Recommended
PPT
PPTX
Basic 8085 Architecture.pptx
DOCX
microprocessor and microcontroller notes pdf
PDF
PPTX
UNIT 1 Microprocessors.pptx
PPT
PDF
Computer system architecture (microprocessor 8085) unit 4
PDF
Architecture diagram of 8085 microprocessor 8085 microprocessor complete tu...
PPTX
Architecture of 8085 microprocessor
PPTX
co-6.pptx mca ist sem computer organization
PPT
PPT Of Unit 1 of Microprocessor & Microcontroller.ppt
PPTX
Introduction to Microprocessor
PPTX
PDF
MPMC UNIT-1. Microprocessor 8085 pdf Microprocessor and Microcontroller
PPT
4-Introduction to Microprocessors-14-12-2024 (1).ppt
PDF
Bus structure of 8085 microprocessor 8085 microprocessor complete tutorial
PPT
PPTX
8085 Microprocessor presentation for Electronics M.Sc. Physics from Yash from...
PDF
8085 microprocessor Architecture and Pin description
PPT
8085_architecture of microprocessor electricals .ppt
PPT
8085 addressing modes(For College Seminars)
PDF
PPTX
Addressing Modes of 8085 Microprocessor.
PPTX
Introduction of CPU part 2
PDF
PPTX
PPT
PPTX
3-addressingmodes-181203034235.pptx
PPTX
Basics of 8085 microprocessor architecture and functional block, 8085 micropr...
PPTX
Program Counter and ROM space in 8051 and register bank
More Related Content
PPT
PPTX
Basic 8085 Architecture.pptx
DOCX
microprocessor and microcontroller notes pdf
PDF
PPTX
UNIT 1 Microprocessors.pptx
PPT
PDF
Computer system architecture (microprocessor 8085) unit 4
PDF
Architecture diagram of 8085 microprocessor 8085 microprocessor complete tu...
Similar to Basics of 8085 microprocessor architecture
PPTX
Architecture of 8085 microprocessor
PPTX
co-6.pptx mca ist sem computer organization
PPT
PPT Of Unit 1 of Microprocessor & Microcontroller.ppt
PPTX
Introduction to Microprocessor
PPTX
PDF
MPMC UNIT-1. Microprocessor 8085 pdf Microprocessor and Microcontroller
PPT
4-Introduction to Microprocessors-14-12-2024 (1).ppt
PDF
Bus structure of 8085 microprocessor 8085 microprocessor complete tutorial
PPT
PPTX
8085 Microprocessor presentation for Electronics M.Sc. Physics from Yash from...
PDF
8085 microprocessor Architecture and Pin description
PPT
8085_architecture of microprocessor electricals .ppt
PPT
8085 addressing modes(For College Seminars)
PDF
PPTX
Addressing Modes of 8085 Microprocessor.
PPTX
Introduction of CPU part 2
PDF
PPTX
PPT
PPTX
3-addressingmodes-181203034235.pptx
More from govindsingh258478
PPTX
Basics of 8085 microprocessor architecture and functional block, 8085 micropr...
PPTX
Program Counter and ROM space in 8051 and register bank
PPT
PPTX
Functional block diagram and pin diagram of 8051
PPTX
Instruction Set and programming with 8085
PPTX
I/O Programming Timer/Counter: Operating Modes
PPTX
Embedded Programming: Data Types, Operators Embedded Programming
PDF
Introduction of IEEE 802.15.4 Technology
PPTX
Instruction set of microprocessor: Data transfer, Arithmetic
PDF
Fundamental components of the Internet of Things unit 1.pdf
PPTX
Off-Chip Peripheral Interfacing And Programming
PPTX
Unit - I : Introduction of Embedded system
PPTX
Interfacing with 8051: LED, LED pattern display
PDF
types of sensors are active, passive, analog, and digital. Active sensors
PPTX
Unit-VI IoT applications like Home automations etc
PPTX
Recently uploaded
PDF
Robert Walker Epps - A Football Coach
PDF
Basics of Electronics Simplified by Akash.pdf.pdf.pdf
PPTX
Phishing Website Detection by Machine Learning Techniques Presentation.pptx
PPT
Smart waste management using internet of things 2025.ppt
PPTX
Epec Engineered Technologies - Corporate Overview – 2026
PPTX
PEMET 413-COMPOSITE MATERIALS-2024 SCHEME-MOD1 LECTURE 5.pptx
PPTX
OPGW-Optical-Ground-Wire-Deployment-Process.pptx
PPTX
mechanical measurements course lecture2.pptx
PPTX
PEMET413 -COMPOSITE MATERIALS -KTU MOD 1 LECTURE 4.pptx
PPTX
Chapter10 Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis.pptx
PPTX
Unit 5 Materials of plant construction.pptx
PPTX
Siemens energy case study interview 2025
PPTX
plastic road.pptxPlastic Roads: A Sustainable Solution
PPTX
introduction-210127111642.pptx hamster frftt
PPTX
Training Notes_ SBPDCL Apprenticeship Program.pptx
PDF
Introduction to Human Computer Interaction .pdf
PPTX
presentation-tenable-corporate-deck-ppt-version-english (1).pptx
PPTX
BITUMINOUS_ROADS_bindu priya civil ppt.pptx
PPTX
Research Methodology (RM) BRMK557 Module-02
PPTX
Reinforcement learning and deep learning.pptx
Basics of 8085 microprocessor architecture 1. 2. 3. 4. Addressing modes in 8085
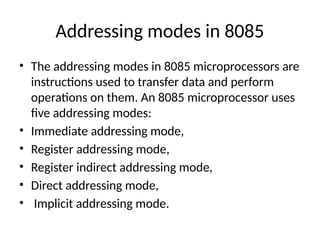
• The addressing modes in 8085 microprocessors are
instructions used to transfer data and perform
operations on them. An 8085 microprocessor uses
five addressing modes:
• Immediate addressing mode,
• Register addressing mode,
• Register indirect addressing mode,
• Direct addressing mode,
• Implicit addressing mode.
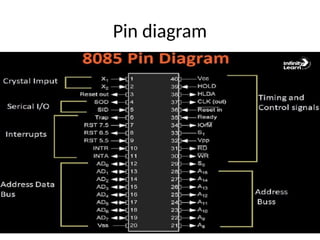
5. • The architecture of the 8085 microprocessor
consists of several key components, including
the accumulator, registers, program counter,
stack pointer, instruction register, flags
register, data bus, address bus, and control
bus. The accumulator is an 8-bit register that
is used to store arithmetic and logical results.
6. • In its simplest form a multi-chip fixed
architecture microprocessor consists of three
circuits:
• (i) The central processor which may have 8-,
12- or 16-bit capability
• (ii) The microprogram sequence control logic
• (iii) The microprogram ROM.