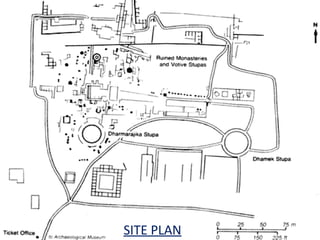
The document presents an overview of Sarnath, highlighting its significance as a Buddhist site with notable stupas including the Dhamekh, Dharmarajika, and Chaukhandi stupas, as well as Ashoka's pillar. Each stupa is detailed in terms of its construction, dimensions, artistic features, and historical context. Sarnath is portrayed as a vital location of spiritual and architectural importance, visited by renowned travelers throughout history.