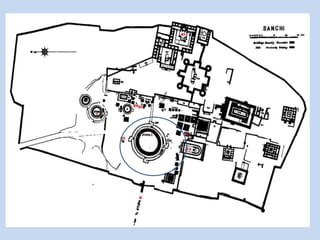
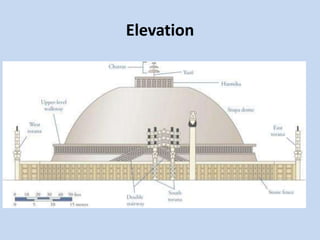
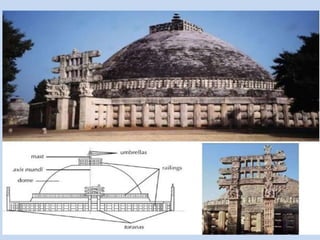
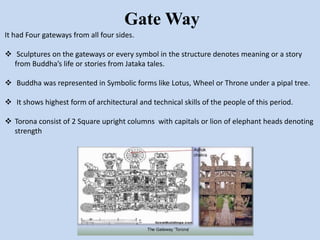
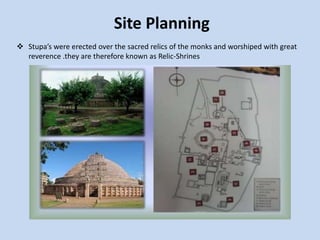
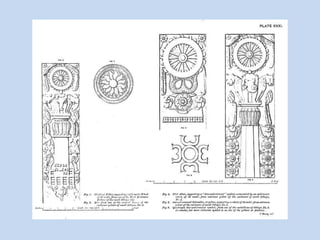
The Sanchi Stupa is located in Sanchi, India and was originally commissioned by Emperor Ashoka in the 3rd century BCE. It is one of the oldest stone structures in India and was built to house Buddhist relics. The stupa has undergone several phases of construction, with Ashoka building the original structure and later additions including four ornately carved toranas or gateways around the 1st century BCE. The stupa complex contains numerous sculptures depicting Buddhist art and symbolism from its various periods of construction and was an important early center of Buddhism, until it fell into disrepair with the decline of the religion in India.