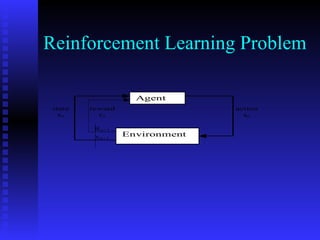
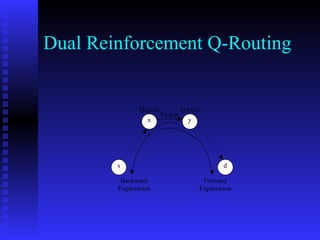
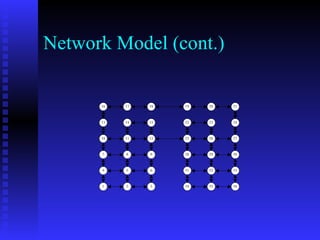
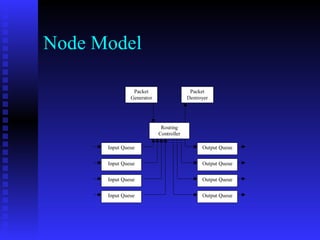
This document discusses the application of reinforcement learning in network routing. It provides an overview of reinforcement learning, including its key elements like the agent, environment, policy, reward function, and value function. It also discusses important reinforcement learning problems like Markov decision processes and elementary methods including dynamic programming, Monte Carlo methods, and temporal-difference learning. Finally, it presents Q-routing and dual reinforcement Q-routing as examples of applying reinforcement learning concepts to optimize network routing.























![References [1] Richard S. Sutton and Andrew G. Barto, Reinforcement Learning—An Introduction [2] Chengan Guo, Applications of Reinforcement Learning in Sequence Detection and Network Routing [3] Simon Haykin, Neural Networks– A Comprehensive Foundation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/applying-reinforcement-learning-for-network-routing4818/85/Applying-Reinforcement-Learning-for-Network-Routing-29-320.jpg)