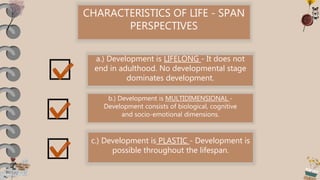
Here is my reflection on the CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE - SPAN PERSPECTIVES:
If I were to choose one CHARACTERISTIC OF LIFE - SPAN PERSPECTIVES to have, I would choose Development is Plastic. The idea that development can occur throughout one's lifespan and is not fixed appeals to me. It suggests an openness to continued growth and change even into adulthood. Rather than plateauing or declining after a certain age, one can keep learning and evolving. Seeing development as plastic implies flexibility and potential for positive transformation at any stage of life. It presents an optimistic view of human capacity and possibility. The changing world we live in demands adaptability, and a plastic view of development supports an individual's