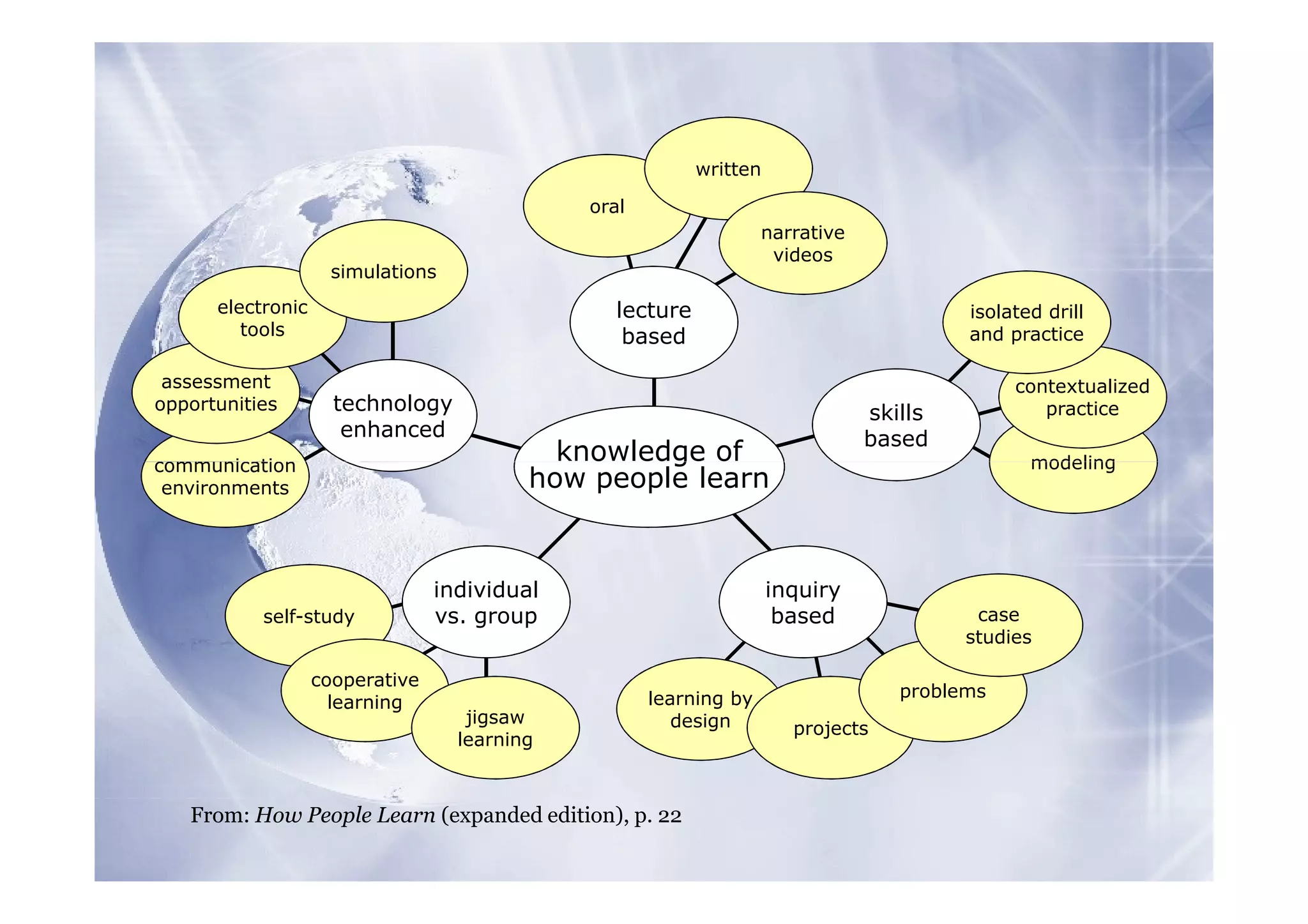
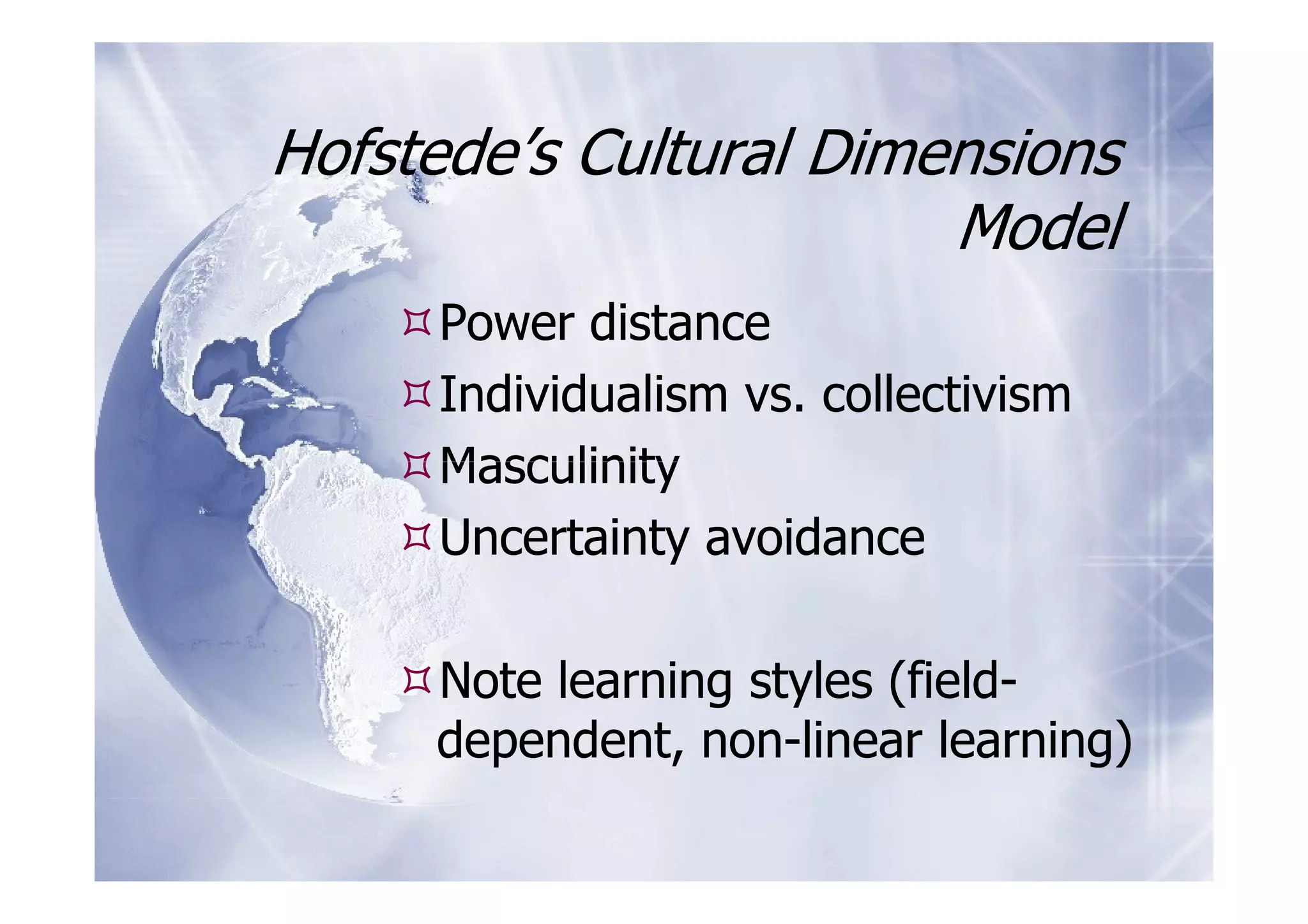
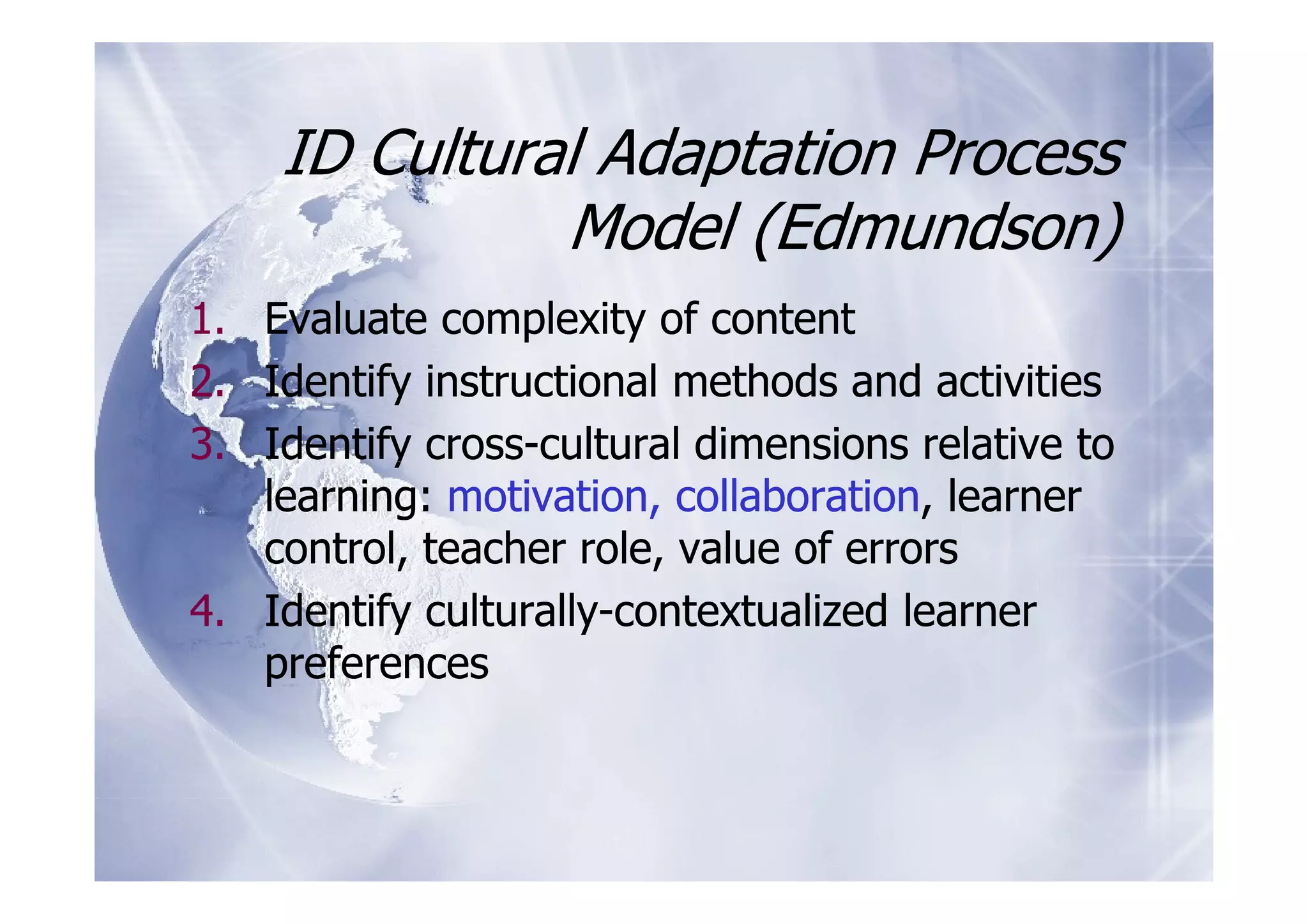
The document discusses culturally-sensitive learning practices in school libraries, emphasizing the importance of understanding cultural factors, language issues, and diverse teaching strategies. It highlights the need for cultural competence and proficiency among educators to effectively engage students and create inclusive learning environments. Future trends indicate a growing need for cultural integration and adaptation in educational practices, supported by technology and learner-centered approaches.