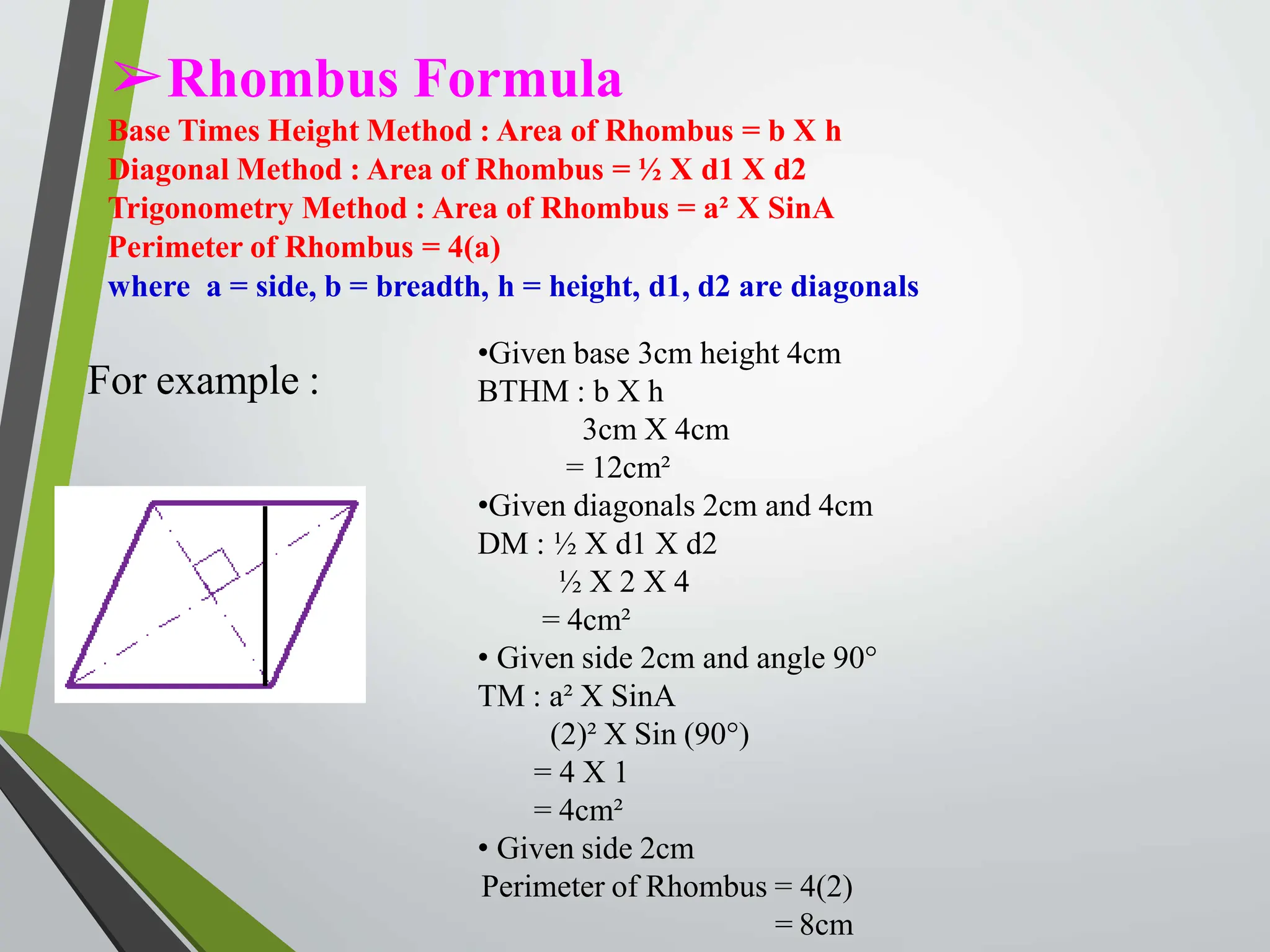
This document defines and provides properties and formulas for various types of quadrilaterals:
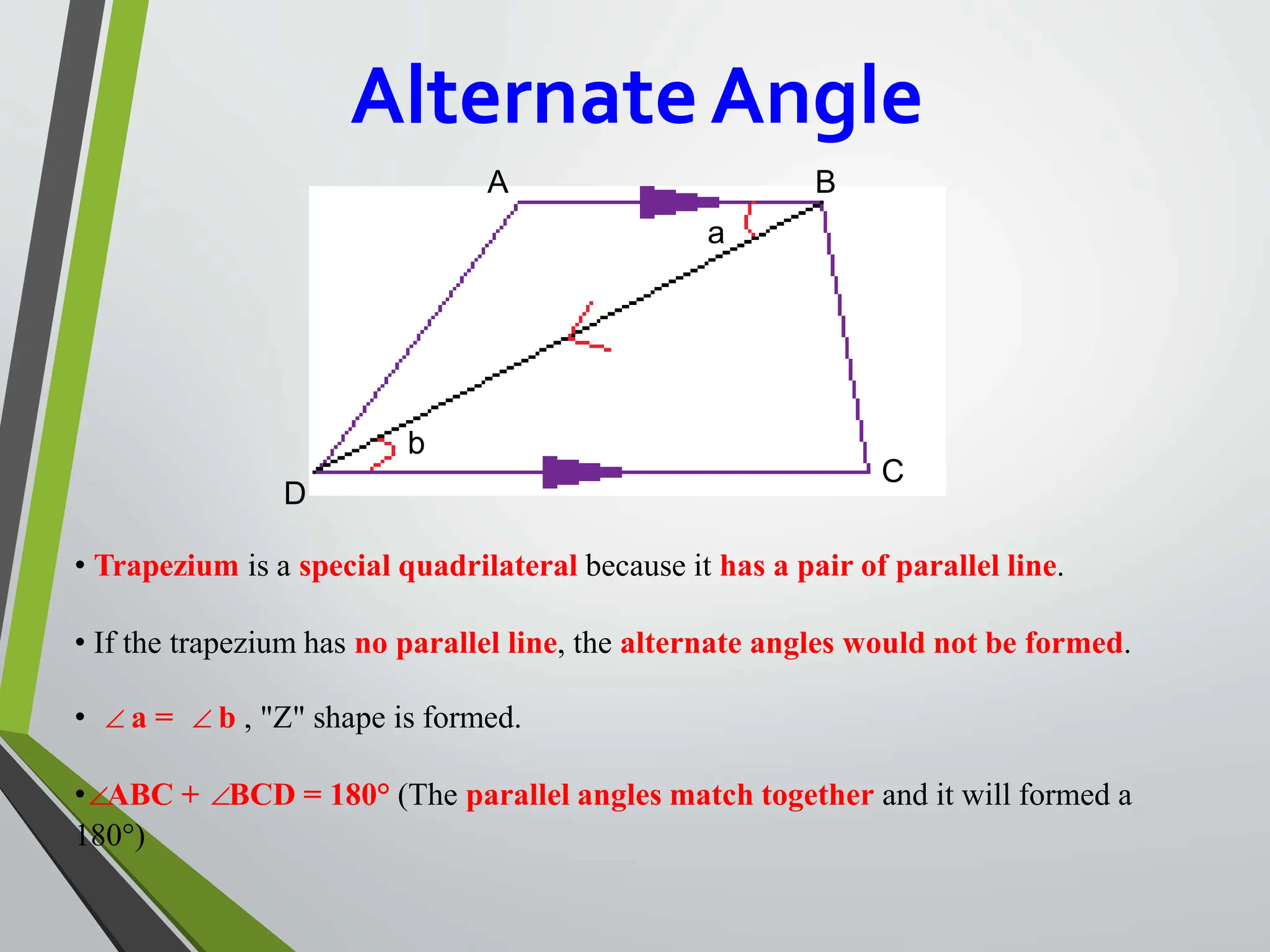
- A quadrilateral is a flat shape with four straight sides. The interior angles sum to 360 degrees.
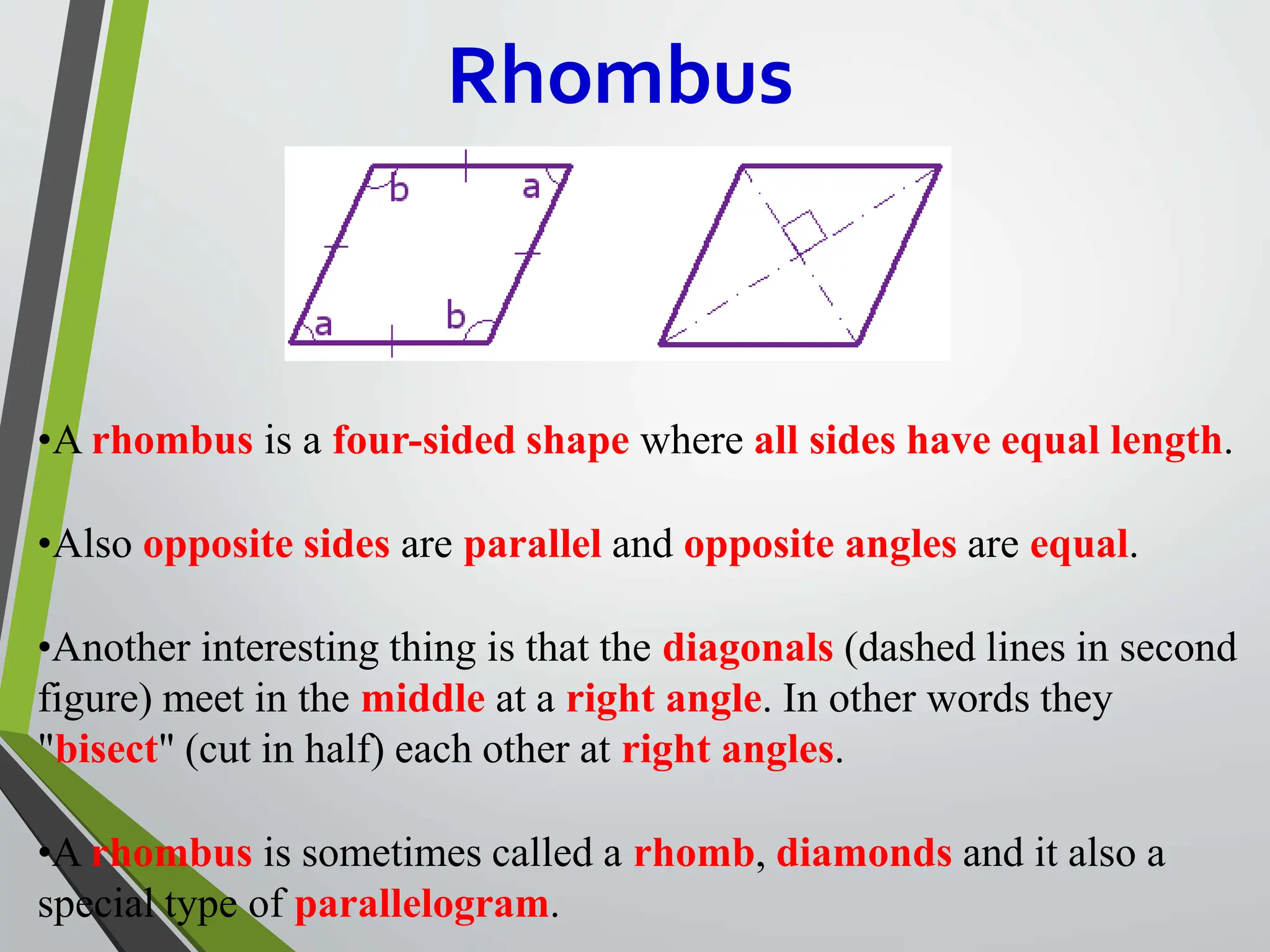
- Types include parallelograms, rectangles, squares, rhombi, trapezoids, kites.
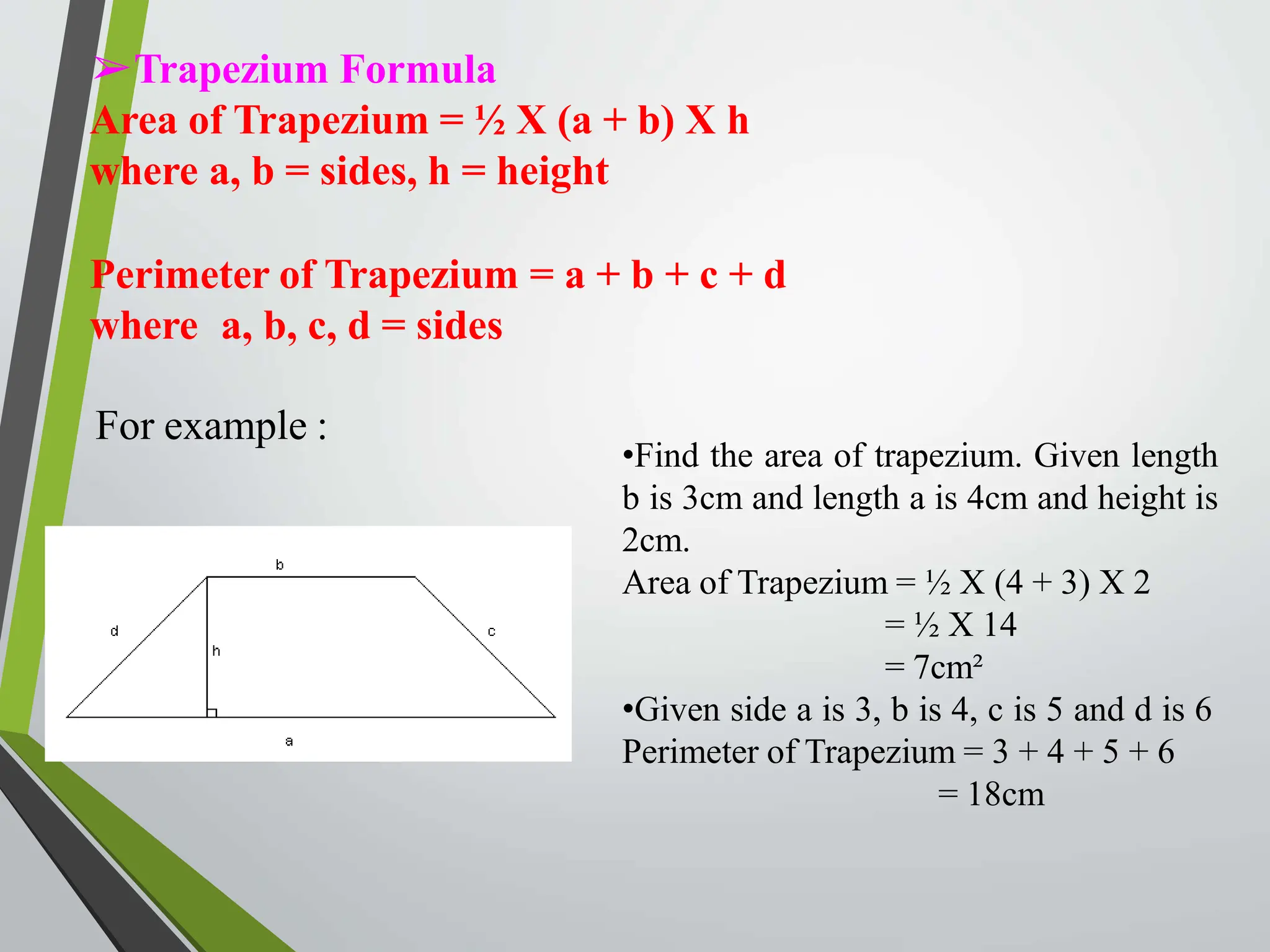
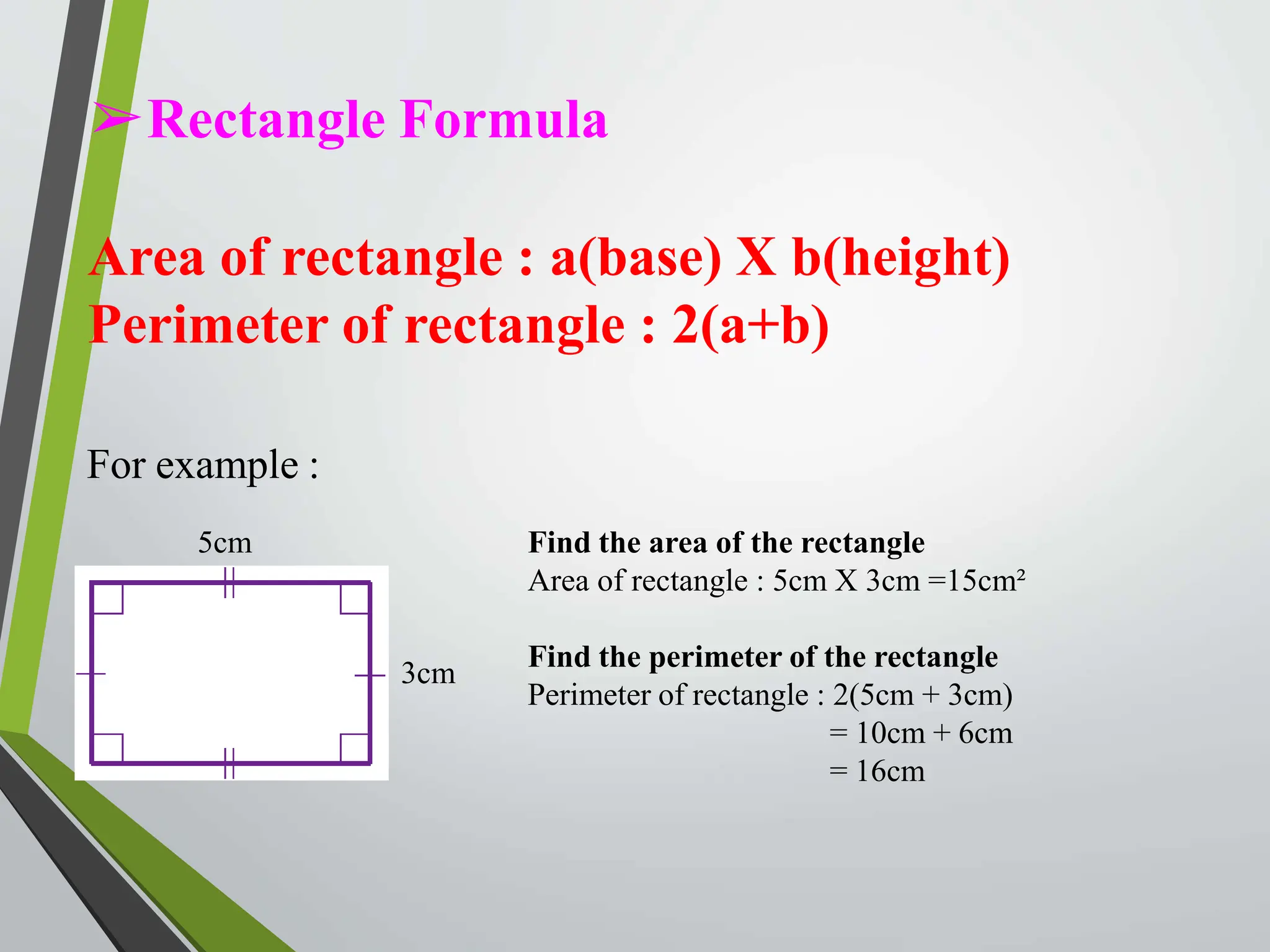
- Formulas are provided for calculating the area and perimeter of each shape based on properties like side length, angles, and diagonals.
- Examples demonstrate using the formulas to solve for values like area, perimeter, and diagonal length.

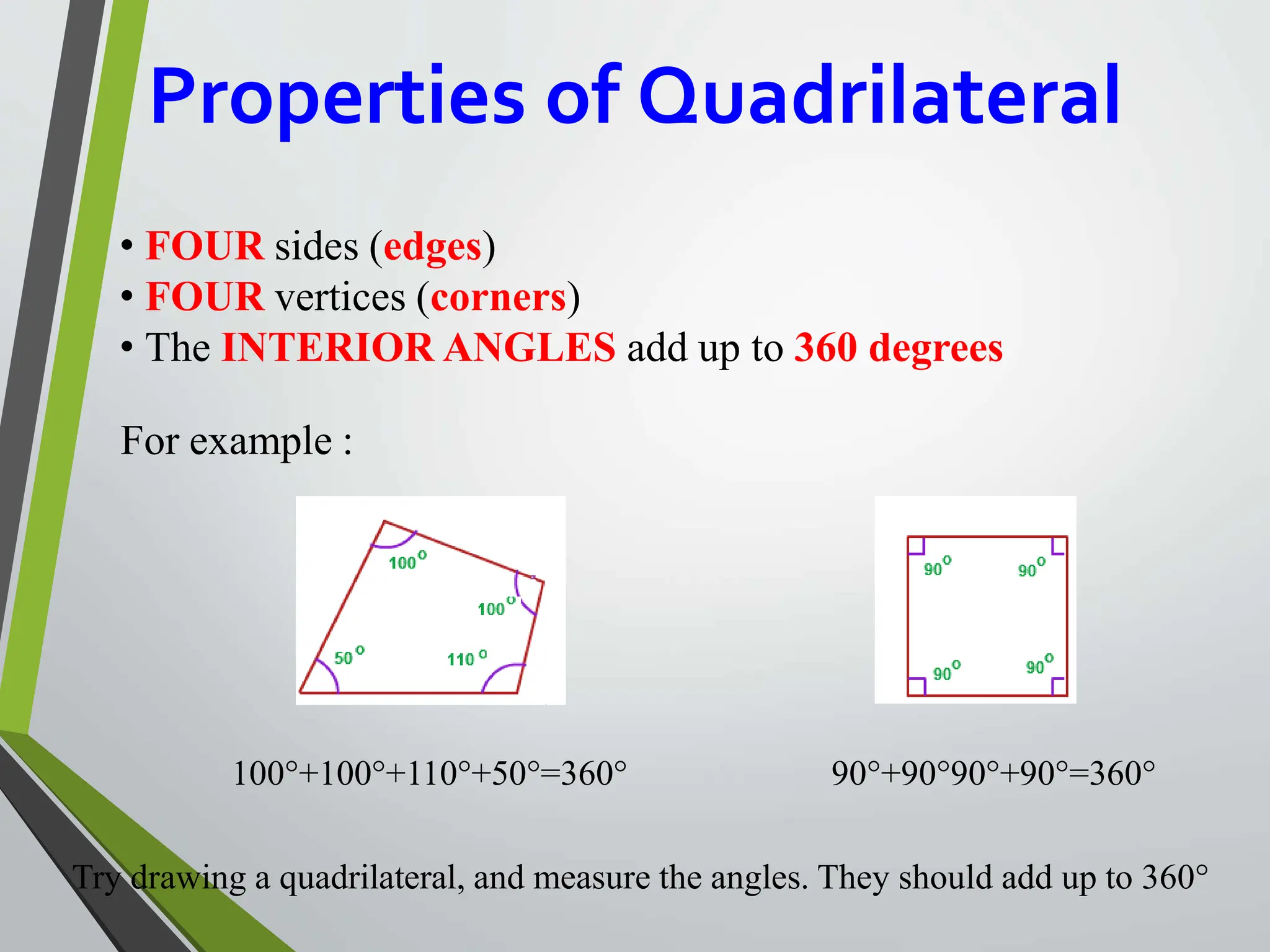


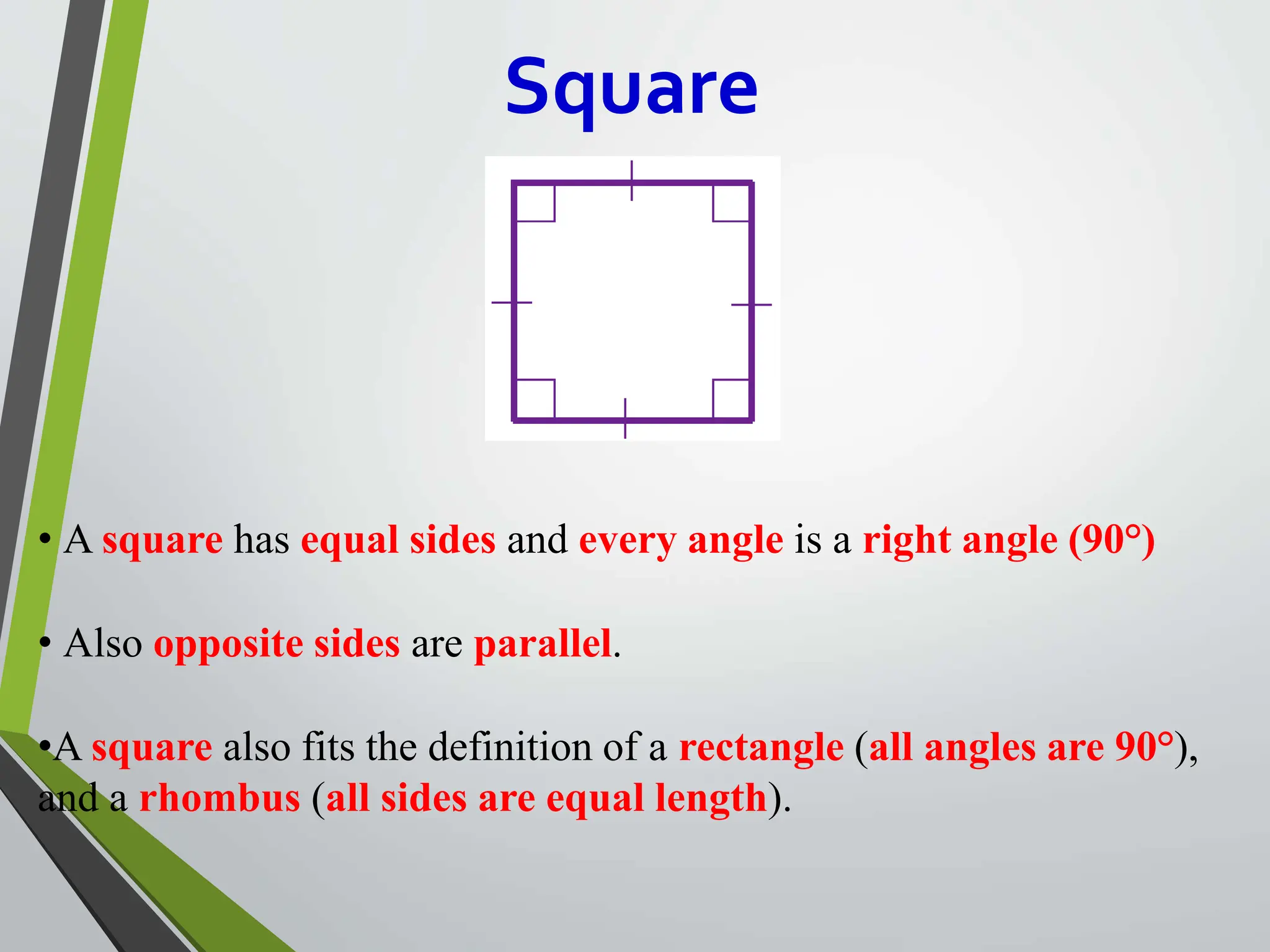
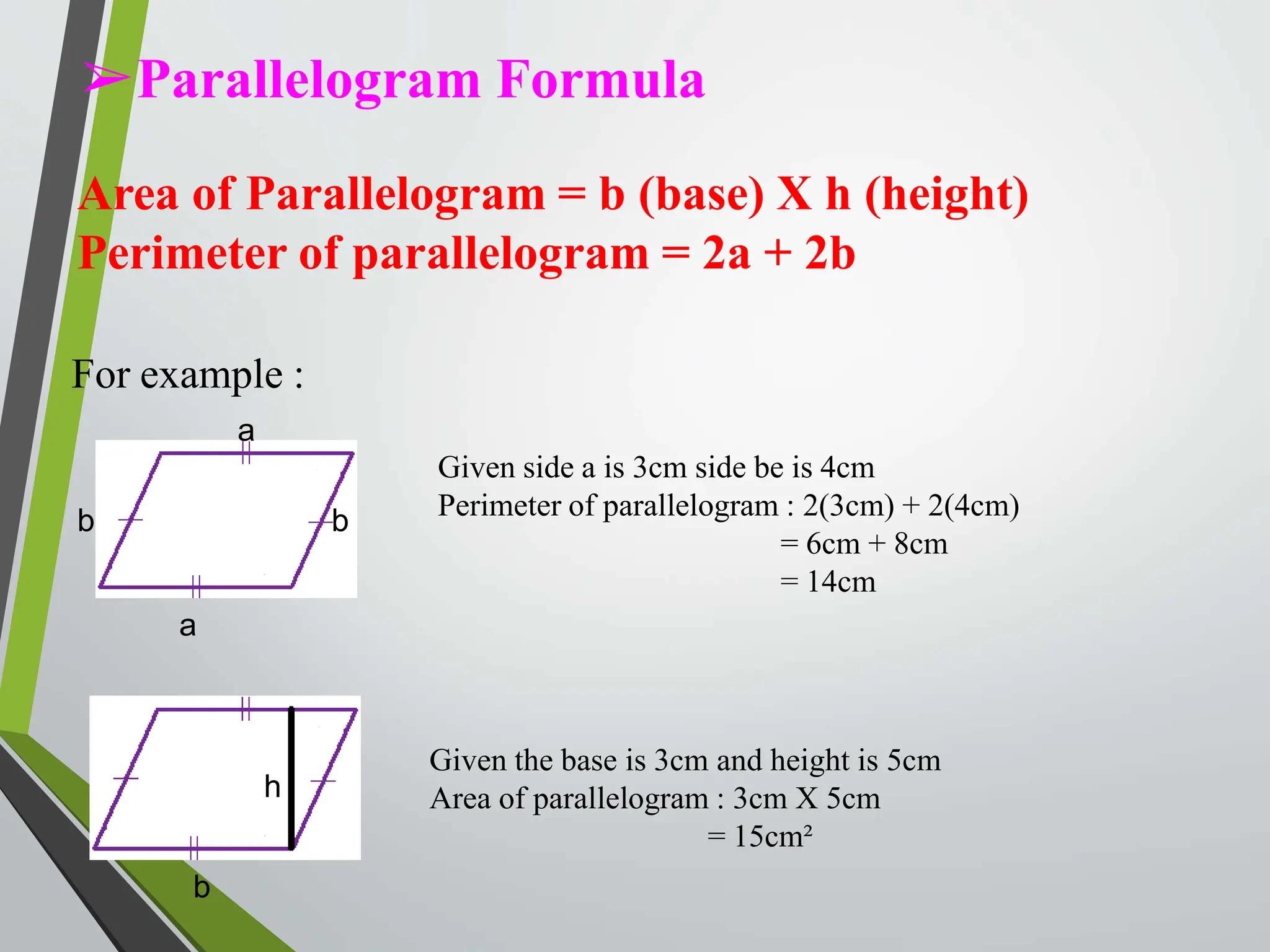
![➢Square Formula
Area of Square = (a)²
Perimeter of Square = 4(a)
Diagonal of Square = (a)[sqrt(2)]
where a = side
For example :
3cm Area of Square = (3cm)²
= 9cm²
Perimeter of Square = 4(3cm)
= 12cm
Diagonal of Square = (3cm)[sq.root(2)]
= 3cm(1.414)
= 4.242cm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quadrilateralclass9-231005180303-8e9be04a/75/quadrilateral-class-9-pptx-11-2048.jpg)