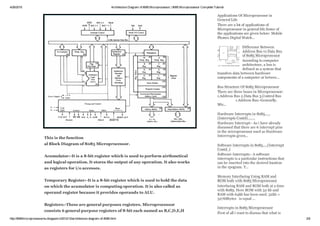
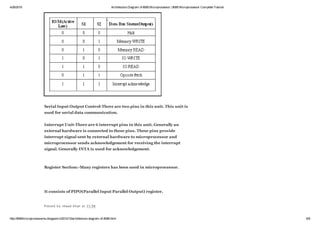
This document discusses the architecture diagram of the 8085 microprocessor. It contains the following key components: an accumulator, temporary register, general purpose registers, arithmetic logic unit (ALU), flag registers, instruction register, instruction decoder, program counter, stack pointer, timing and control unit, and interrupt unit. The diagram shows the data flow between these components and their functions in performing arithmetic and logical operations on data stored in memory or registers.